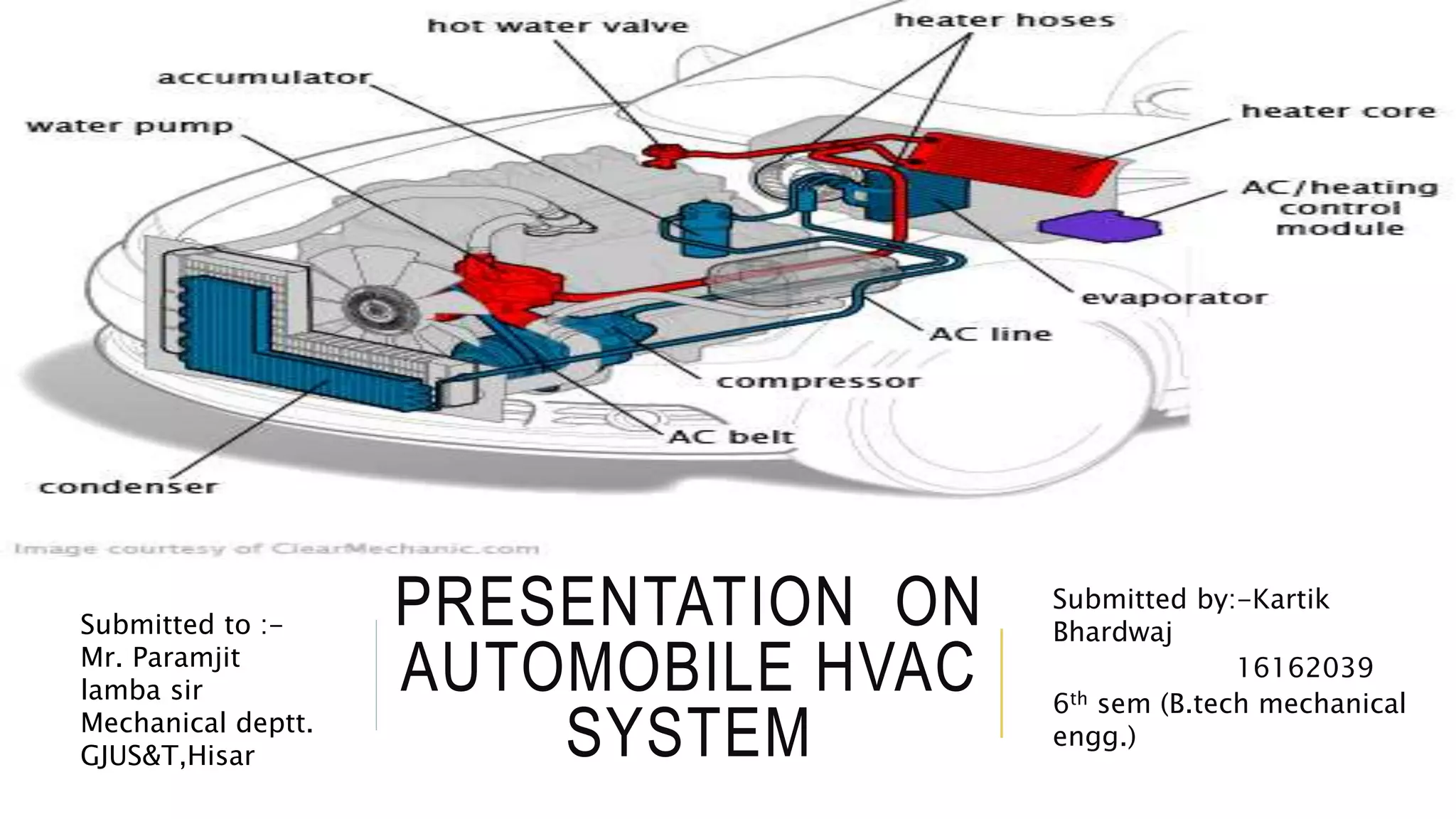
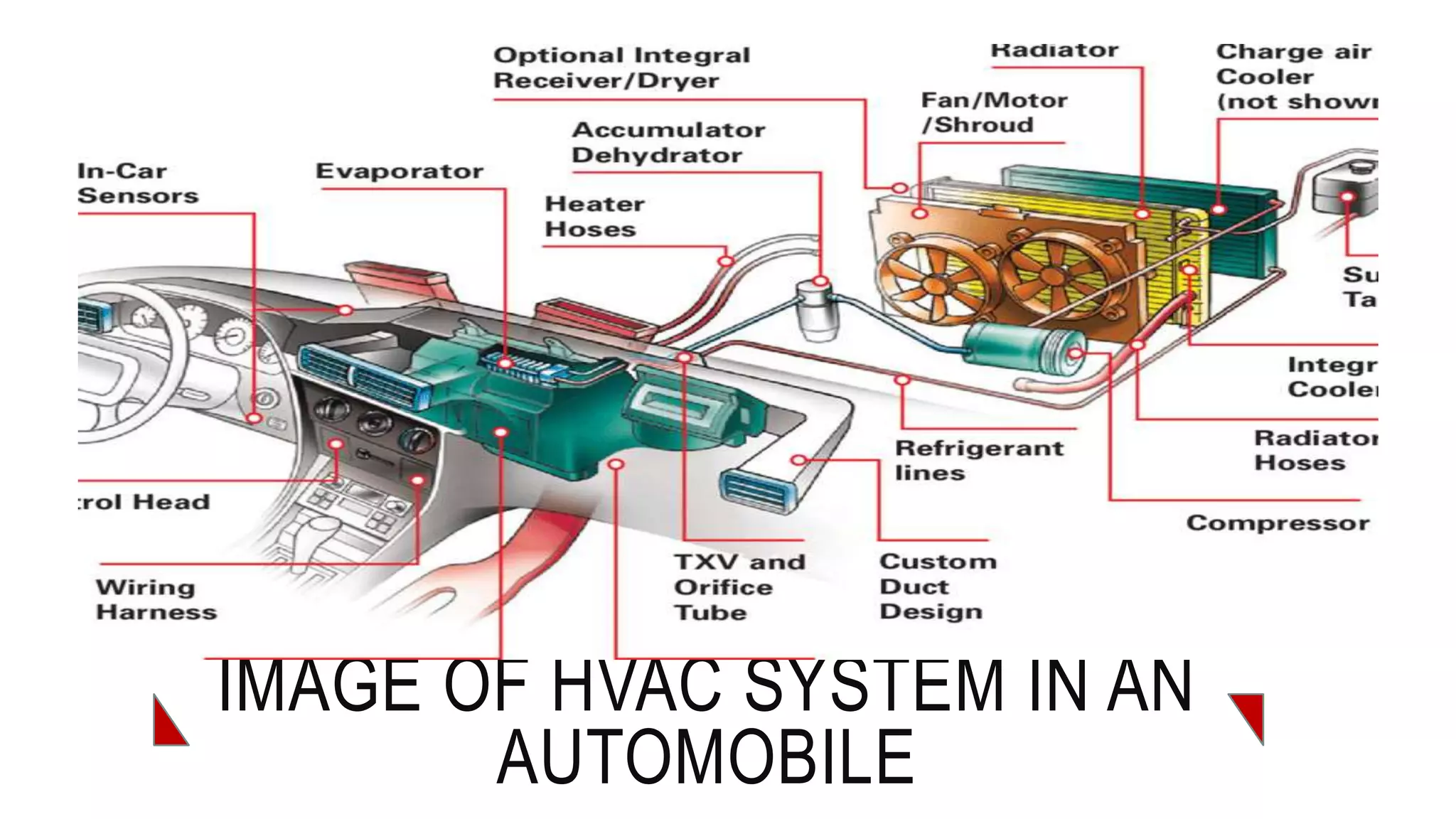
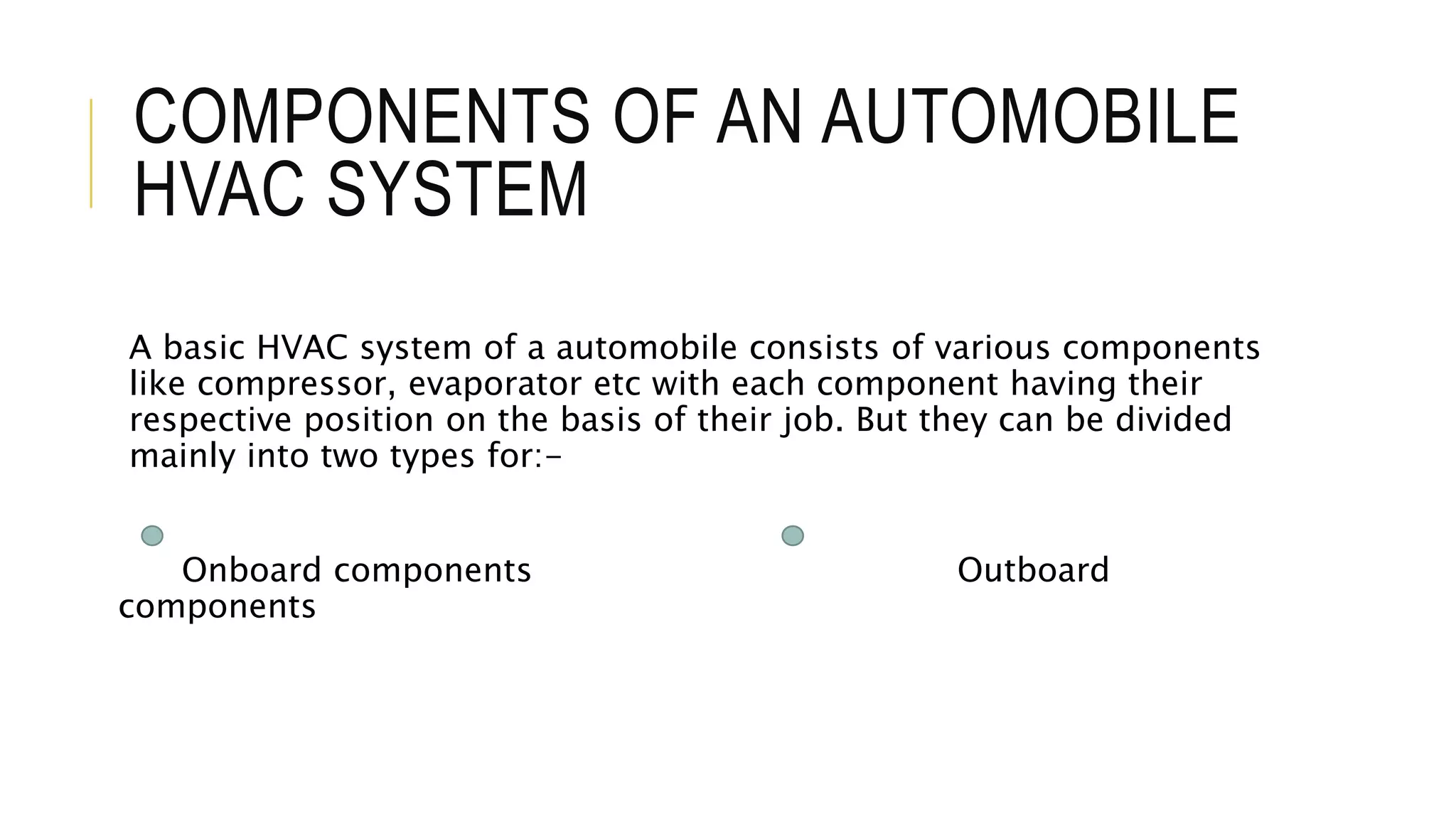
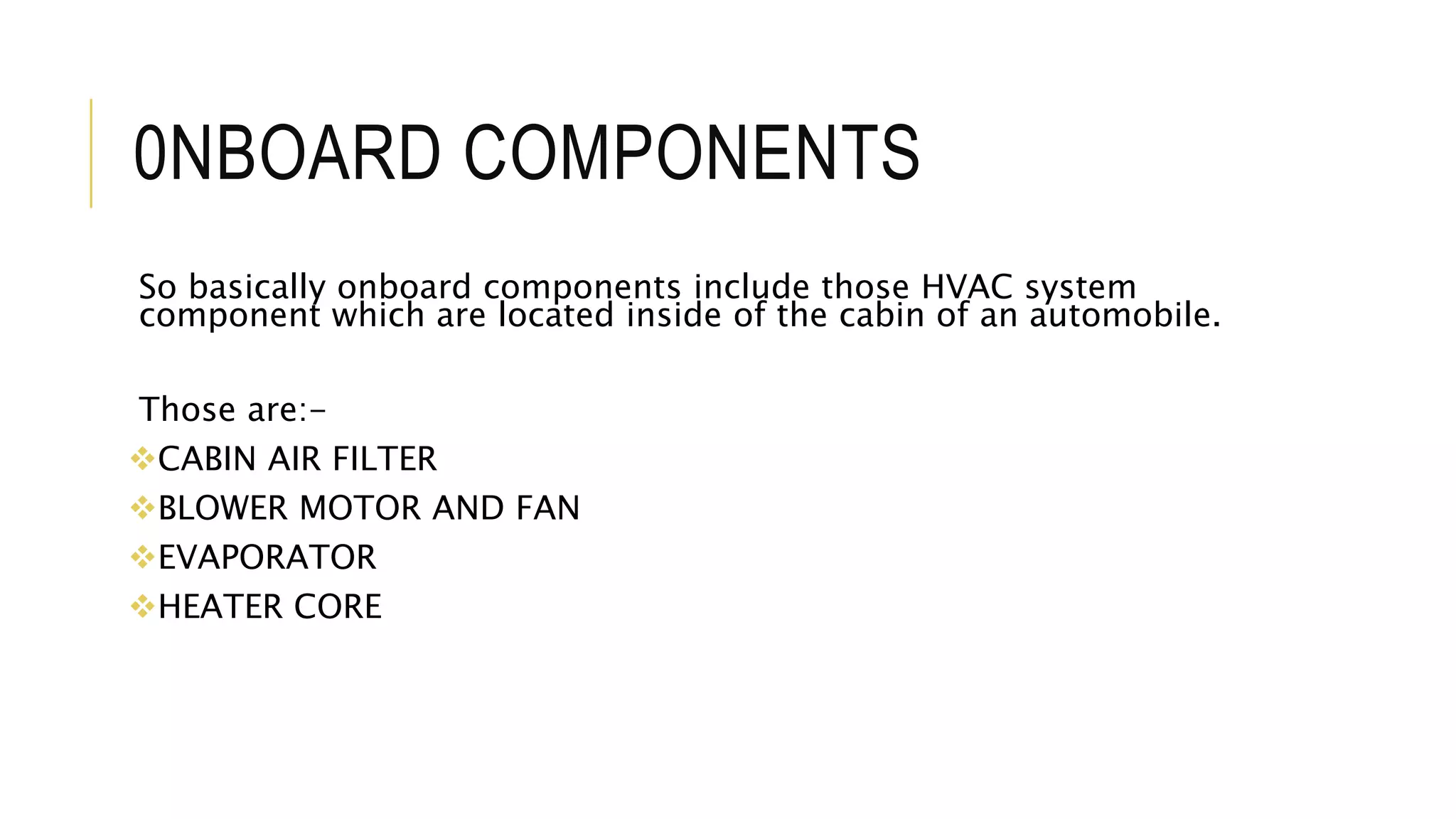
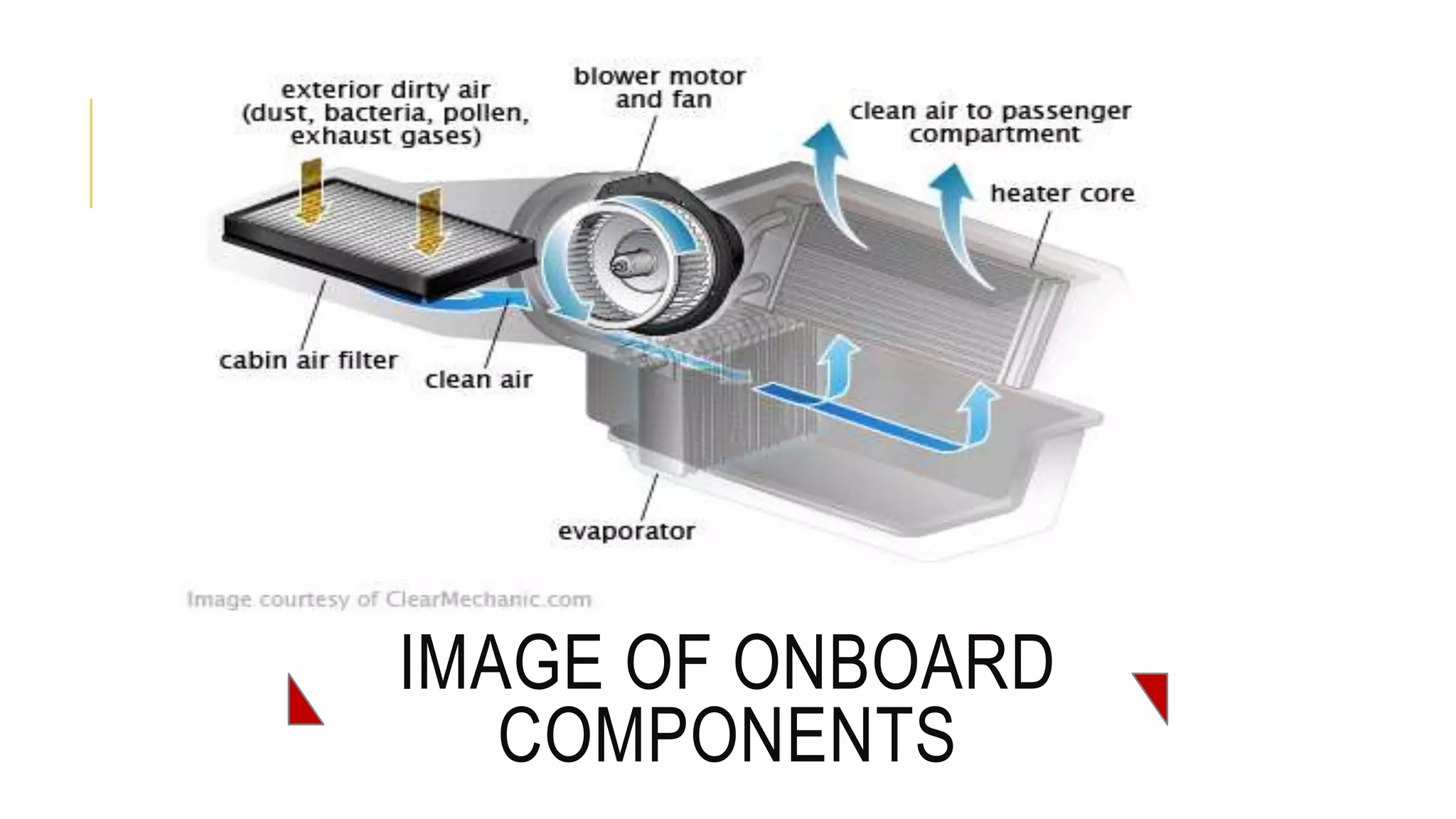
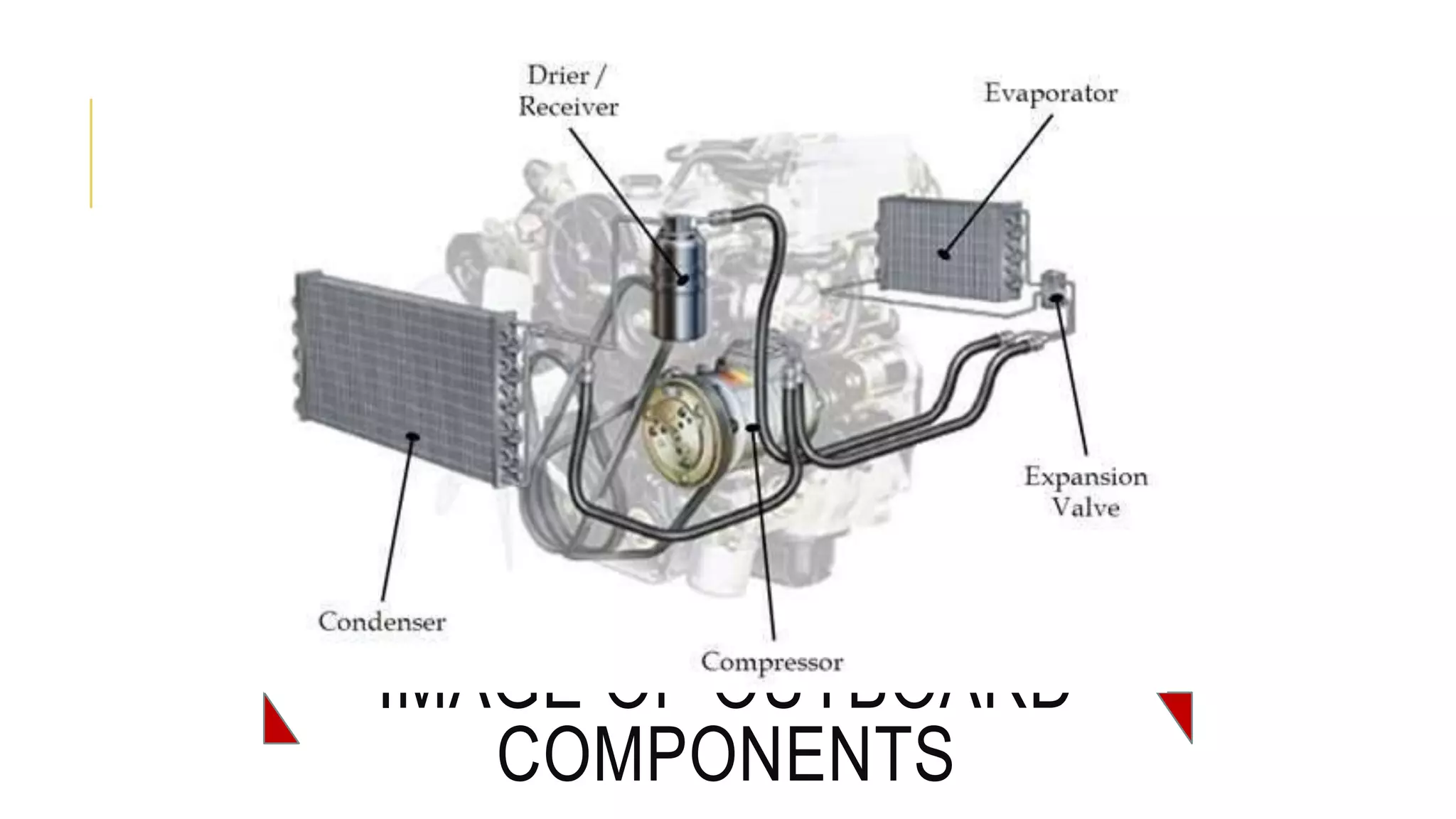
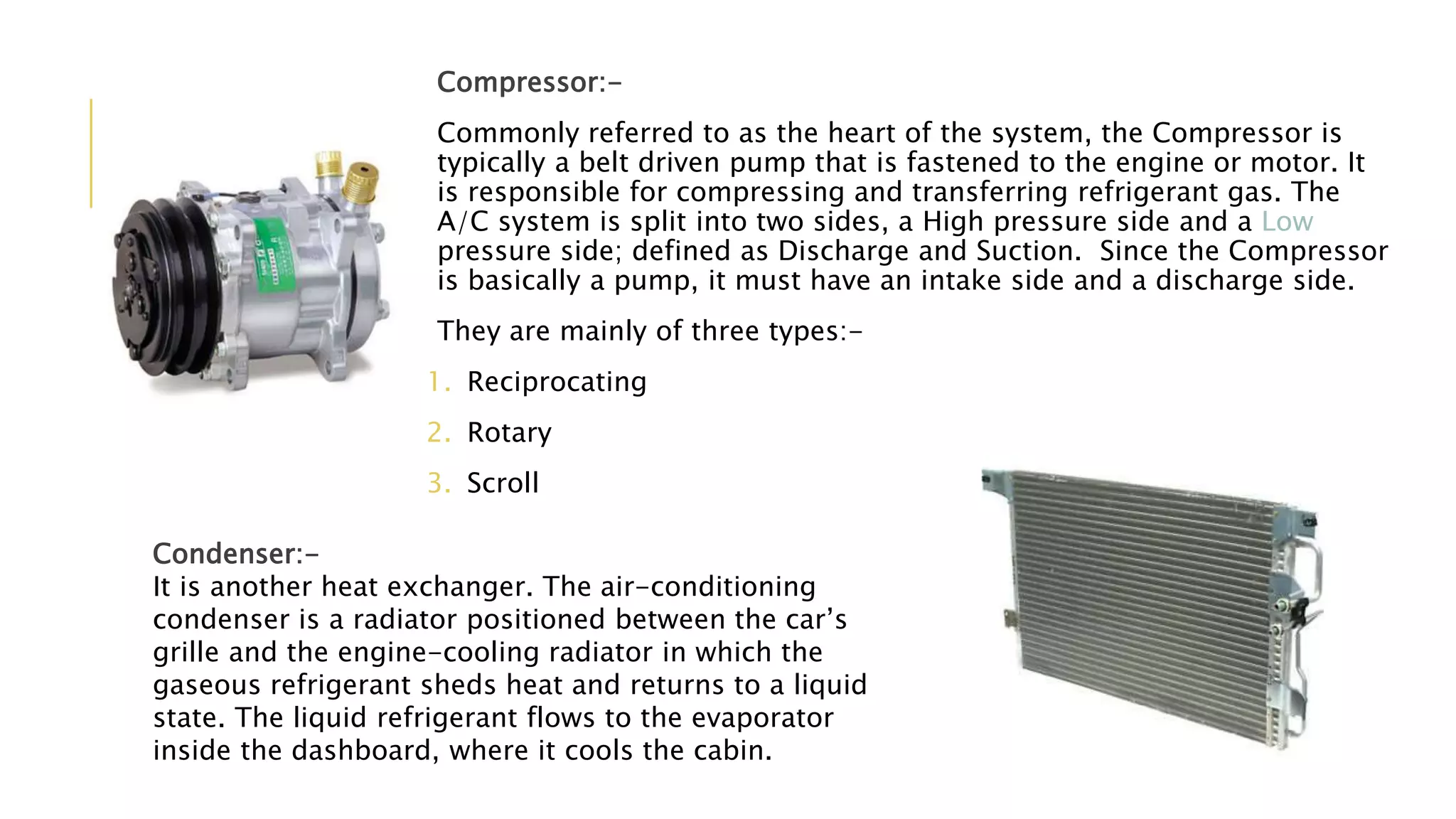
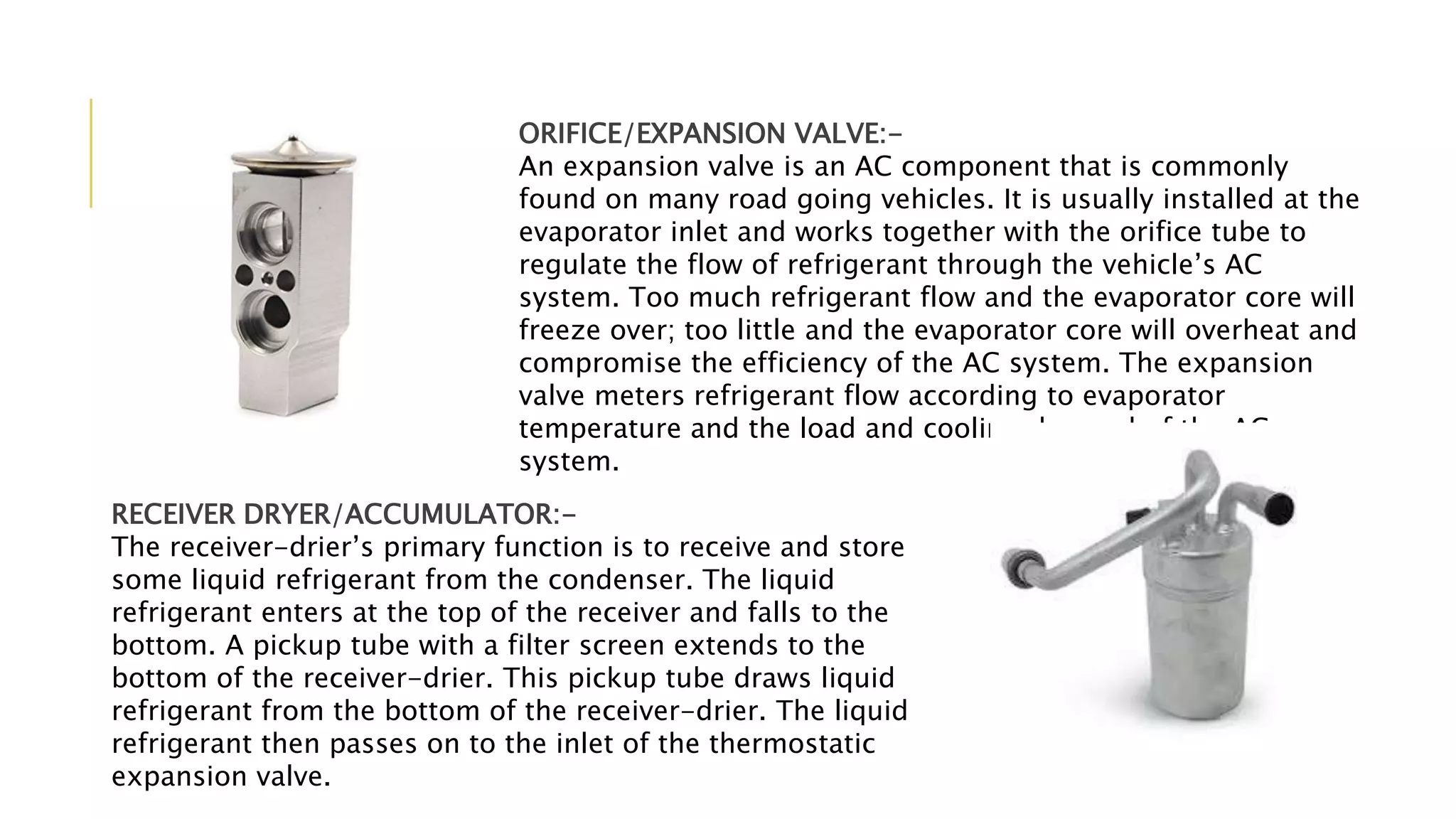
The document discusses the principles and components of an automobile HVAC system, explaining how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems operate within vehicles. It outlines the historical development of HVAC systems from ancient civilizations to modern technology and details the main components of automotive HVAC systems, including onboard and outboard parts. It also covers the types of refrigerants used in these systems and emphasizes the importance of proper functioning for maintaining vehicle comfort.