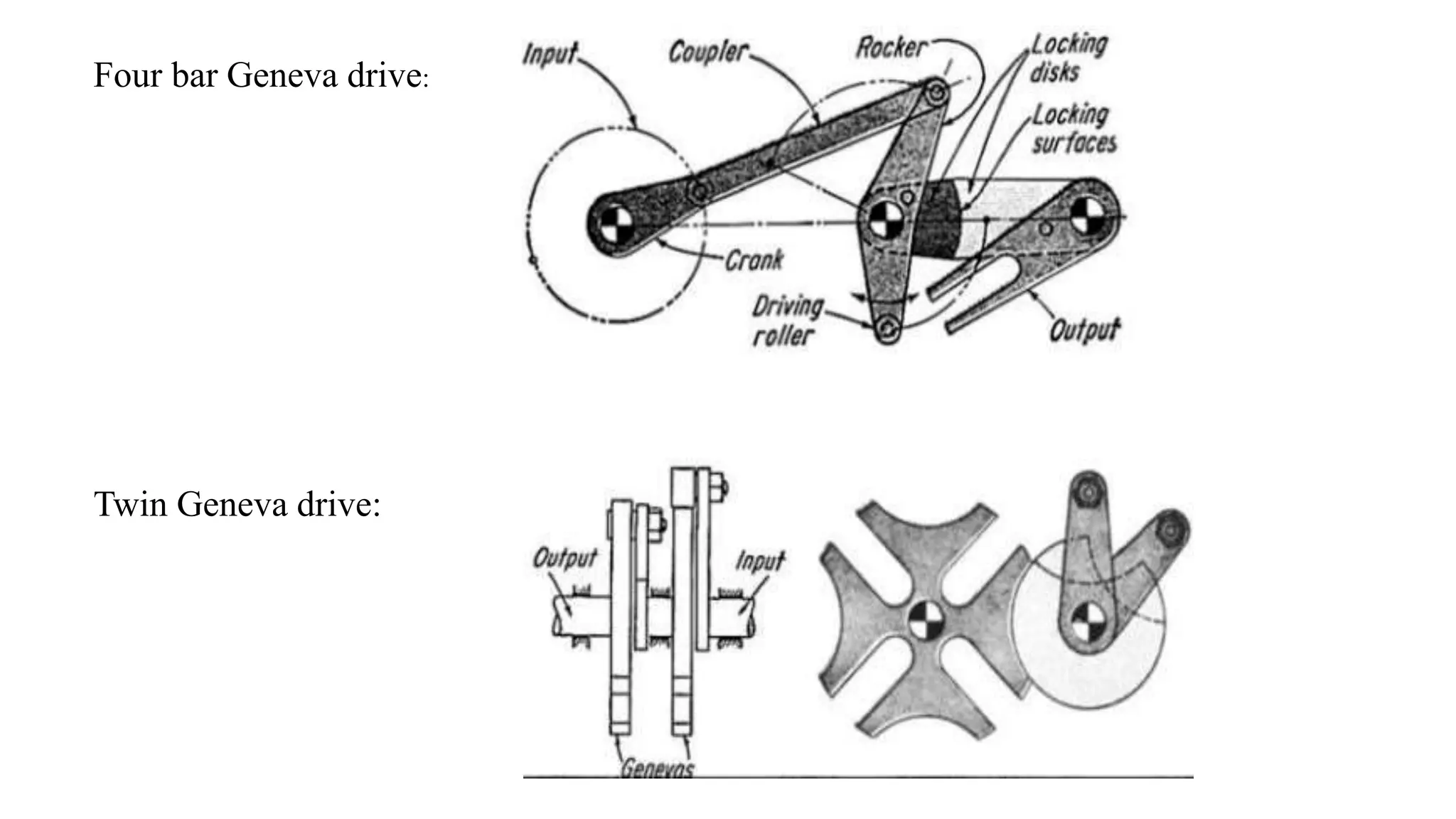
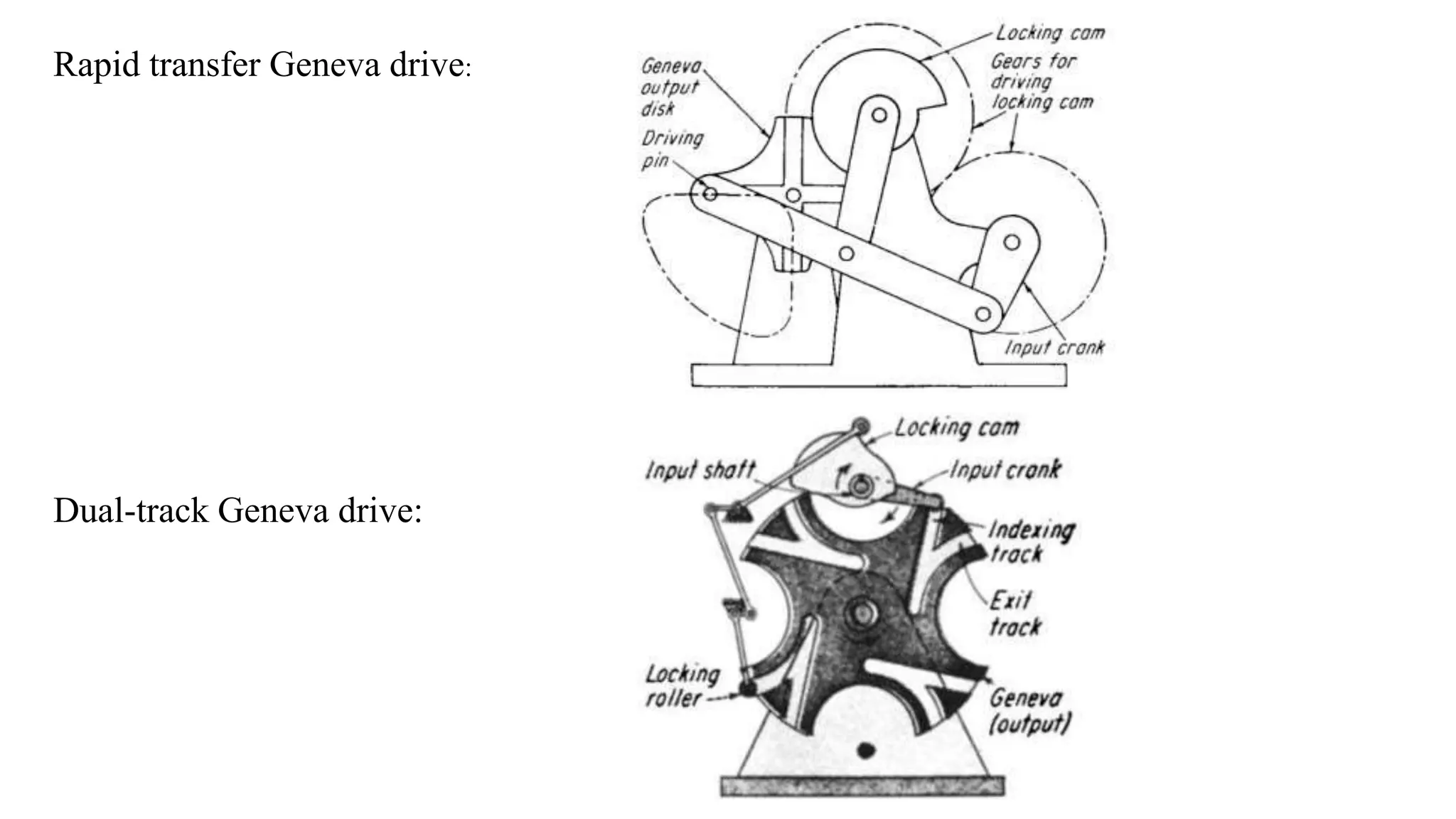
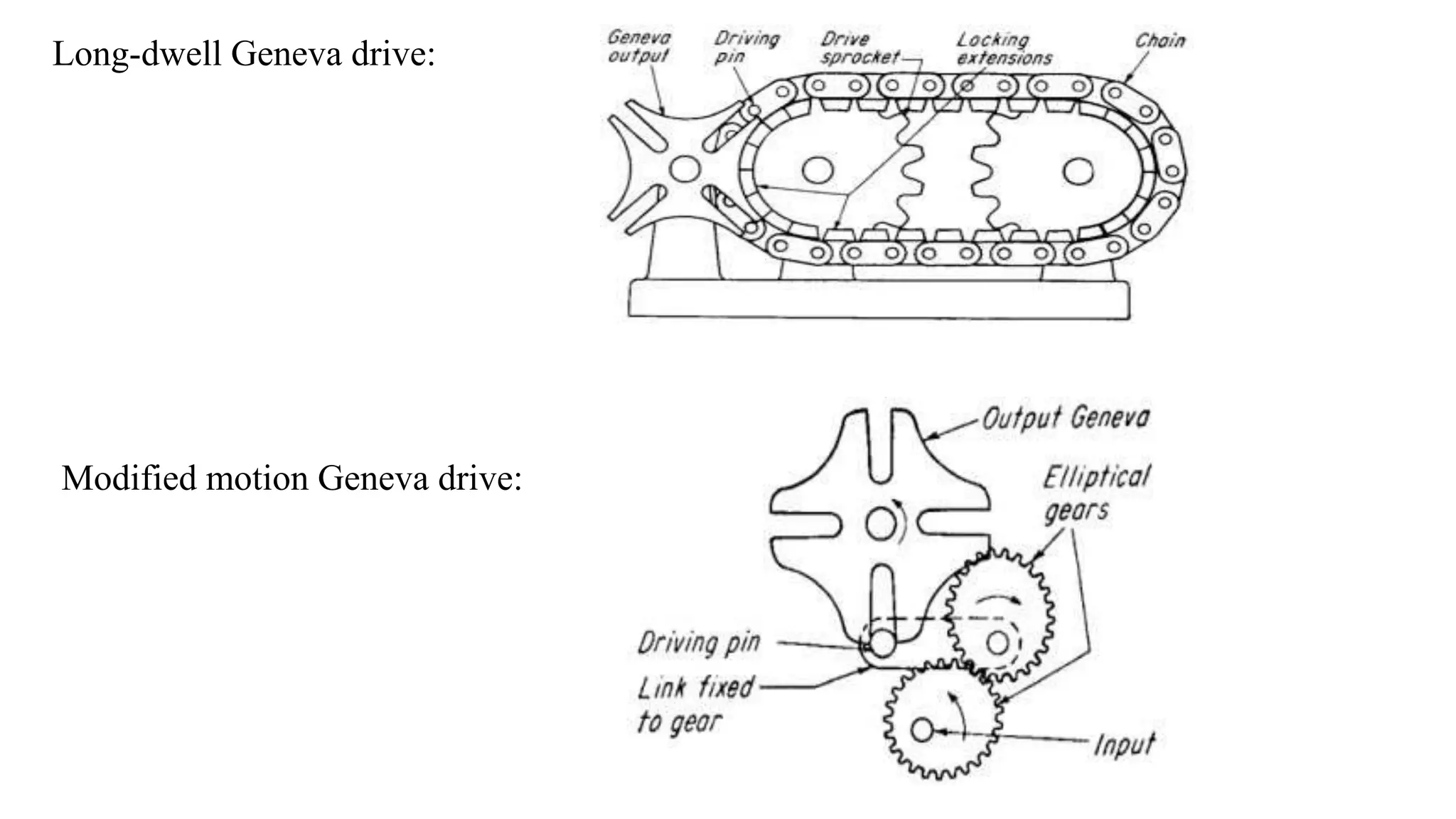
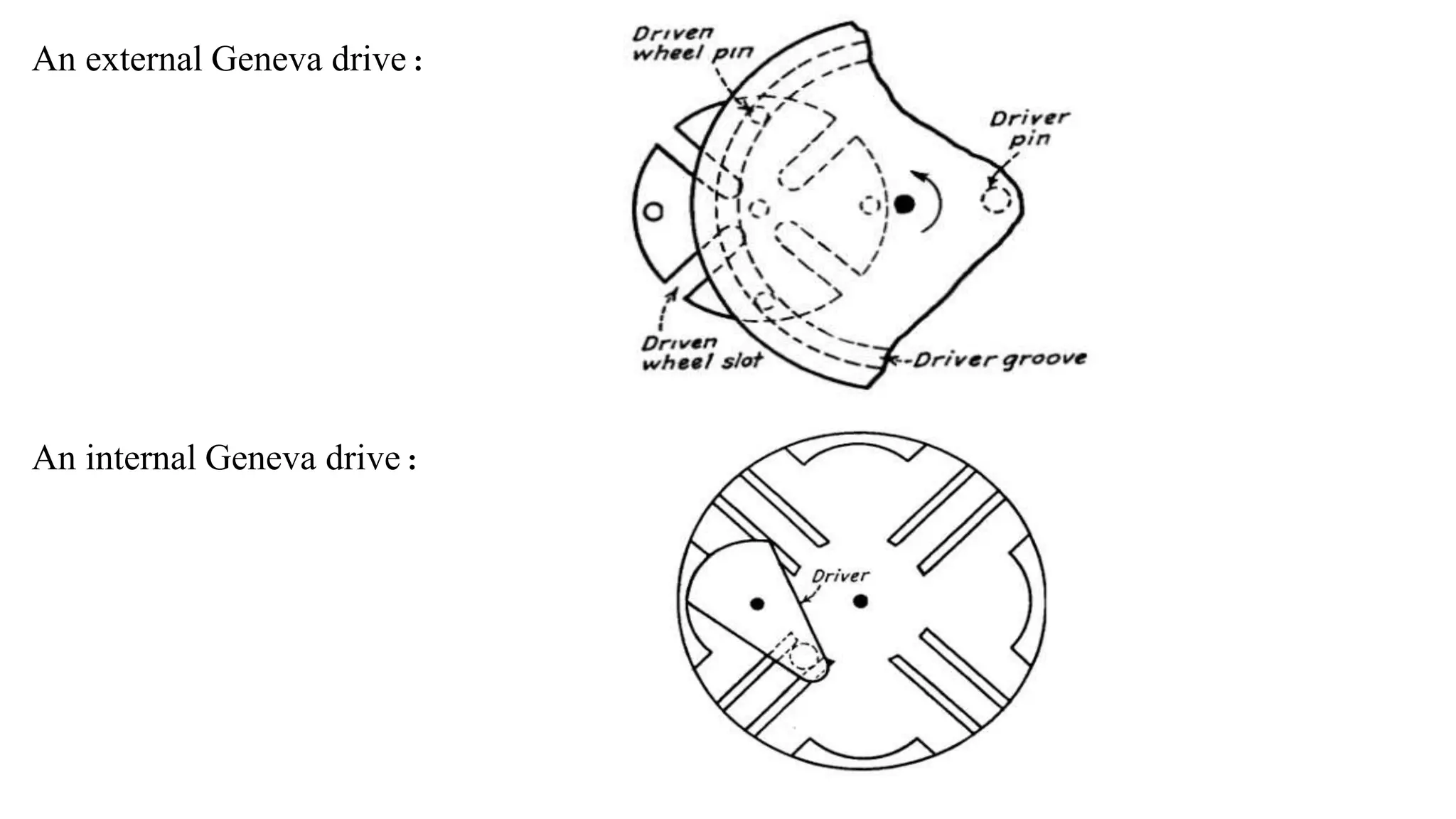
The document provides an overview of the Geneva drive mechanism, detailing its function in converting continuous rotation into intermittent motion and its various types. It discusses applications in industries like pharmaceuticals and movie projectors, highlighting advantages such as precise control and long lifespan, along with limitations like a fixed number of dwells and design rigidity. Additionally, it outlines the creation of a computer program for designing and manufacturing the Geneva mechanism components using CAD software.