Electrolysis: Ionic Conduction and Redox Reactions
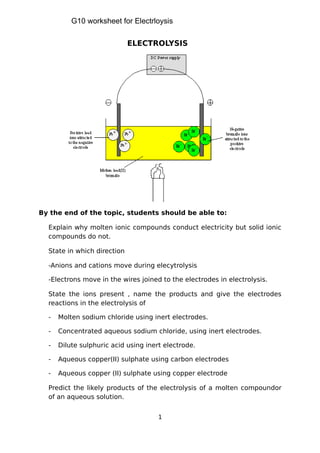
- 1. By the end of the topic, students should be able to: Explain why molten ionic compounds conduct electricity but solid ionic compounds do not. State in which direction -Anions and cations move during elecytrolysis -Electrons move in the wires joined to the electrodes in electrolysis. State the ions present , name the products and give the electrodes reactions in the electrolysis of - Molten sodium chloride using inert electrodes. - Concentrated aqueous sodium chloride, using inert electrodes. - Dilute sulphuric acid using inert electrode. - Aqueous copper(II) sulphate using carbon electrodes - Aqueous copper (II) sulphate using copper electrode Predict the likely products of the electrolysis of a molten compoundor of an aqueous solution. 1 ELECTROLYSIS G10 worksheet for Electrloysis
- 2. Explain what happen in refining copper. Describe electroplating (e.g. copper plating) Describe the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis. Please tick in the box if you can do the above. ELECTROLYTES • Electrolytes are ionic compounds that conduct electricity. The electrolyte can be either a molten ionic compound or an aqueous solution of an ionic compound. • Electrolytes conduct electricity because they contain positive and negative ons that can move freely throughout the liquid. Solid ionic compounds do not conduct electricity. Why? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ • When an electric current flows through an electrolyte, the compound is decomposed in a chemical reaction. This is called electrolysis. TERMS USED IN ELECTROLYSIS 2
- 3. The diagram below shows the flow of electrons to and from the battery in an electrolytic cell. ELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN IONIC COMPOUNDS • When a molten ionic compound is electrolysed, -the positive cations go to the _______________and are discharge by ______________ electrons to become _________________________. -the negative anions go to the ________________ and are discharge by _____________ electrons to become neutral _____________________________. -the ionic compound is decomposed into its _________________________. Example 1: Electrolysis of molten potassium iodide. a) What ions are present? _______________ b) Which one will move towards the cathode? __________________. c) Which one will move towards the anode? ____________________. d) Write the anode half equation. ________________________________________ 3
- 4. e) Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________ f) Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________ Electrolysis of molten sodium chloride a) What ions are present? _______________ b) Which one will move towards the cathode? __________________. c) Which one will move towards the anode? ____________________. d) Write the anode half equation. ________________________________________ e) Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________ f) Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________ Why is it important to keep on heating the crucible throughout the electrolysis? ________________________________________________________________________ When these ions react this is called “discharging the ions”. Why? ________________________________________________________________________ Please proceed to do exercise from: 4
- 5. WORKSHEET 1 ELECTROLYSIS OF AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS • There are 2 major differences here. The temperature is room temperature and there is water in the reaction. A small number of water molecules ionise H2O(l) → H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) • So all aqueous solutions have small concentration of H+ and OH- ions. • In electrolysis, when more than one type of cation or anion is present in a solution, only ONE cation and one anion are preferentially discharged. This is called selective discharge of ions. • How do you decide which ion is discharged? It depends on three factors - The position of the metal (producing the cation) in the reactivity series. - The relative ease of discharge of an anion. - The concentration of the anion in the electrolyte. The ease of discharge of cations and anions is shown below. Electrolysis of dilute sodium chloride solution 5
- 6. In dilute NaCl (aq) –what cations are present? _______________________ - what anions are present? ________________________ Using the reactivity series of metal and the relative ease of discharge of anion: - Which cation is reduced? ___________________________________ - Which anion is oxidised? ___________________________________ -Write the anode half equation. _________________________________________________ -Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________________ - Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________________ Please proceed to do exercise from: WORKSHEET 2 ELECTROLYSIS WITH REACTIVE ELECTRODES Electrodes can be inert. These do not react, they are just conductors of electricity to transfer electrons. E.g. platinum and graphite (carbon) Other electrodes can be reactive and be oxidized and are made from most of the other metals. These electrodes are oxidised before anions. 6
- 7. Please proceed to do exercise from: WORKSHEET 3 SUMMARY 7
- 8. INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION OF ELECTROLYSIS 1) Electroplating 8
- 9. • Electroplating is coatingan object with a metal by electrolysis. • The object is the cathode. The metal to be plated is the anode. The electrolyte is a solution of the metal ions to be plated. • During electroplating, metal from the anode dissolves in the electrolyte as metal ions. These ions go to the cathode where they are discharged onto the objectas a layer of metal. • An example of electroplating copper is shown in the diagram below. Metal Use Reason for use Chromium Tin Silver 2) Purifying (Refining) of metals • Similar to plating but the impure metal is the anode so it is oxidised and then reduced to a pure metal. • This electrolysis is used to refine copper (see diagram) 9
- 10. -Write the anode half equation. _________________________________________________ -Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________________ - Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________________ 3) Extraction of metals from their ores • Metals can be extracted from their ores by electrolysis. Electricity is expensive, so electrolysis is only used to extract very reactive metals such as sodium, calcium and aluminium. • These metals, ‘high up’ in the reactivity series, cannot be extracted by other methods. • Pure Al2O3 is extracted from bauxite. Al2O3 has a very high melting point (>2000°C) so it is added to molten cryolite (Na3AlF6) which dissolves the Al2O3 at about 950°C. The mixture is now electrolysed using carbon electrodes. Why is it an advantage to use a lower melting point to extract Al? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 10
- 11. Recycling of Aluminium • Aluminium is recycled because it saves the cost of extracting new metal from aluminium ore. About 90% of the cost of aluminium is due to the expenses of electrolysis. ELECTRIC CELLS • A simple electric cell consists of two different metals in an electrolyte. An example is shown in the diagram. The metals are zinc and copper, and the electrolyte is aqueous sodium chloride. • The more reactive metal (higher up in the reactivity series) is the negative electrode. It becomes negative because the electrode dissolves in the electrolyte leaving electrons on the electrode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- • Electrons go from the negative electrode through the wire to the positive electrode. 11
- 12. • The less reactive metal (lower down in the reactivity series) is the positive electrode. It becomes positive because positive ions in the electrolyte take electrons from the electrode and are discharged. • For example, if the electrolyte is NaCl (aq), hydrogen ions from the solution are discharged: 2H+ + 2e- → H2 • The further apart in the reactivity series the two metals are, the bigger is the voltage. • So a magnesium + copper cell has a bigger voltage than a zinc + copper cell. USES OF ELECTRIC CELLS • Electric cells are also known as batteries. Batteries are used in small flashlights and cars because a) They can be carried about without attached electrical cables. b) They can be used outdoors where there is no mains electricity available. Please proceed to do exercise from: Chemistry Insights, Pg 354, Questions, Question 1-2 WORKSHEET 4 12
- 13. WORKSHEET 1 13 Prepared by Kartini Ishak
- 14. WORKSHEET 2 Electrolysis of Concentrated Aqueous Sodium Chloride In dilute NaCl (aq) –what cations are present? _______________________ - what anions are present? ________________________ Using the reactivity series of metal and the relative ease of discharge of anion: - Which cation is reduced? ___________________________________ - Which anion is oxidised? ___________________________________ -Write the anode half equation. _________________________________________________ -Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________________ - Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________________ Electrolysis of Dilute Sulphuric Acid In dilute H2SO4 (aq) –what cations are present? _______________________ - what anions are present? ________________________ Using the reactivity series of metal and the relative ease of discharge of anion: - Which cation is reduced? ___________________________________ - Which anion is oxidised? ___________________________________ -Write the anode half equation. _________________________________________________ -Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________________ - Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________________ Electrolysis of Aqueous Copper (II) Sulphate 14 Prepared by Kartini Ishak
- 15. In dilute CuSO4 (aq) –what cations are present? _______________________ - what anions are present? ________________________ Using the reactivity series of metal and the relative ease of discharge of anion: - Which cation is reduced? ___________________________________ - Which anion is oxidised? ___________________________________ -Write the anode half equation. _________________________________________________ -Write the cathode half equation. _______________________________________________ - Write the overall redox reaction. _______________________________________________ WORKSHEET 3 15
- 17. 18 y9 revision