LANGUAGE TEACHING METHODS COMPARED
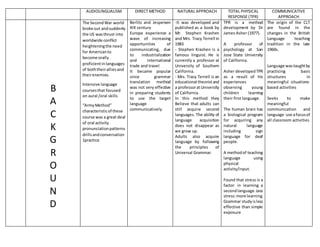
- 1. AUDIOLINGUALISM DIRECT METHOD NATURAL APPROACH TOTAL PHYSICAL RESPONSE (TPR) COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH B A C K G R O U N D The Second War world broke out andsuddenly the US wasthrust into worldwide conflict heighteningthe need for Americanto become orally proficientinlanguages of boththeiralliesand theirenemies. Intensive language coursesthat focused on aural /oral skills “ArmyMethod” characteristicof these course was a great deal of oral activity pronunciationpatterns drillsandconversation 1practice Berlitz and Jespersen XIX century Europe experience a wave of increasing opportunities of communicating, due to industrialization and international trade and travel It became popular since grammar translation method was not very effective in preparing students to use the target language communicatively. -It was developed and published as a book by Mr. Stephen Krashen and Mrs. Tracy Terrell in 1983 - Stephen Krashen is a famous linguist. He is currently a professor at University of Southern California. - Mrs. Tracy Terrell is an educational theoristand a professoratUniversity of California. In this method they Believe that adults can still acquire second languages. The ability of language acquisition does not disappear as we grow up. Adults also acquire language by following the principles of Universal Grammar. TPR is a method development by Dr James Asher (1977). A professor of psychology at San Jose State University of California. Asher developedTPR as a result of his experiences observing young children learning their first language. The human brain has a biological program for acquiring any natural language including sign language for deaf people. A methodof teaching language using physical activity/input. Found that stress is a factor in learning a secondlanguage.Less stress:more learning. Grammar studyisless effective than simple exposure The origin of the CLT are found in the changes in the British Language teaching tradition in the late 1960s. Language wastaughtby practicing basic structures in meaningful situations- based activities Seeks to make meaningful communication and language use afocusof all classroom activities
- 2. A P P R O A C H E S T H E O R Y O F L A N G U A - Process oriented - Structural linguistics influenced audiolingualism - Elements in a language are linearly produced in ruled governed way - Linguistic levels are pyramidally structured (sentences, phrases, morphology phonology - The structural linguistic believed that language is speech Language is for oral use. Each language is unique. There is a direct relation between form and meaning. No other language should interfere when learning language. The learner will acquire rules of grammar inductively. The best method of teaching meaning is the one using sensory experience, generally visual perception Reflecting the cognitive psychology and humanistic approach prominentinthe fieldof education at that time, the natural approach shifted the culture of language classroom 180 degrees and brought a sense of community to the students by their sharing of the experience of learning the same language together The essence of language is meaning. Vocabulary, not grammar, is the heart of language TPR reflects a grammar- based view of language Asher states that “most of the grammatical structure of the target language and hundreds of vocabulary items can be learned from the use of the imperative by the instructor He view the verb in imperative as the central linguistic motif around which language use and learning are organized. The method came as a reaction against the grammar- based approaches such as the audio-lingual method and grammar translation method of foreign language instructionthatignored that goal of language learning is COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE Hymes (19729 coined this term in order to contrast a communicative viewof language and Chomsky’s theory of competence Hyme’s view, a person who acquires communicative competence acquires both knowledge and ability for language use with respect to: - Whether something is formally possible - Whether something is appropriate in relation to a context in whichitis used - Whether something is convenient - Whether something is in
- 3. G E fact done, actually performed,and what it’s doing entails A P P R O A C H E S T H E O R Y O F L E A R N I N G - Habit formation - Behaviorism - Learning is learning structures, sound, words - Depended on three elements stimulus, bring out behavior. Response: triggered by stimulus reinforcement: marks the response as being appropriate or nor not and encourages repetition which is vital learning process) - Inductive learning is essential. - There is a direct relation between form and meaning L2 learning is similar to L1 acquisition. There is direct exposure to the target language. Exposure of long chunks in the target language. Learning occur naturally. - the learner should be actively involvedin using the language in realistic everyday situation Acquisition/Learning Hypothesis: Thisapproach states that there are two distinctive waysof developingcompetence ina secondlanguage. ADQUISITION isthe “natural”way, as children’slanguage development (unconscious) Learning referstoa processin whichconsciousrules aboutlanguage are developed. - Specific innate bio- program for language learning. - Brain lateralization: defines different learning functions - Stress intervenes between learning and what is to be learned Activities that involve real communication promote learning. Activities in which language is used for carryingoutmeaningful tasks promote leaning. Language that is meaningful to the learner promote learning D O B J - To get accurate pronunciation and grammar. - The ability to respondquickly and accurately in speech situation and knowledge of sufficient - To give learners access to literature in the target language, develop them for an understanding To help beginners become intermediate To help adults in learning foreign language naturally To depend on learner needs and skills and level being taught. To teach oral proficiency at a beginning level Comprehension is a meansto an end,and the ultimate aim is to teach basic speaking skills Use language as : Means of communication Object of learning Means of expressing values
- 4. E S I G N E T I V E vocabulary to use with grammar patter - Listening comprehension - Recognition of speechsymbols as graphicsigns - The ability to reproduce these symbols in writing of foreign language, - To build in them the kinds of grammar, reading, vocabulary and translation skills necessary to read and pass some kind of written tests. - There is to be a direct connection between concepts and the language to be learned To pick up the grammar by themselves when they are ready. Four broad areas basic personal communicative skills ( oral/ written) academic learning skills ( oral /Written) A TPR course aims to produce learnerswho are capable of an uninhibited communication that is intelligible to a native speaker Specific instructional will depend on a particular needs of the learners using action-based drills in the imperative form Focus on communication rather than structure Language learning within the school curriculum Focus meaningful task collaboration D E S S Y L L A Linguistic syllabus: contains the key items of phonology, morphology,andsyntax of the language Structures are sequencedbymeansof contrastive analysisand taught one at a time Lexical syllabus Order: Listening Speaking Reading writing - Is based upon situations (language that people woulduse at a bank or when going shopping) or topics (such as geography, money, or the weather - Grammar is taught inductively - Students practice vocabulary by using newwordsincomplete sentences. Typical goals for languages courses or particular needs and interest of student’s topics and situation. Provide awide exposure to vocabulary that may be useful to basic personal communication Resist any focus on grammatical structures Aim to create a low affective filter by being interestingandfostering a friendly, relaxed atmosphere TPR uses a sentence- based grammatical syllabus Is predictable from the exercises used in the class TPR requires initial attention to meaning rather than to the form of items. Grammar is thus taught inductively Grammar based Skills based (listening, speaking, writing, reading) Function based (greetings, introducing, telling stories Task based (discover the differences, solve the problem A functional syllabus: Communicative competence is viewed as a mastery of functions needed for communication across a wide range of situation Grammar and vocabularyare chosen according to the function being taught This syllabus is oftenused as the bases for listening and speaking courses. A content-based syllabus: the propose is to teach specific information and content using the language
- 5. I G N B U S that learners are also learning The course is arranged around topics related to the subject being taught A skill based syllabus: It focuses on the integration of the four macro skills. The teaching of each skills is done throughits component micro skills D E S I G N TYPES OF LEARNING AND TEACHING ACTIVITIES Dialogue and drills, Repetition and memorization pattern practice. Repetition: students repeat an utterance aloud as soon as they can heard it Inflection: one word in an utterance appear in another form when repeated Replacement:one word in an utterance is replaced by another Teacher ask questions of any nature and the students answer Dictation: the teacher chooses a grade appropriate passage and reads the text aloud. Teacher reads the passage three times Reading aloud: student take turn reading sections of a passage, play or dialogue out aloud Map drawing: paragraph writing. Fill in the blank exercise, paragraph writing - Comprehensible input is presentedinthe target language - Using techniques such as TPR mime and gesture - Group techniques are similar CLT - Learnersstartto talk when they are ready. Vocabulary Classroom language Imperatives drills to elicitphysical actions Functional communicative activities: Comparing sets of pictures and noting similarities and differences,discovering missing features in a map or picture, one learner communicating behind a screen to another one giving instructions on how to draw a picture or shape . Social interaction activities: Conversation and discussion sessions, dialogues, role plays, simulation, skits, improvisation and debates
- 6. D E S I G N LEARNER’S ROLES - Theyrepeated, imitated teacher’s model,form habits - Requiredto pronounce or readrepeated wordby word that givenby the teacher - Invite (in English Directly) withouthaving to bringnative language Students are very active Oral communication skills areemphasized There is a largeamount of Learner-Learner interaction - Processor of comprehensible input - Pre-production stage - Early production stage - Speech emergentphase Learner to learner interactionencouragein pair and small group. Students involve themselves in role plays , games etc. - They have the primary roles of Listener and performer - They monitor and evaluate their own progress - -Develop independence, autonomy and responsibility. - is a negotiator between themselves, the learning process and the object of learning) - chooses proper expressions in a given set of circumstances and situations - Develop inner criteria and correct themselves - Learn to work cooperatively rather than competitive. The student give and receive information D E S I G TEACHER ROLES - Model, conductor, guider and controller - Central and active teacher dominated method. - Provides model control de direction and pace. - Teacher is like and orchestra leader Direct classactivities Encourage students to participatein class Let the students correct their mistakes immediately As demonstrator As facilitator As partner of student As monitor As initiator by usingvarious techniques, the teacher - Primary source of comprehensible input - Creates atmosphere - Learner centered - Facilitator - Orchestra classroom activities. - Most exude authority and confidence - Teacher plays and active and direct role - They control the language input - In giving feedback, the teacher follows the example of parents - Teacher has responsibility of providing the best kind of exposure to language so that the learner can internalize - They have to assume the role of facilitator and monitor - Had to develop a differentview of learner’s errors and of her/his own role in facilitating language teaching - As a needs analyst - As a counselor - As a group process manager
- 7. N tries to get students to self-correctwhenever possible the basic rules of the target language D E S I G N ROLE OF INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL - They are primary teacher oriented - Audiovisual equipment often have central roles - The direct method is the 2nd language for instruction is taught, but it is no interference of mother tongue everyday vocabulary and sentence are taught - Materials come from realia more than textbooks - Primary aims is to promote comprehension and communication - They make classroom activities as meaningful as possible by supplying “the extra-linguistic context that helps the acquirer to understand and thereby to acquire - Picture are othervisual aids facilitate acquisition of a large vocabulary within the classroom - Nobasictexts in TPR - Teacher’s voice, action and gestures may be sufficient - Supporting material collected by the teacher - - A wide variety of material have beenused to support communicative approaches to language teaching - CLT view materials as a way of influencing the quality of classroom interaction and language use - The primary role of materials is to promote communicative language use - There ae three kinds of material currently used in CLT: text-based, task-based and realia P R O P R O - Extensive oral instruction is required where the target language is used - Model dialogue. Studentshasa reading passage The st are called on one by one and the read the text loudly. The teacher answer the student’s - Start with a TPR commands - Direct method, activities in which mime gesture, context are used The majority of class time in TPR lessons is spent doing drills in which the instructor gives commands using the imperative mood The methodological procedures reflect a sequence of activities representedasfollows: Pre-communicative activities: - Structural activities
- 8. C E D U R E C E D U R E Repeat. Correction of mistakes. Memorize. - Dialogues are adopted and then acted out - Key structures are selected and used for pattern drills - Textbook. Follow-up reading,writing or vocabulary activities may be introduced - Follow-up activities in a language laboratory questionsinthe target language Work together on pronunciation. Give questions to the students Ss make up own questions and statements The teacher instruct the studentstoturnan exercise The students read a sentence outloudand supply the missing word as they are reading Gives dictation - CLT group- work activities Students respond to these commandswith physical actions. Initially, students learn the meaning of the command they hear by direct observation. After they learn the meaningof the words in these commands, the teacher issues commands that use novel combination of the words. The students have learned - Quasi- communicative activities Communicative activities: - Functional communication activities - Social interaction activities ( role plays, jigsaw tasks, dialogues)