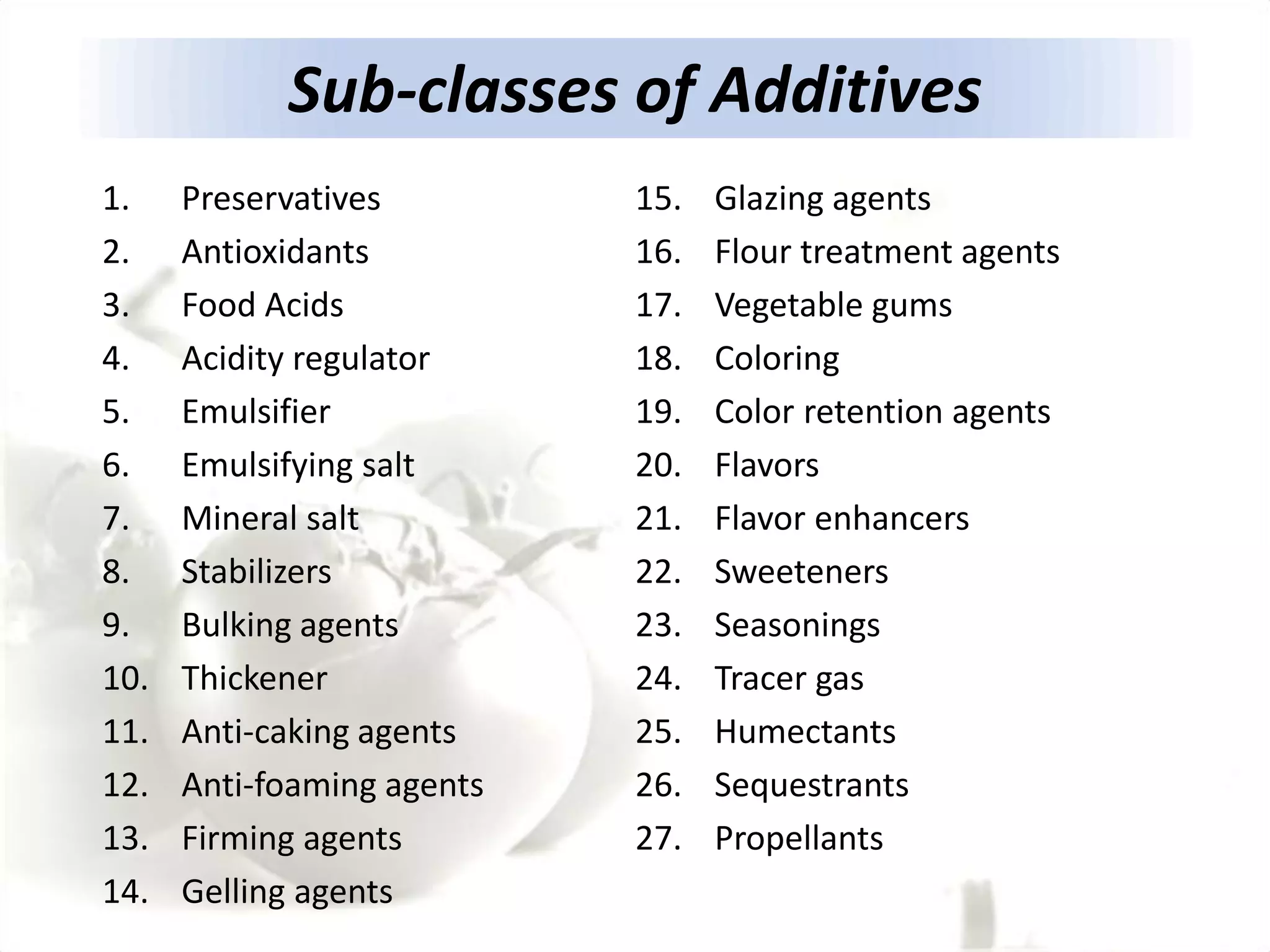
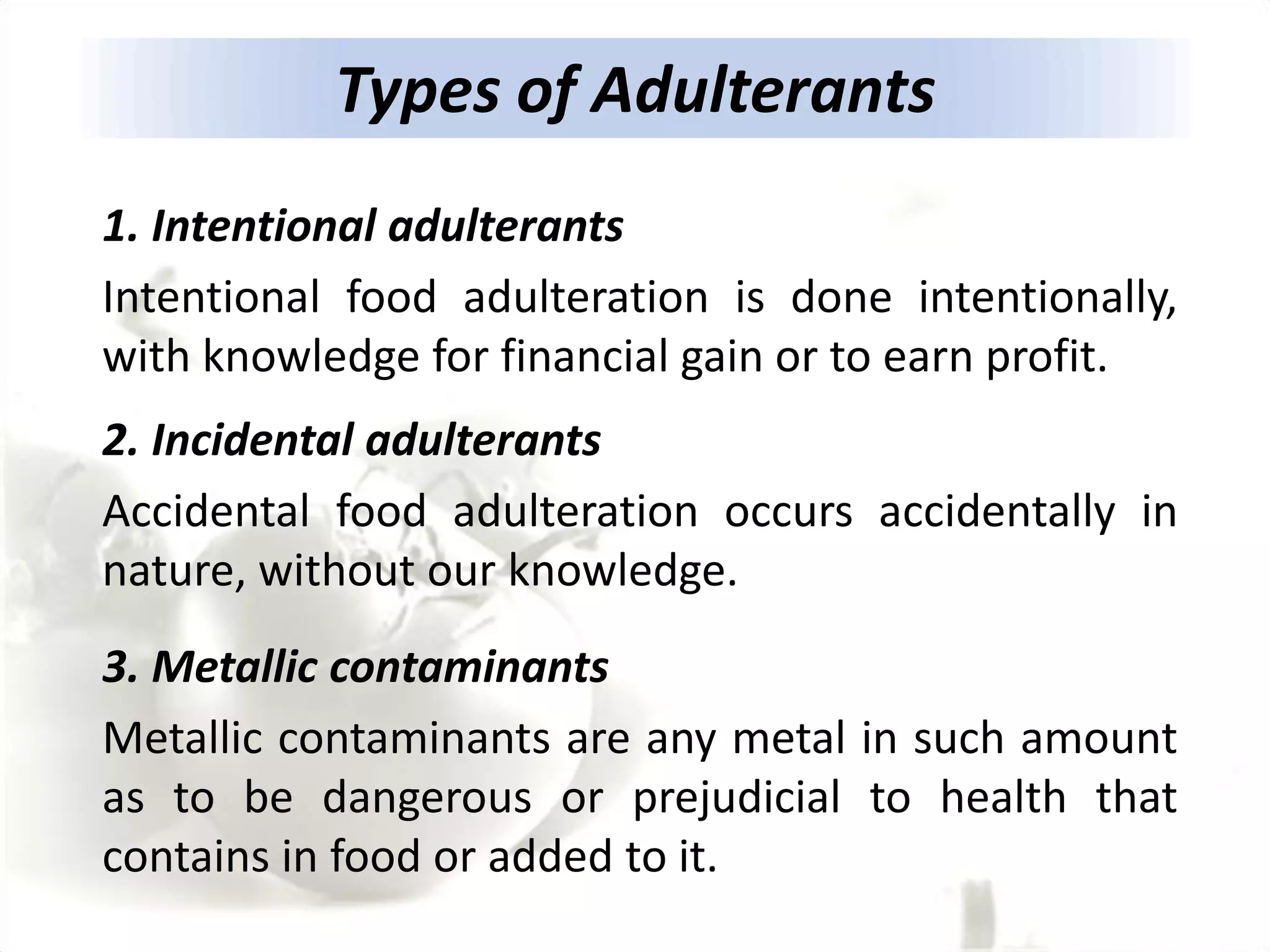
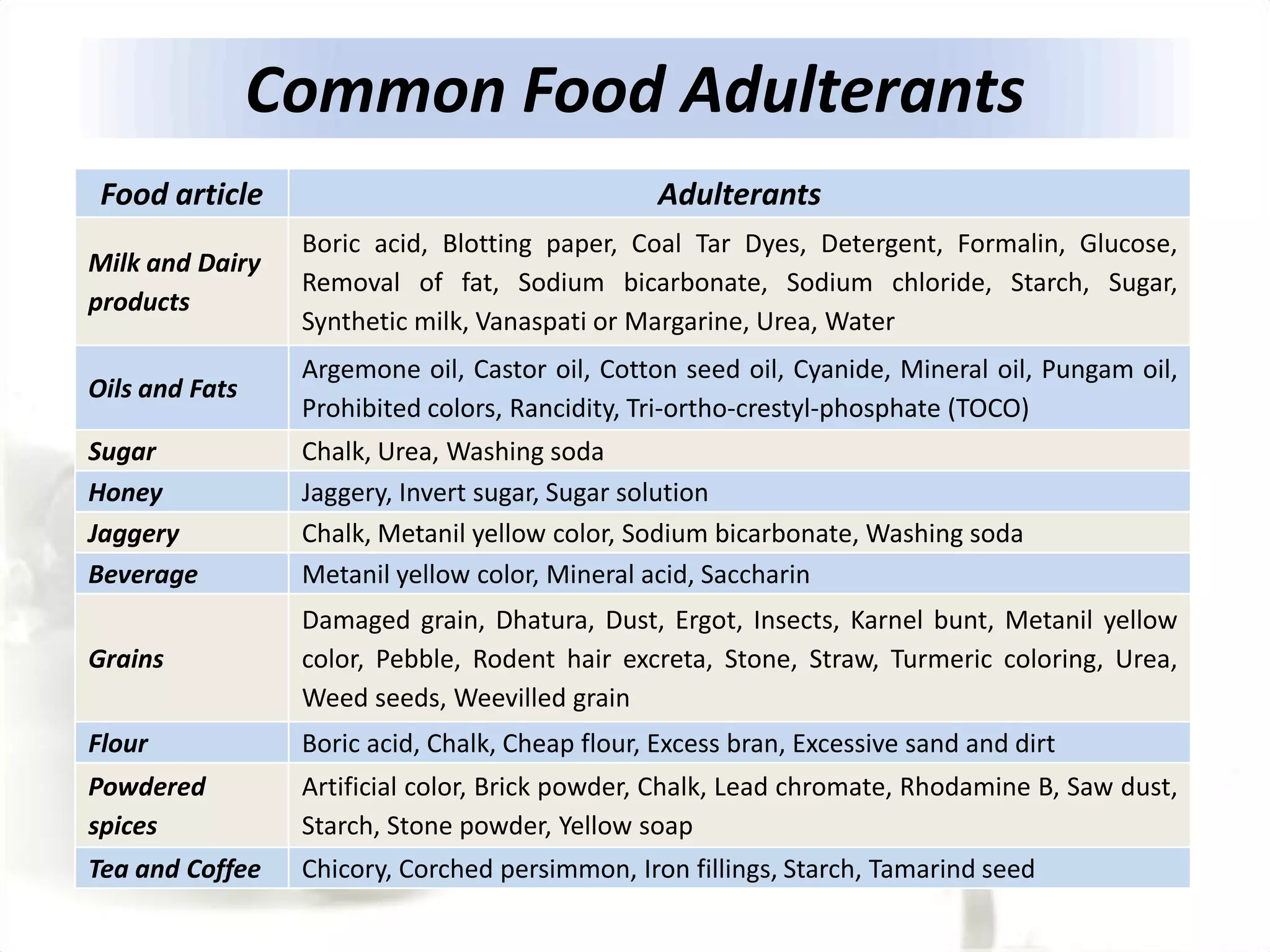
The document discusses food additives, their types, safety concerns, and the issues of food adulteration and misbranding. It categorizes additives into preservatives, nutritional additives, flavoring agents, and more, explaining their purposes and potential health risks associated with certain artificial additives. Additionally, it outlines the definition of food adulteration and misbranding, providing examples of common adulterants and their health hazards.