This document outlines the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act of 1954 in India. The key points are:
- The objectives are to protect public health from harmful food, prevent sale of substandard food, and protect consumer interests by eliminating fraudulent practices.
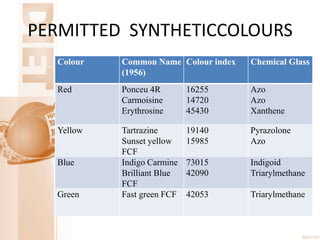
- It defines food and adulterants, and what constitutes food adulteration. Food is considered adulterated if it contains harmful or inferior substances, among other criteria.
- It describes procedures for food inspectors to sample and analyze foods suspected of adulteration. Penalties include imprisonment and fines for those found guilty of adulteration.
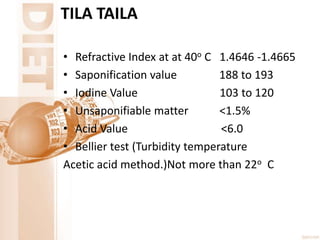
- It lists various miscellaneous provisions regarding food labeling, storage, and quality standards. It also