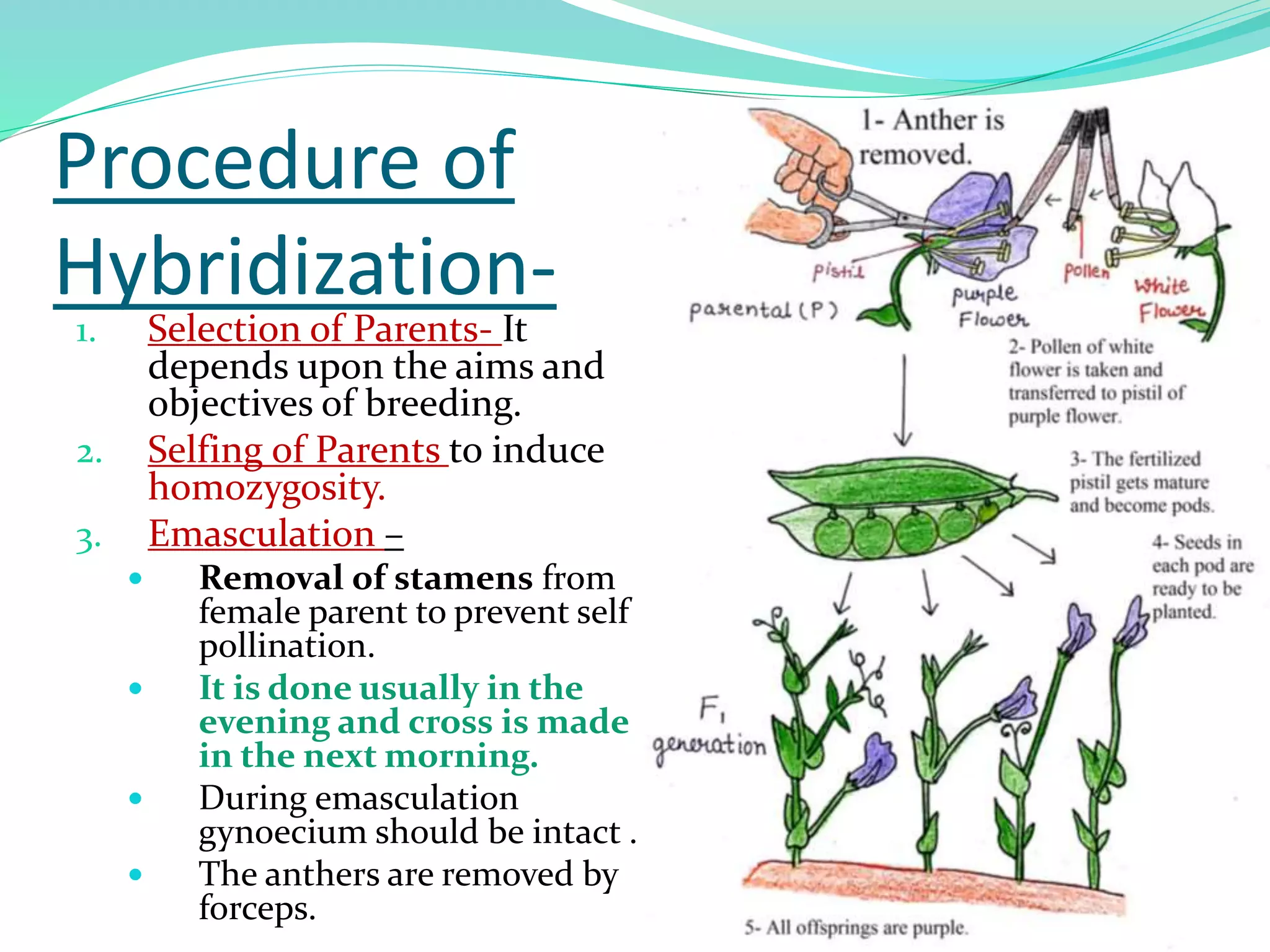
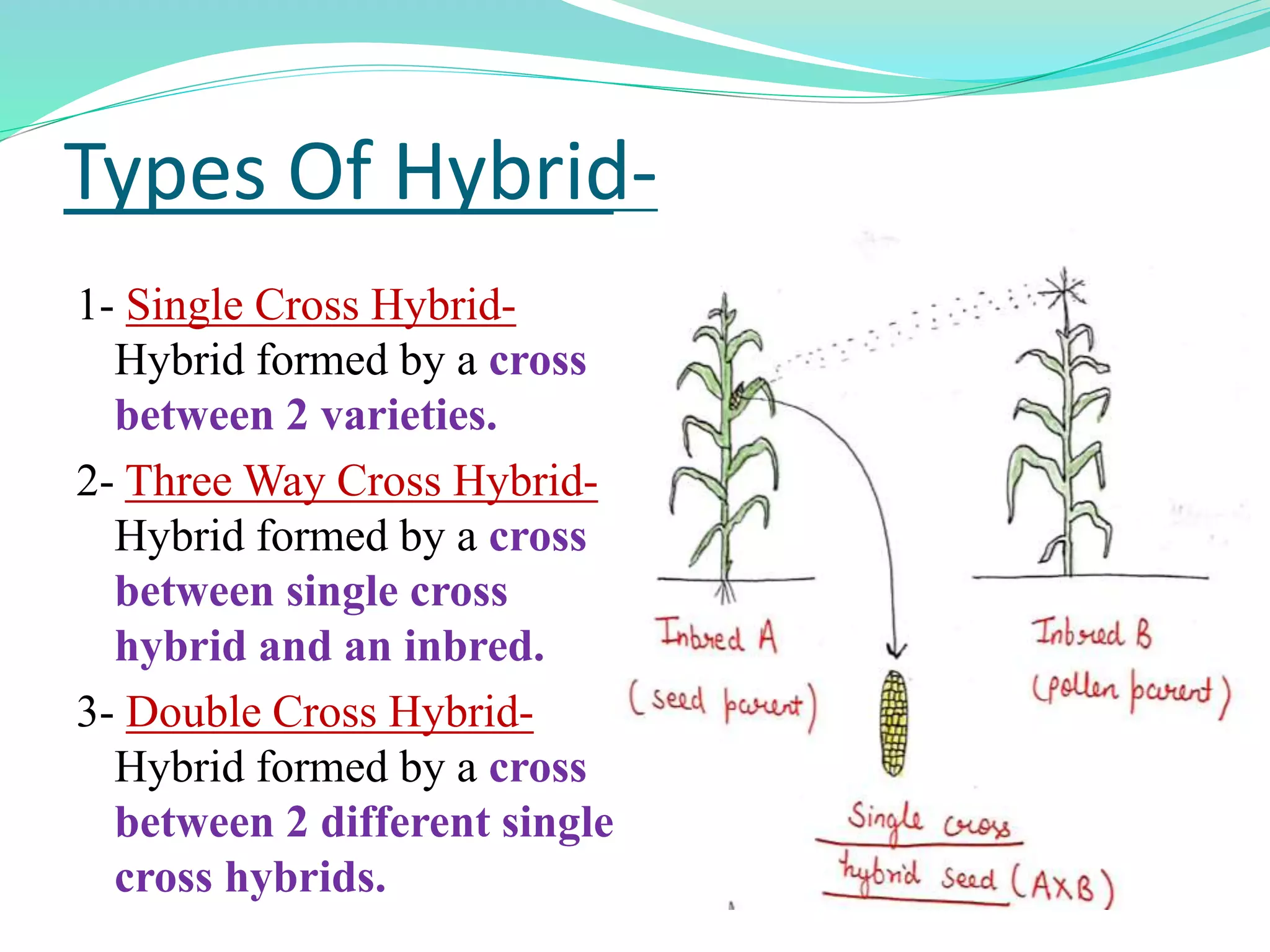
The document details the process and advantages of hybrid breeding, which involves crossing different plant species to create hybrid varieties with desirable traits. It outlines the steps of hybridization, from selection of parents to crossing and harvesting F1 seeds, along with types of hybrids such as single cross, three-way, and double cross. Additionally, it highlights specific hybrid varieties, including nutrient-rich maize, black rice with anti-carcinogenic properties, and various hybrid tomatoes and watermelons.