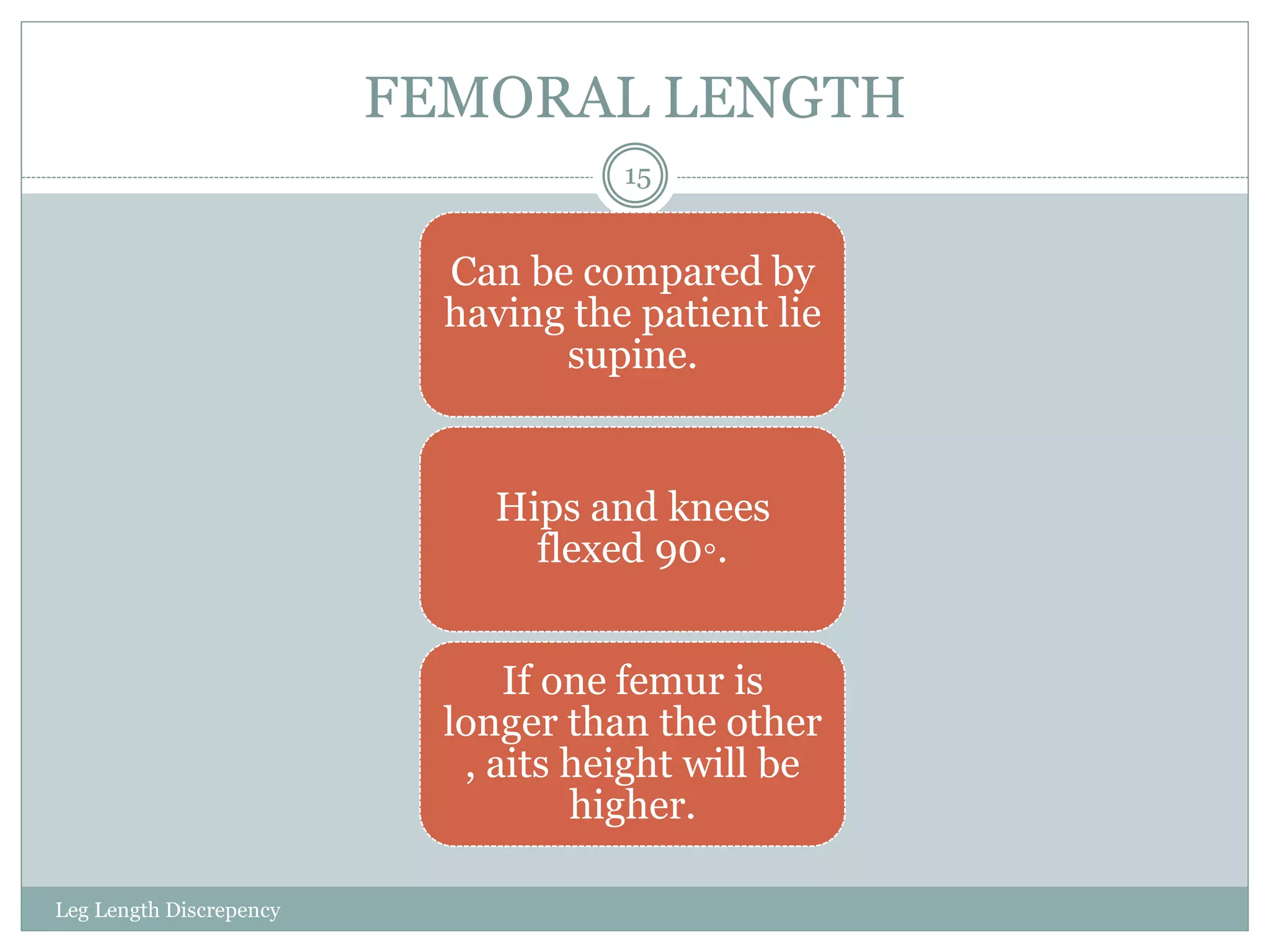
This document discusses leg length discrepancy (LLD), which is when the paired lower extremities have an unequal length. There are two types of LLD - structural (true) shortening caused by anatomical changes, and functional (apparent) shortening from positioning. Causes of LLD include developmental abnormalities, soft tissue shortening, degenerative disorders, trauma, and fractures. LLD is measured from the anterior superior iliac spine to the medial malleolus, with 1-1.5cm being normal. Additional measurements may be needed depending on the location of shortening. Visual tests like the Weber Barstow Maneuver can also detect LLD.