ANGLE SUM PROPERTY.pdf
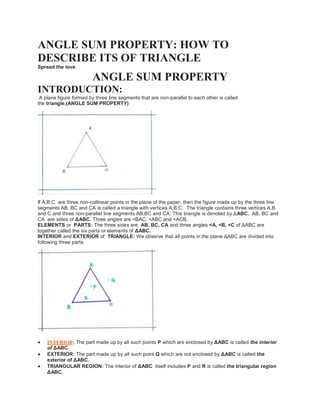
- 1. ANGLE SUM PROPERTY: HOW TO DESCRIBE ITS OF TRIANGLE Spread the love ANGLE SUM PROPERTY INTRODUCTION: A plane figure formed by three line segments that are non-parallel to each other is called the triangle.(ANGLE SUM PROPERTY) If A,B,C are three non-collinear points in the plane of the paper, then the figure made up by the three line segments AB, BC and CA is called a triangle with vertices A,B,C. The triangle contains three vertices A,B and C and three non-parallel line segments AB,BC and CA. This triangle is denoted by ΔABC. AB, BC and CA are sides of ΔABC. Three angles are ˂BAC, <ABC and <ACB. ELEMENTS or PARTS: The three sides are AB, BC, CA and three angles <A, <B, <C of ΔABC are together called the six parts or elements of ΔABC. INTERIOR and EXTERIOR of TRIANGLE: We observe that all points in the plane ΔABC are divided into following three parts: INTERIOR: The part made up by all such points P which are enclosed by ΔABC is called the interior of ΔABC. EXTERIOR: The part made up by all such point Q which are not enclosed by ΔABC is called the exterior of ΔABC. TRIANGULAR REGION: The interior of ΔABC itself includes P and R is called the triangular region ΔABC.
- 2. TYPES OF TRIANGLES Naming of triangles by considering the lengths of their sides:- Scalene Triangle: A triangle whose no two sides are equal is called a scalene triangle. ΔABC is a scalene triangle. Isosceles Triangle: A triangle whose two sides are equal is called an isosceles triangle. ΔABC is an isosceles triangle so AB = AC. Equilateral Triangle: A triangle whose all sides are equal to one another, is called an equilateral triangle. ΔABC is an equilateral triangle where AB = AC = BC. Naming triangles by considering the measures of their angles:- Acute Triangle :
- 3. A triangle whose all the angles are acute is called an acute angled triangle or an acute triangle. ΔABC is an acute-angled triangle where <A, <B and < C are acute angles. Equilateral triangle is an acute- angled triangle because the measure of its each angle is 60°. Right Triangle: A triangle whose one angle is a right angle, is called right-angled triangle or a right triangle. The side opposite to the right triangle is known as hypotenuse and other two sides are called the legs of the triangles. ΔABC is a right-angled triangle, where <B = 90° remaining two angles are acute. Obtuse triangle:
- 4. A triangle whose one angle is obtuse, is called an obtuse-angled triangle or an obtuse triangle, where <E is an obtuse angle. ANGLE SUM PROPERTY OF A TRIANGLE PROPERTY: The sum of the angles of a triangle is two right angles or 180° PROOF: Let ΔABC be any triangle. Through A, a line XY parallel to the side BC . Since, XY||BC and the and the transversal AB cuts XY and BC at A and B respectively. <1 = <4 [ as alternate interior angles are equal ] Similarly , XY ||BC and the transversal AC cuts XY and BC at A and C respectively. <2 = <5 [ as alternate interior angles are equal] Also <3 = <3 Adding the angles on the respective sides, we get <1 + <2 + <3 = <4 + <5 + <3 But, <4 + <5 + <3 = 180° = 2 right angles. Hence, the sum of the angles of a triangle is two right angles or 180°. From the above property, we obtain the following useful results:- A triangle cannot have more than one right angle. A triangle cannot have more than one obtuse angle i.e if one angle of the triangle is obtuse, then other two are acute. In a right triangle, the other two angles are always acute and their sum is 90°. EXTERIOR ANGLE PROPERTY OF A TRIANGLE PROPERTY: When a side of a triangle is produced then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angle.
- 5. To prove, in ΔABC, BC has been produced to point D, forming an exterior angle <ACD. To prove : <ACD = <CAB + < ABC CONSTRUCTION: from C, CE is drawn which parallel to BA. PROOF: Since CE||BA and AC is transversal. So we have <ACE = < CAB [ alternate angle] Again, CE ||BA and BCD is a transverse So, <ECD = <ABC [corresponding angle] Adding the corresponding sides <ACE + <ECD = <CAB + <ABC <ACD = <CAB + < ABC Therefore, it is proved that exterior angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of its interior opposite angle. Let’s discuss some problem on the angle sum property of triangle: Problem 1: Two angles of a triangle measures 63° and 47° respectively. Find the measure of the third angle of the triangle. Solution: Let the measure of the third angle be x°; since the sum of all the three angles of a triangle is 180°, we have 63 + 47 + x = 180 Or, 110 + x = 180 Or, x = 180 – 110 = 70 Therefore, the measure of the third angle is 70° Problem 2: The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2: 3: 4, find the measure of each angle of the triangle. Solution: Let the measures of the given angles be 2x° , 3x° , 4x°, Since the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°, so we have : 2x + 3x + 4x = 180 Or, 9x = 180 Or, x = 180/9 = 20 Angles are : 2 X 20 = 40 3 X 20 = 60 4 X 20 = 80
- 6. Therefore, the measures of three angles are 40° , 60° , 80°. Problem 3: Calculate the value of x in the downward figure. ( what is angle sum property of a triangle) Solution: In ΔABC, we have: <BAC + <ABC + <BCA = 180° Or, 40°+ <ABC + 90 = 180° Or, <ABC + 130° = 180° Or, <ABC = 180 – 130 = 50° IN ΔBDE , we have: <EBD + <BDE + < DEB = 180° Or, <ABC + <BDE + < DEB = 180° Or, 50° + x° + 100° = 180° Or, x° + 150°= 180° Or, x° = 180 – 150 = 30° Therefore, the value of x = <DEB = 30°. Problem 4 : Calculate the value of x in the downward figure. Solution: AD is joined to produce to E. Since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of interior opposite angles, so
- 7. In ΔACD, <CDE = <DCA + <CAD…………………………(i) In ΔABD, < EDB = <DAB + <ABD………………………….(ii) Adding (i) and (ii) , we have; <CDE + <EDB = <DCA + <CAD + <DAB + <ABD Or, x° = 30° + (<CAD + <DAB) + 45° Or, x° = 30° + 55° + 45° = 130° Or, x° = 130° Therefore, the value of x = 130°. Problem 5: In a right triangle, one of the acute angles is 58°. Find the other acute angle. Solution: Let the measure of the other acute angle be x°, then the angles of the triangle are 90°, 58° and x° . Since sum of all three angles of triangle is 180◦ according to the angle sum property, So, 90° + 58° + x° = 180° Or, 148° + x° = 180° Or, x = 180 – 148 Or, x = 32° Therefore, the measure of the other acute angle is 32°. Problem 6: In the adjoining figure ΔABC is right-angled at <C, and CD ḻ AB , also <A = 65°. Find (i) ACD ; (ii) <BCD; (iii) <CBD. Solution: ΔABC is right-angled triangle, <C = 90° <A = 65° So, <B = 180° – (90° + 65°) Or, <B = 180 – 155 = 25° Or, <CBD = 25° As, CD ḻ AB, Therefore, <ADC = <CDB = 90° In, ΔACD, we have,
- 8. <ACD + <CAD + <ADC = 180° Or, <ACD + 65°+ 90° = 180° Or, <ACD = 180 – (90 +65) = 25° In ΔBCD, we have, <BCD + <CBD + <BDC = 180° Or, <BCD + 25° + 90° = 180° Or, <BCD = 180 – ( 90 + 25) = 65° Therefore, <ACD = 25° , <BCD = 65° , <CBD = 25°. Problem 7: In ΔABC, D,E are points on sides AB and AC in such a way that DE||BC. If <B = 30° and <A = 40°, find x°,y°, z°. ( what is angle sum property of a triangle) Solution: In ΔABC, we have, <A = 40° and <B = 30° So, <A + <B + <C = 180° Or, 40°+ 30° + <C = 180° Or, <C = 180° – (40° +30°) Or, <C = 110° DE||BC and transversal AB cuts them at E and c respectively. <ACB = <AED ……………………. (corresponding angles) So, y° = z° = 110° Again, DE||BC and transversal AB cuts them at D and B respectively. <B = <ADE ………………………….(corresponding angles) x° = 30° Therefore, x° = 30° ; y° = 110° ; z° =110°. Problem 8: This figure has been obtained by using two triangles. Find out <A+<B+<C+<D+<E+<F
- 9. Solution: We know that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180° In ΔACE, we have <A +<C+<E = 180°……………..(i) In ΔBDF, we have <B+<D+<F = 180°………………(ii) Adding the corresponding sides of (i) and (ii) We get : <A+<C+<E+<B+<D+<F= 180° + 180°, So, <A+<B+<C+<D+<E+<F = 360° Therefore, sum of the six angles are 360°. Problem 9 : Calculate the value of of x. Solution: DBC is a straight line, we have: <ABD + <ABC = 180° <ABC = 180 – (<ABD) = 180 – 138 = 42°. BC = AC = < BAC = <ABC = 42°. In ΔABC, we have; <BAC +<ABC +<BCA = 180° Or, 42° + 42° + x° = 180° Or, 84° + x° = 180°
- 10. Or, x° = 180 – 84 = 96° Therefore, value of x = 96° Problem 10: Calculate the value of x. (what is angle sum property of a triangle) Solution: AB = AC ; so, <ACB = <ABC ………(angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal) Now, in ΔABC, we have; <BAC + <ABC +<ACB = 180° Or, 90°+ 2<ABC = 180° Or, 2<ABC = 180 – 90 So, <ABC = <BCA = 45° AC = CD <CAD = <ADC = x° Since, exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of interior opposite angles, So we have <ACB = <CAD +<ADC = 45°……..( <ACB = x° + x° ) 2x° = 45° Or, x° = (221/2)° Therefore, the value of x = (221/2)°.