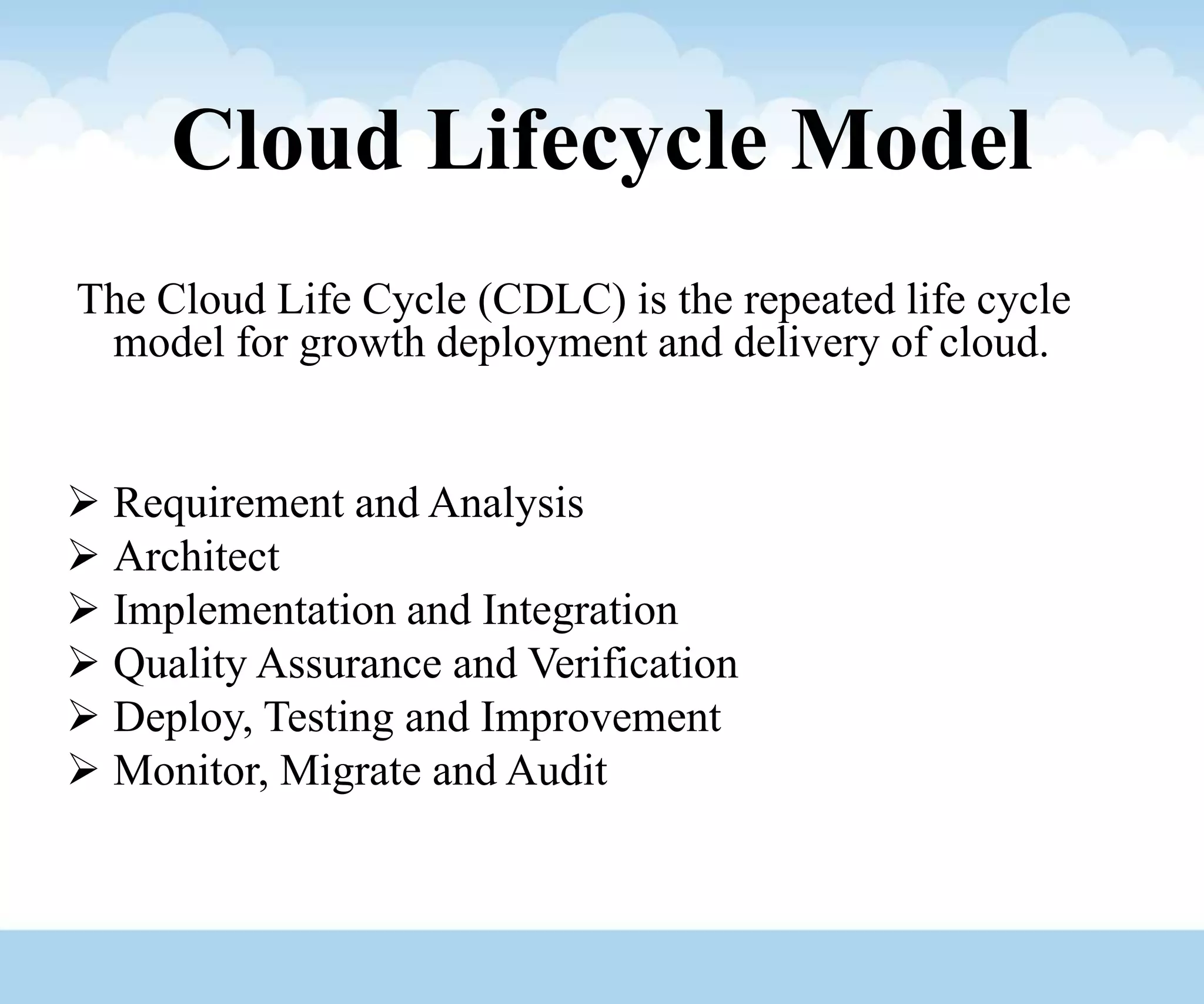
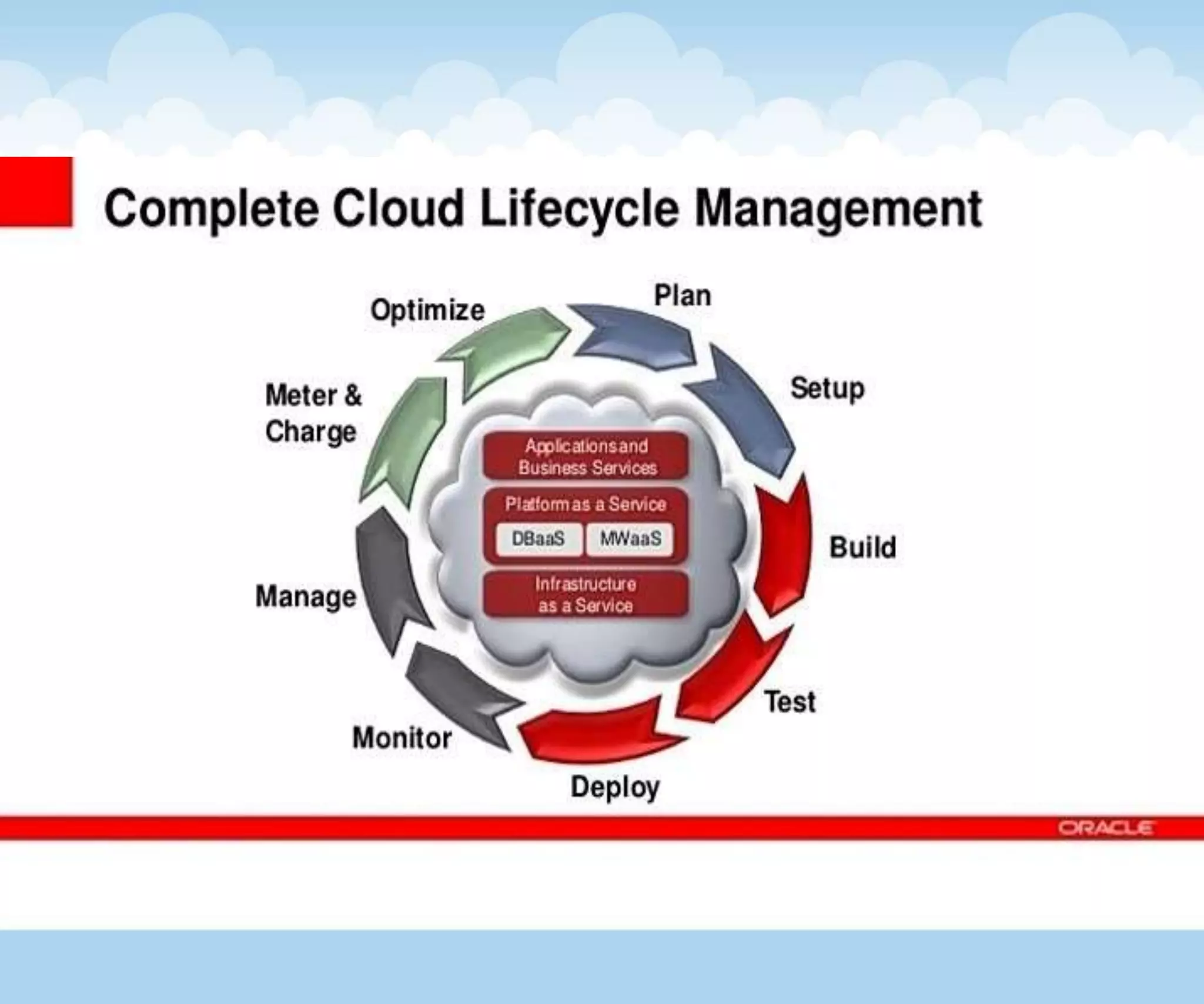
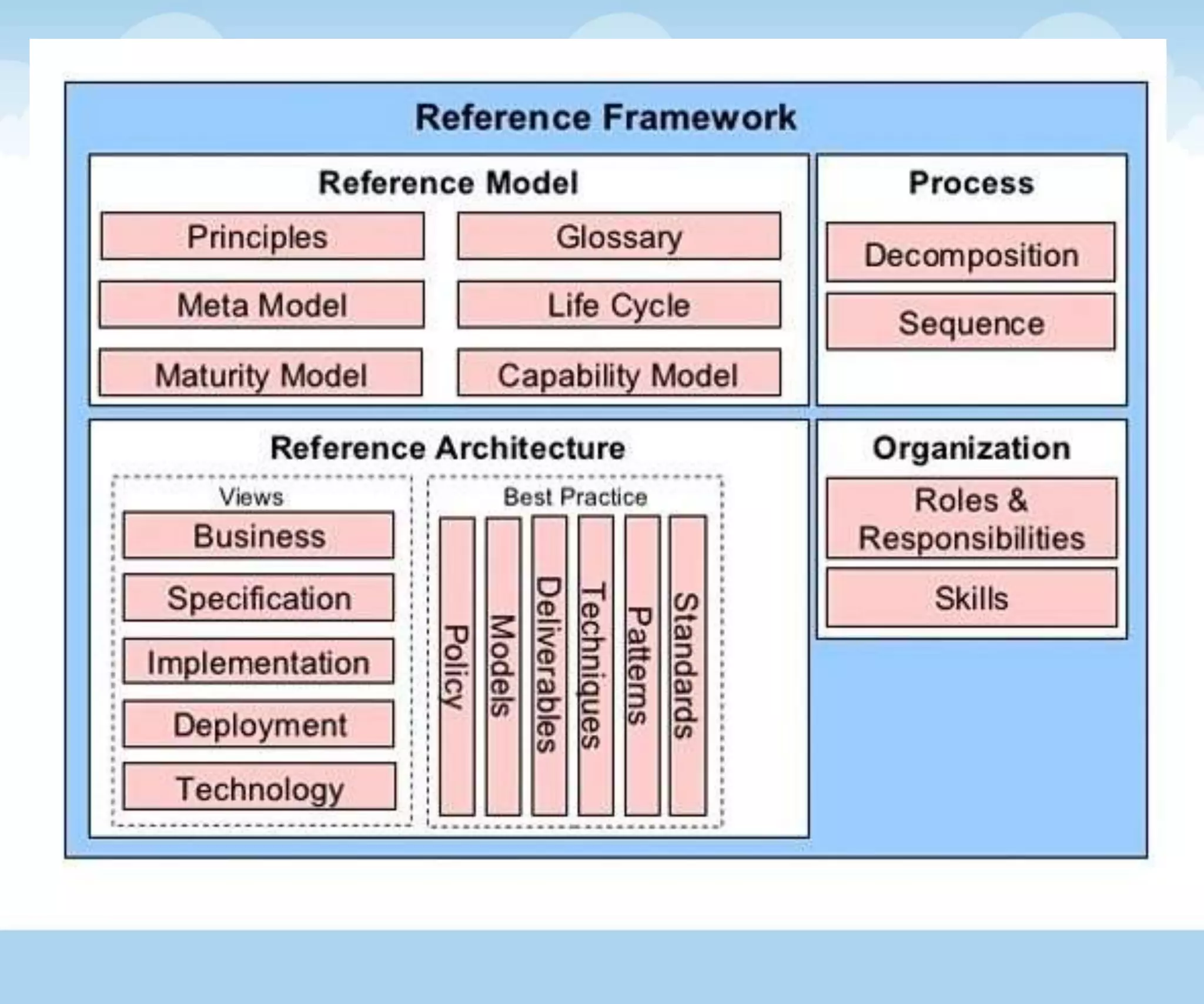
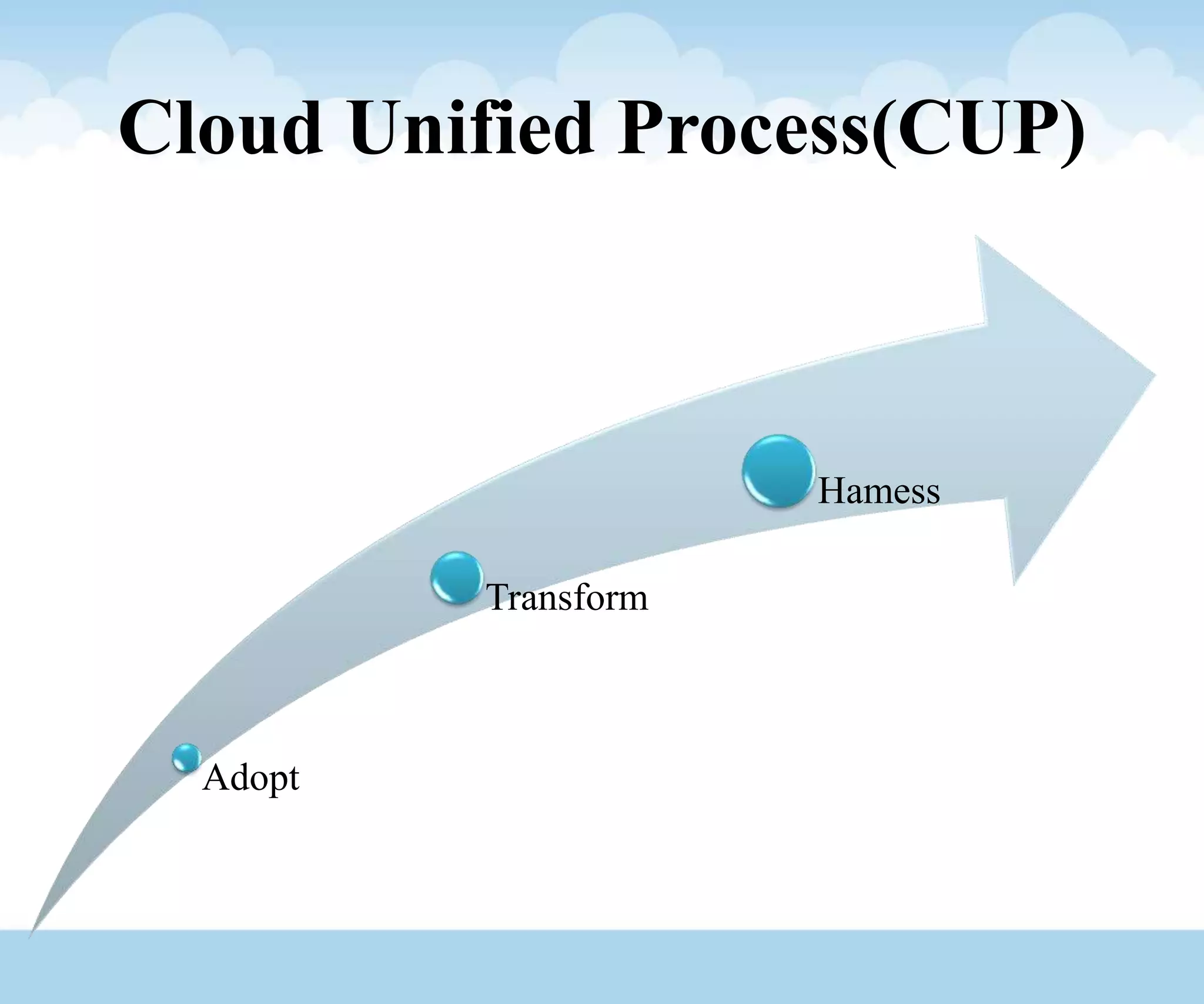
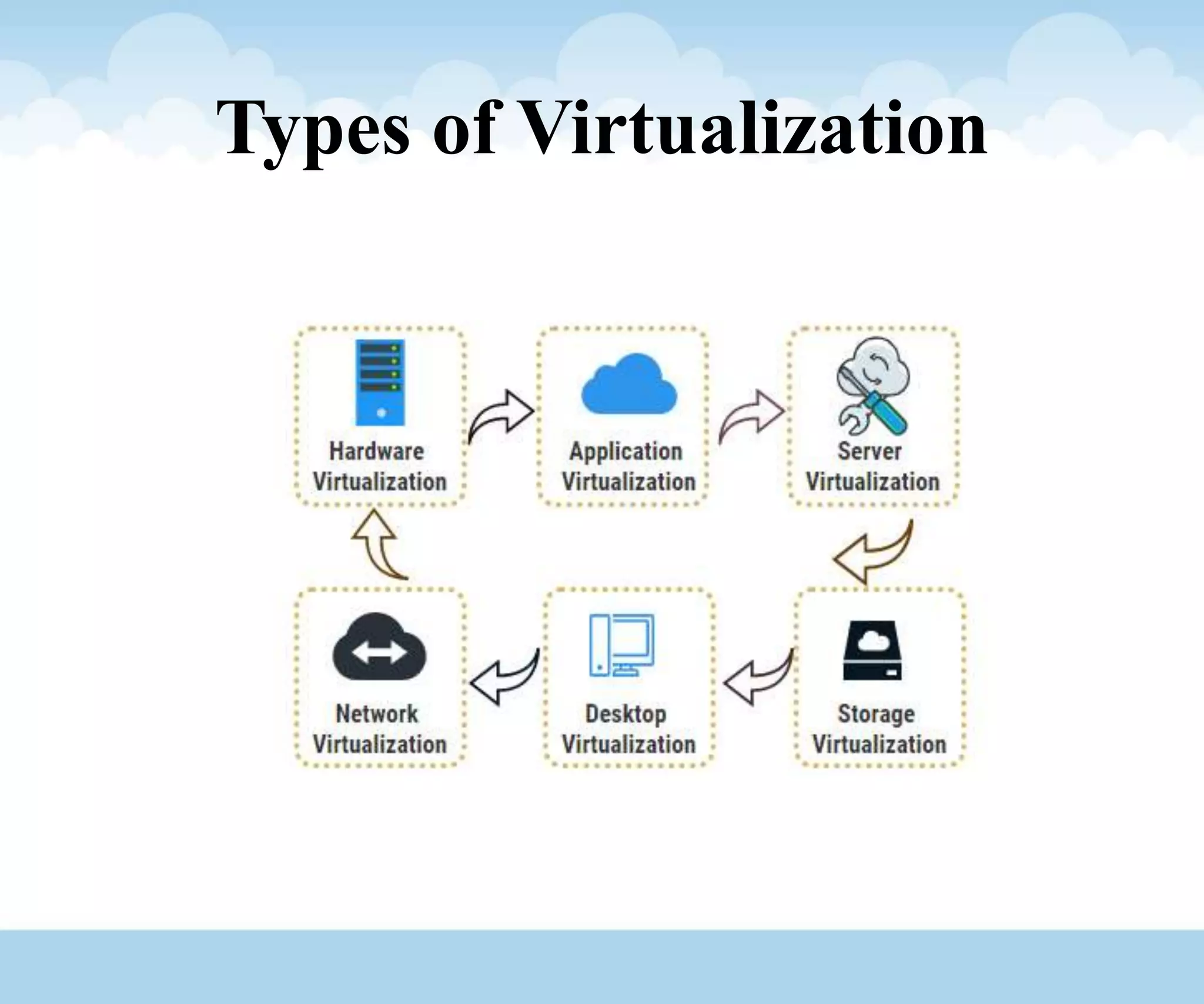
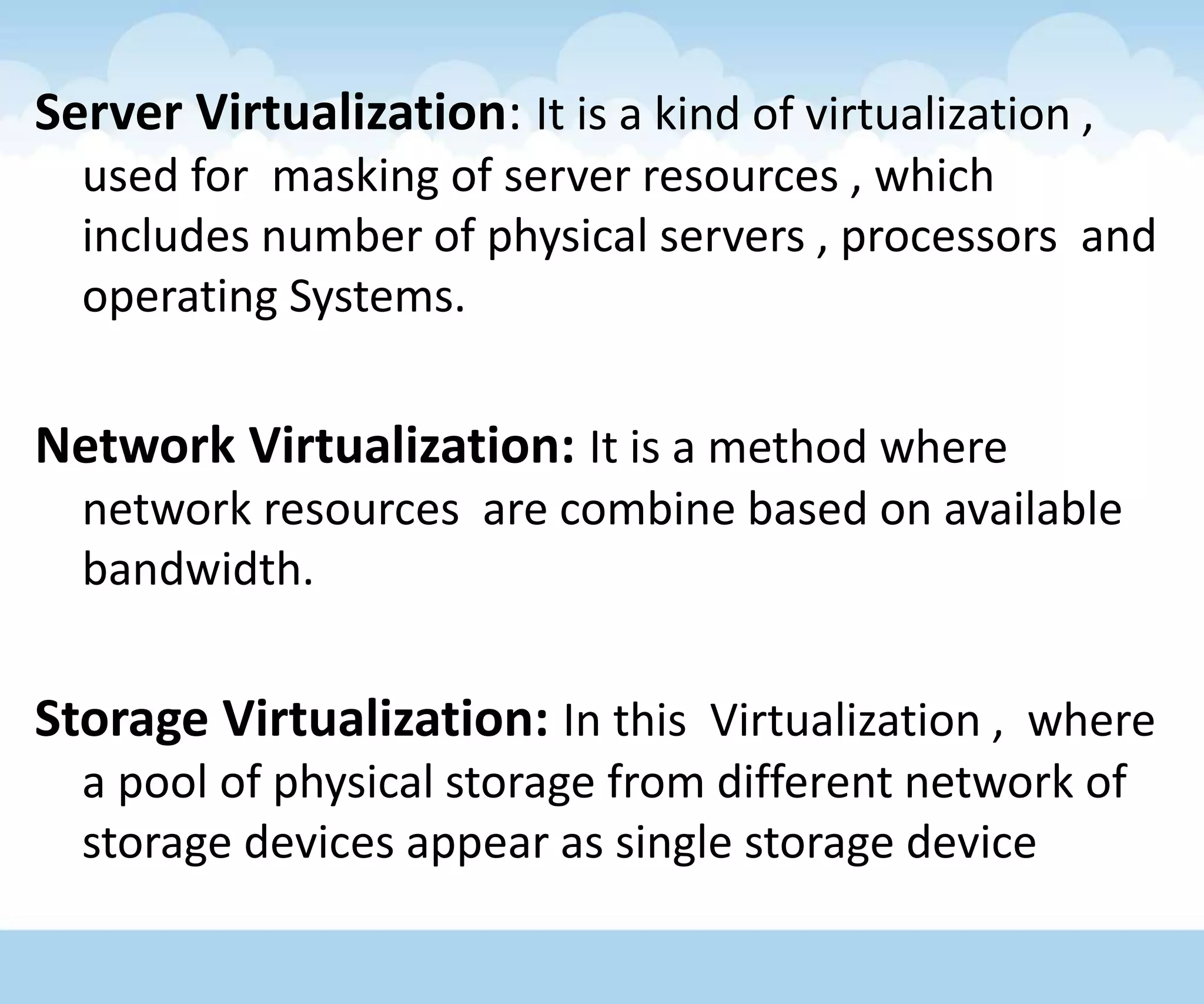
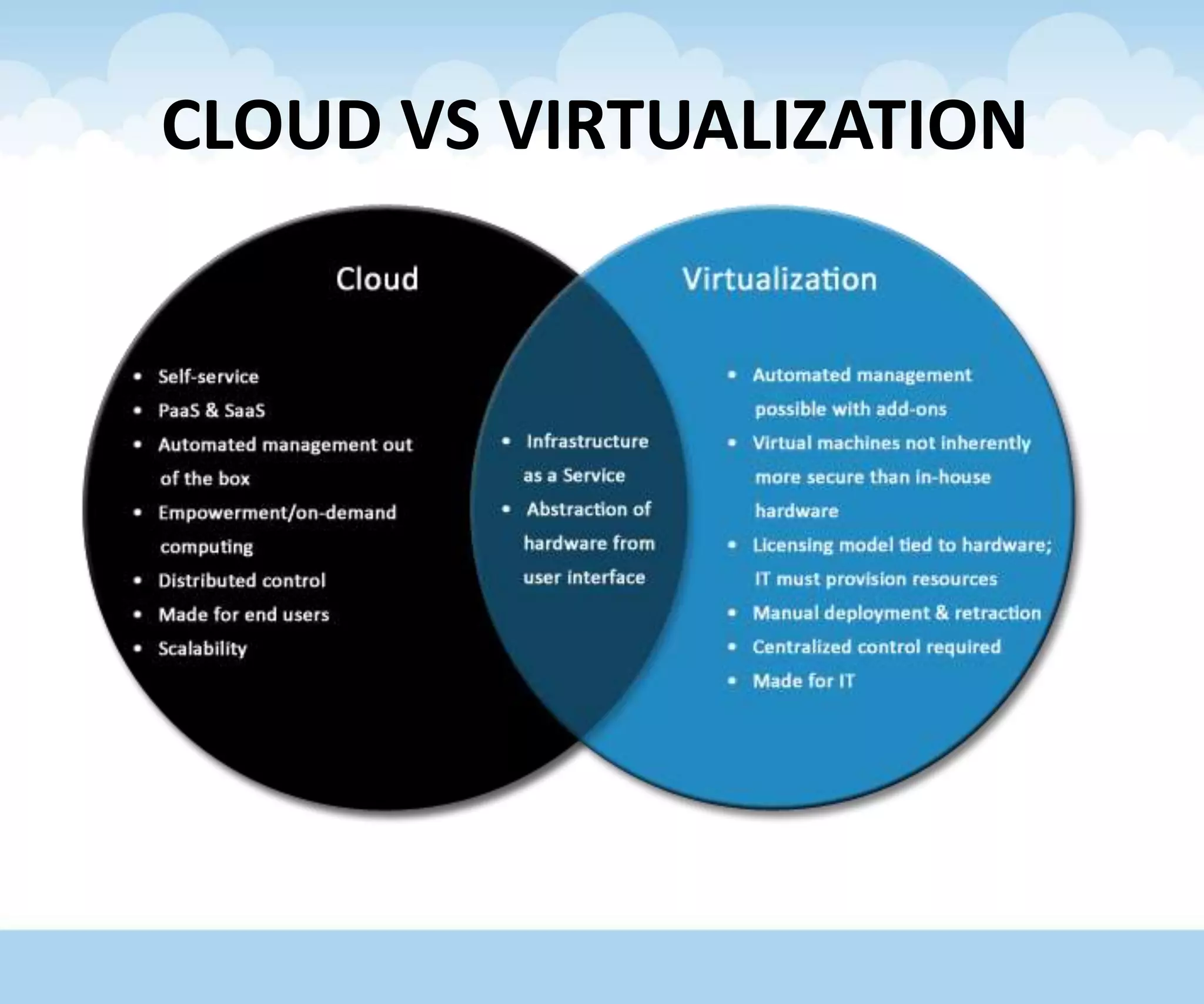
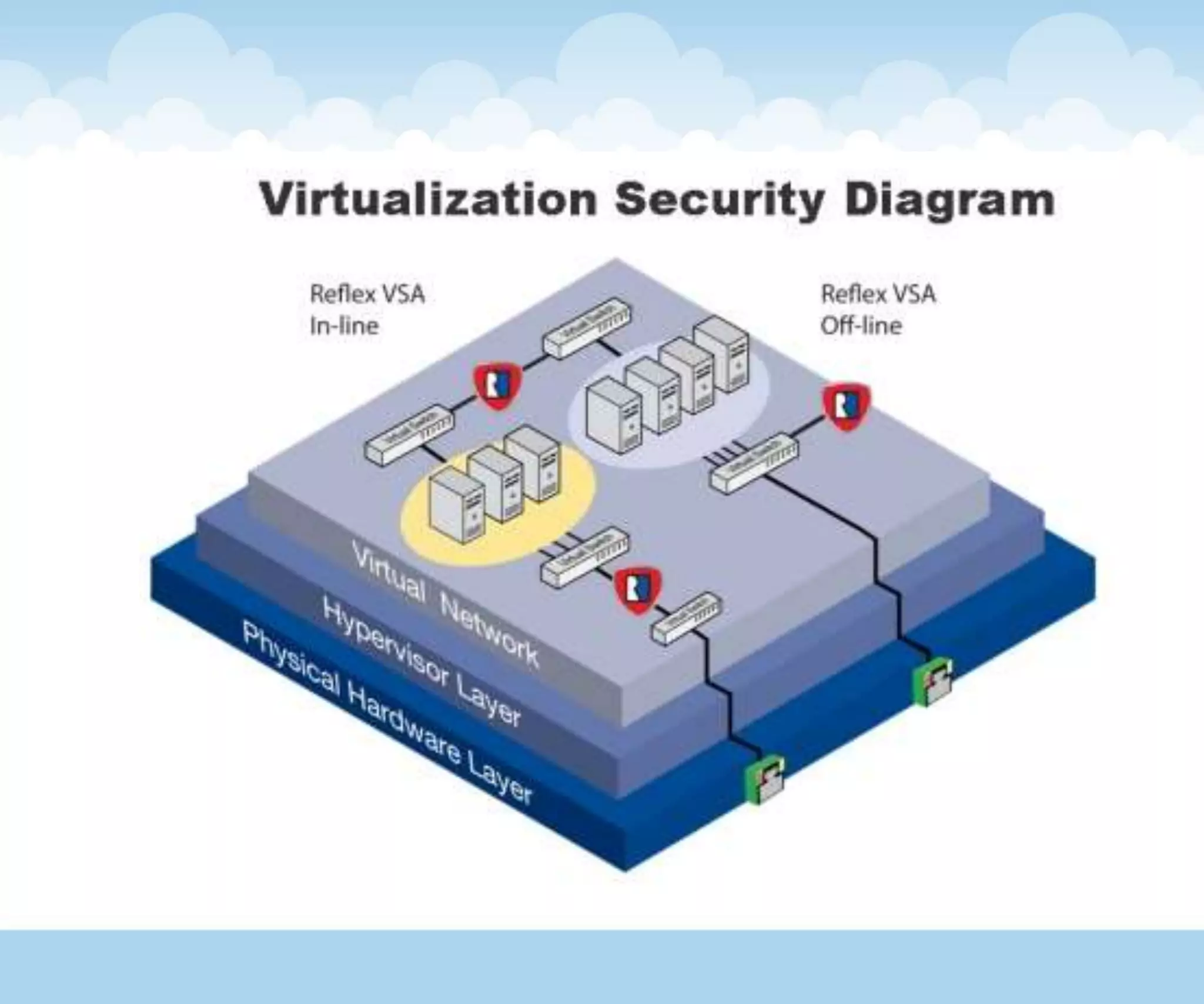
The document discusses the architecture and lifecycle of cloud computing, detailing key concepts such as cloud technology, deployment models (private, public, hybrid), and various service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS). It also covers virtualization methodologies and types, emphasizing their roles in cloud systems, and highlights the complexities and interdependent components of cloud ecosystems. Additionally, it addresses concerns related to cloud computing, such as availability, security, and data integrity.