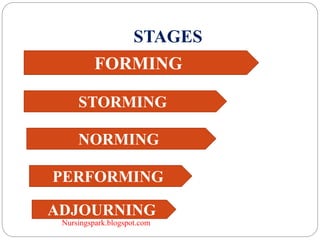
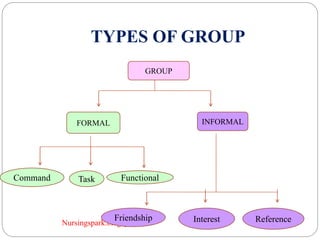
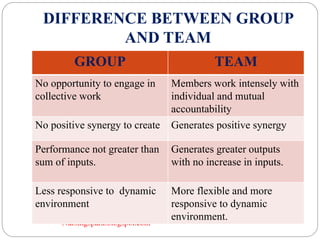
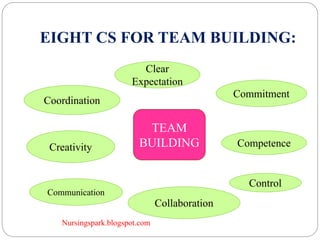
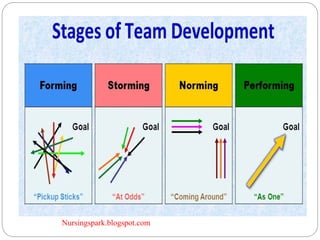
This document discusses group dynamics and teamwork in nursing education. It defines groups and their characteristics, and describes the stages of group development. It also defines formal and informal groups, and discusses factors that affect group behavior. The document emphasizes that teams are different from groups in that teams generate positive synergy and greater outputs. It outlines various types of teams and the benefits of teamwork in nursing, including improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.