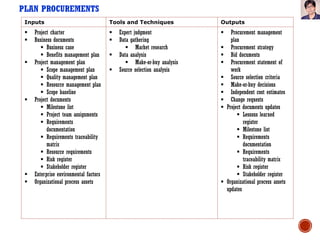
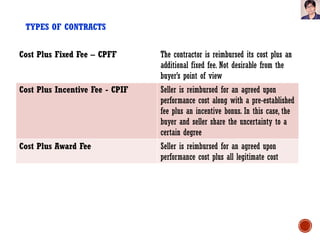
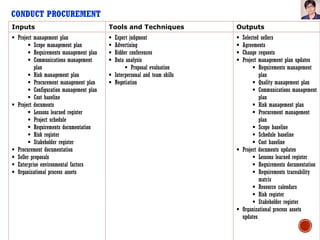
Project Procurement Management involves processes to purchase or acquire products, services or results from outside the project team. It includes three main processes: Plan Procurements, Conduct Procurements, and Control Procurements. Plan Procurements involves documenting procurement decisions, specifying the approach, and identifying potential sellers. Conduct Procurements obtains seller responses, selects a seller, and awards a contract. Control Procurements manages procurement relationships, monitors contract performance, and makes changes as needed.