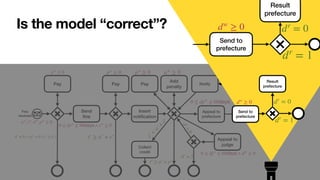
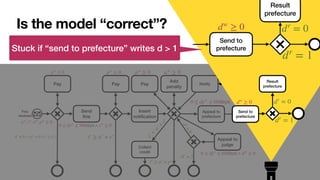
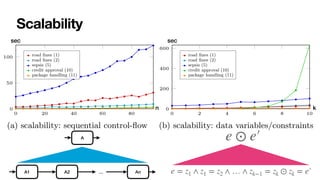
The document discusses the soundness of data-aware processes in information systems, focusing on static and dynamic constraints in process-oriented views. It examines various models, including data petri nets, for soundness checking with arithmetic conditions and explores the challenges of reachability and decidability. The paper highlights advancements in methodologies for formal analysis and practical applications, including improvements in scalability and performance.


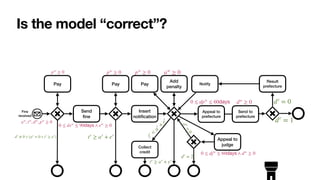
![A process model with case data and conditions
Adapted from [Mannhardt et al., Computing 2016]
Fine
received
Send
fi
ne
Appeal to
prefecture
Pay
Insert
noti
fi
cation
Pay
Appeal to
judge
Pay
Send to
prefecture
Result
prefecture
Notify
Collect
credit
Add
penalty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-6-320.jpg)
![Adapted from [Mannhardt et al., Computing 2016]
Fine
received
Send
fi
ne
Appeal to
prefecture
Pay
Insert
noti
fi
cation
Pay
Appeal to
judge
Pay
Send to
prefecture
Result
prefecture
Notify
Collect
credit
Add
penalty
amount total
amount
dismissal
code
points
deducted
expenses ds dp dj
A process model with case data and conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-7-320.jpg)
![Adapted from [Mannhardt et al., Computing 2016]
Fine
received
Send
fi
ne
Appeal to
prefecture
Pay
Insert
noti
fi
cation
Pay
Appeal to
judge
Pay
Send to
prefecture
Result
prefecture
Notify
Collect
credit
Add
penalty
amount total
amount
dismissal
code
points
deducted
expenses ds dp dj
dj
A process model with case data and conditions
x
xw
xr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-8-320.jpg)
![Adapted from [Mannhardt et al., Computing 2016]
Fine
received
Send
fi
ne
Appeal to
prefecture
Pay
Insert
noti
fi
cation
Pay
Appeal to
judge
Pay
Send to
prefecture
Result
prefecture
Notify
Collect
credit
Add
penalty
aw
, tw
, dw
, pw
≥ 0
pw
≥ 0
0 ≤ dsw
≤ 90days ∧ ew
≥ 0
pw
≥ 0 pw
≥ 0 aw
≥ 0
tr
≥ ar
+ er
dr
≠ 0 ∨ (pr
= 0 ∧ tr
≥ ar
)
t
r
<
a
r
+
e
r
tr
≥ ar
+ er
0 ≤ djw
≤ 60days ∧ dw
≥ 0
d
r
=
0
dr
= 2
0 ≤ dpw
≤ 60days dw
≥ 0 dr
= 0
dr
= 1
amount total
amount
dismissal
code
points
deducted
expenses ds dp dj
A process model with case data and conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-9-320.jpg)

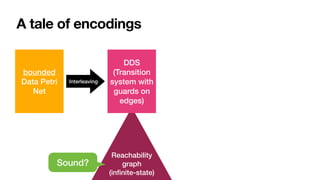
![Data Petri Nets
[Mannhardt,PhD2018; _____,ER2018; _____,ACSD2019]
• Petri nets enriched with typed variables
(ranging over in
fi
nite domains)
• Transitions access variables via read and
write guards
• State: marking + variable assignment
• Transition
fi
ring: usual
fi
ring semantics +
variable assignment update given a binding
for the written variables
In
fi
nite reachability graph even when the net is bounded
Which language to express conditions? We want (linear) arithmetic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-14-320.jpg)



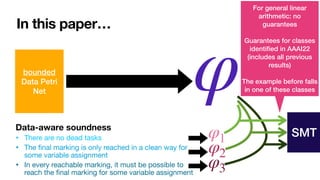
![Data-Aware Soundness for Data Petri nets
[____,ER2018;____,ACSD2019]
Always “option to complete”:
• There are no dead tasks
• The
fi
nal marking is only reached in a clean way for
some variable assignment
• In every reachable marking, it must be possible to
reach the
fi
nal marking for some variable assignment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-18-320.jpg)


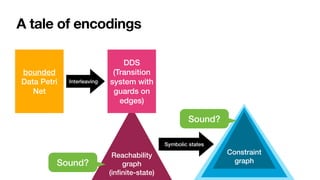
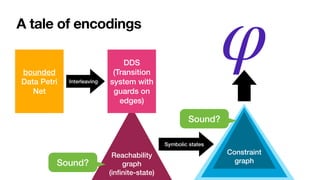
![A tale of encodings
Reachability
graph
(in
fi
nite-state)
bounded
Data Petri
Net
DDS
(Transition
system with
guards on
edges)
Interleaving
Sound?
Constraint
graph
Symbolic states
Sound?
[ER2018]: variable-to-constant
[ACSD2019]: variable-to-variable
no arithmetic
Direct,
fi
nite abstractions!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-23-320.jpg)
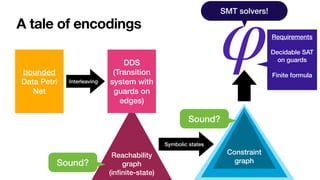
![A tale of encodings
Reachability
graph
(in
fi
nite-state)
bounded
Data Petri
Net
DDS
(Transition
system with
guards on
edges)
Interleaving
Sound?
Constraint
graph
Symbolic states
Sound?
φ
SMT solvers!
[AAAI2022]
Semantic notion of
fi
nite-summary
Identi
fi
ed syntactic
classes inducing
fi
nite-
summary
Linear-time properties
Requirements
Decidable SAT
on guards
Finite formula](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-26-320.jpg)

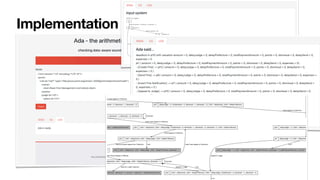
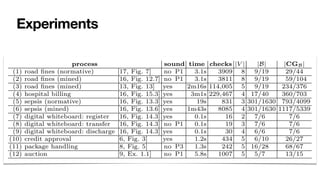
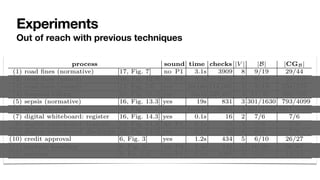
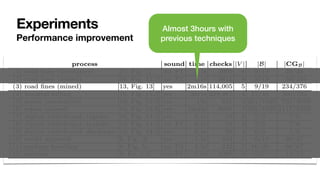
![General framework for DPNs with arithmetic
Formal analysis paired with data abstraction techniques
No ad-hoc algorithms: SMT as a Swiss Army knife
Recent progress: CTL* model checking [IJCAR22]
SMT for discovery, tight discovery-reasoning integration
On-
fi
eld validation?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caise-2022-dpn-arithmetics-220819230134-968fb223/85/Soundness-of-Data-Aware-Processes-with-Arithmetic-Conditions-39-320.jpg)