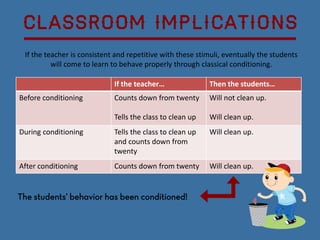
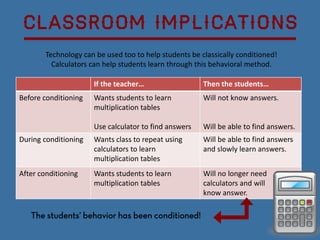
Classical conditioning is a learning theory developed by Ivan Pavlov where he found that dogs could learn to associate a neutral stimulus with a natural reflex. For example, Pavlov found that dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with receiving food. John Watson furthered this research by conditioning an infant, known as Little Albert, to fear a white rat through repeated pairing of the rat with a loud noise. Classical conditioning involves using triggers to train organisms to perform certain responses through repetitive associations between stimuli.