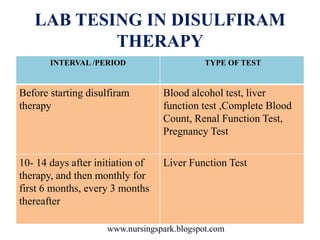
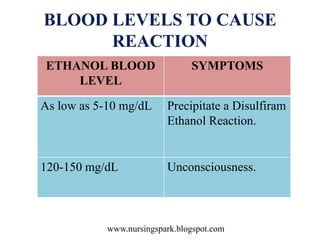
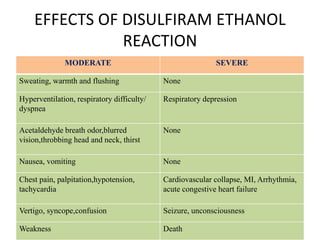
Disulfiram ethanol reaction (DER) occurs when alcohol is consumed after taking disulfiram or similar drugs, causing a buildup of toxic acetaldehyde. Symptoms range from flushing and headache to life-threatening hypotension, heart problems or liver failure. Treatment focuses on supportive care, with activated charcoal or hemodialysis for severe cases. Patients must be strongly warned to completely avoid alcohol and products containing alcohol while taking disulfiram to prevent dangerous DER.

























![www.nursingspark.blogspot.com
SYMPTOMS OF NEUROLOGIC
TOXICITY
Neurologic toxicity increases with dose and duration of
therapy and includes the following:
• Central and peripheral sensory motor neuropathy [7]
• Diffuse toxic axonopathy
• Psychosis - Limbic system stimulation by dopamine
• Choreoathetosis - Basal ganglia stimulation by
dopamine
• Parkinsonism - Caused by low-density lesions in the
basal ganglia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/disulfiram-200514160139/85/Disulfiram-ethanol-reaction-28-320.jpg)