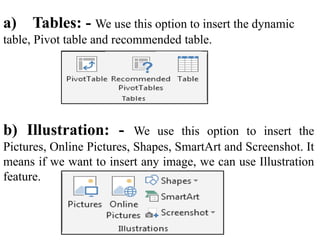
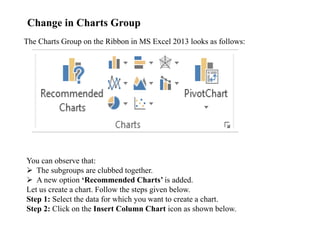
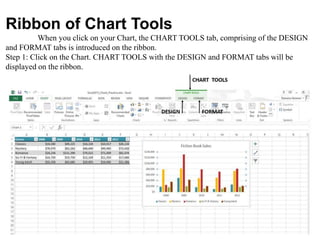
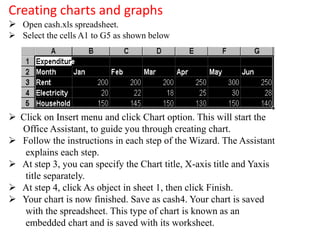
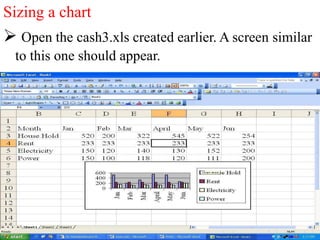
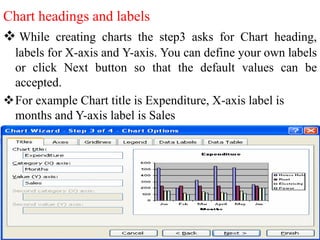
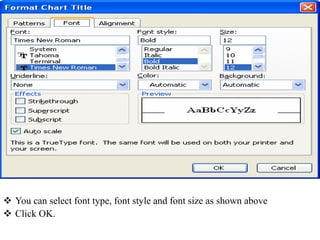
The document discusses various features and functions of the Insert tab in Microsoft Excel, including how to insert tables, illustrations, charts, reports, and other objects. It provides details on different types of charts like column, bar, and line charts that can be created in Excel and how to modify chart properties. The document also summarizes steps for creating, editing, moving, deleting, and formatting charts in Excel worksheets.