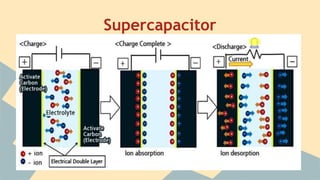
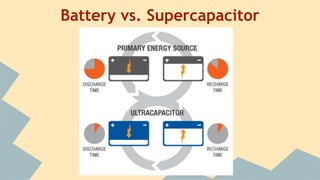
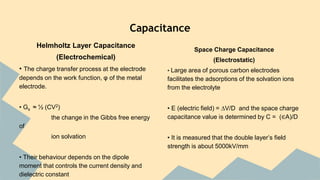
Supercapacitors can store electric charge through a process called double layer capacitance. They have a higher power density than batteries but a lower energy density. A supercapacitor increases its capacitance and energy storage capacity by increasing the surface area of its electrodes and decreasing the distance between them. While supercapacitors have limitations like lower energy density and higher cost than batteries, they charge and discharge much faster than batteries and can be cycled millions of times, making them useful for applications that require bursts of energy or regeneration of energy. Recent research is focused on improving supercapacitors' energy density to make them a viable alternative to batteries for more applications.