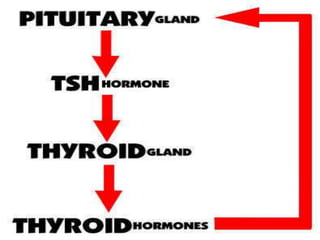
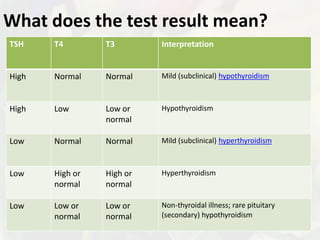
The document discusses thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), and thyroxine (T4) blood tests. TSH is produced in the brain and triggers the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4, which regulate metabolism. The tests are used to diagnose hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, and monitor treatment. Reference ranges, test procedures, and potential signs and symptoms of thyroid disorders are provided.