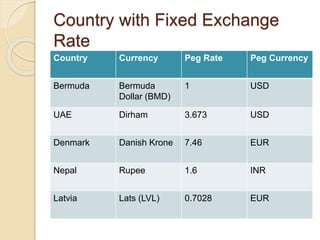
This document discusses and compares fixed and floating exchange rate systems. Under a fixed exchange rate system, a country's currency is pegged to another currency at a fixed rate. This stabilizes currency values but the system is vulnerable to speculation. Most currencies now float freely based on supply and demand. A floating exchange rate allows independent monetary policy and automatic balance of payments adjustments. While no system is definitively better, advanced economies tend to use floating rates while developing economies may benefit more from fixed rates initially.