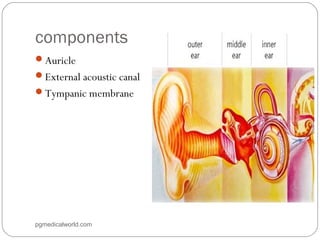
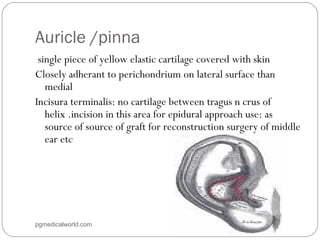
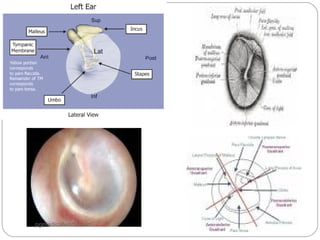
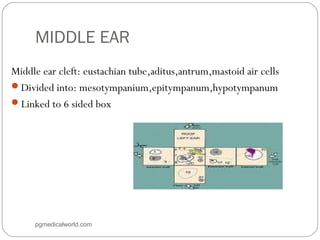
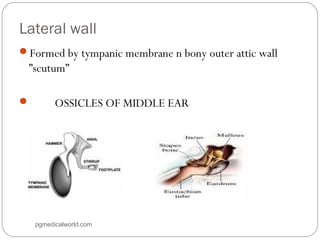
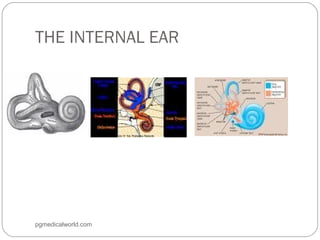
The document summarizes the anatomy of the ear. It describes the three main parts of the outer ear: the auricle, external acoustic canal, and tympanic membrane. It then discusses the middle ear in detail, including the bones (malleus, incus, stapes) and muscles (tensor tympani, stapedius). Finally, it briefly outlines the three sections of the inner ear: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. The ear has a complex anatomy that allows it to receive sound waves and transmit signals to the brain.