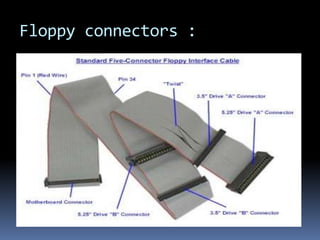
A floppy disk is a magnetic storage medium sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier that is read and written by a floppy disk drive. Floppy disks were commonly used to store files and boot systems when hard drives were less common. They came in 5.25 inch and 3.5 inch sizes, with storage capacities ranging from 100KB to 1.44MB. Floppy disks worked by using read/write heads very close to a magnetic disk coated with particles that could hold data bits.





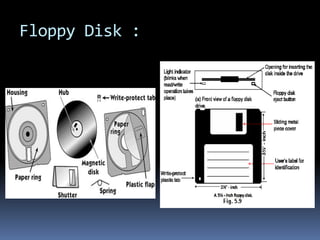


![Floppy drive construction :
Made of ferrite type to make them electromagnetic.
Head contacts much closer compared to HDD due to
low rpm [300 rpm]
3.5 Floppy disk has only 80 tracks per side so the
actuator doesn’t need to be much precise as HDD.
Unlike HDD, FDD has 3 heads :
One is Read/Write head
And other two is tunnel –erase head to clean up after r/w head
as there is a magnetization that overlaps two adjacent tracks
while writing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floppydiskdrive-131004010719-phpapp01/85/Floppy-disk-drive-10-320.jpg)