Embed presentation
Downloaded 59 times






















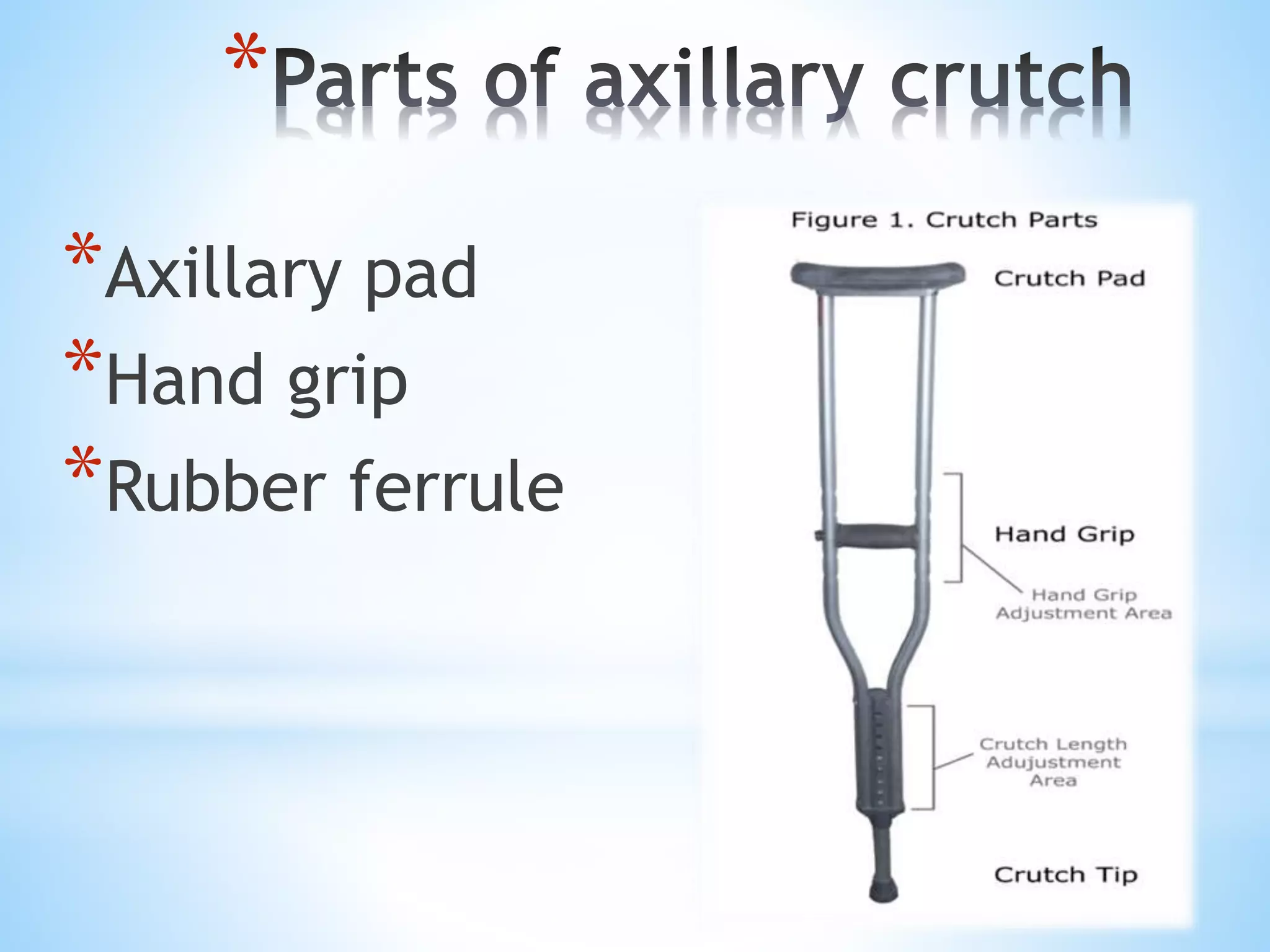

















































































































The document provides a comprehensive overview of various mobility aids, including crutches, canes, walkers, and wheelchairs, describing their types, parts, usage, and measurement for fitting. It emphasizes the importance of weight-bearing restrictions and proper techniques for using these aids to ensure safety and effectiveness. The content serves as guidance for both patients needing mobility assistance and healthcare practitioners involved in rehabilitation.







































































































































