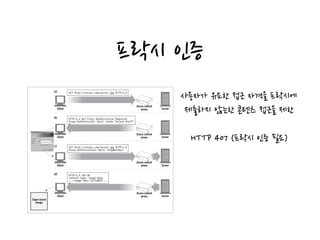
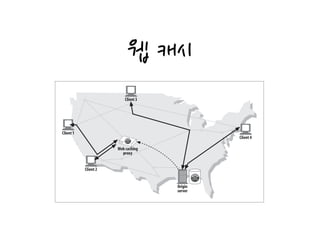
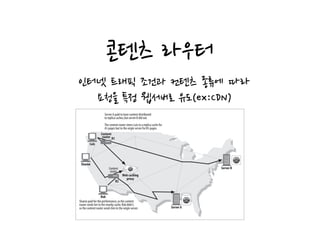
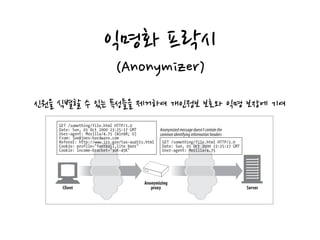
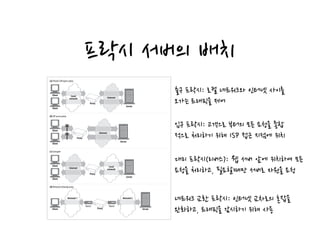
HTTP proxies act as both servers and clients by receiving requests from web clients and forwarding the requests to web servers, while also sending requests to servers on behalf of clients. Proxies are commonly used for filtering content, access control, security firewalls, caching, load balancing, transcoding content formats, and providing anonymity. Proxies can be configured in various network architectures including private networks, ISP access points, as reverse proxies in front of servers, and at network exchange points.












![URI 자동 확장과 프락시(2/3)
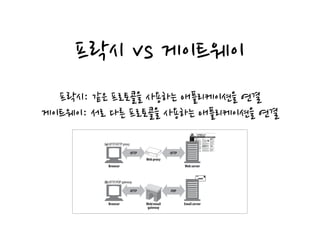
명시적인 프락시를 사용할때 URI 분석
브라우저는 명시적인 프락시가 있는 경우 호스트명을 확장하지 않음.
• In Step 3a, the browser auto-expands the hostname and asks the DNS to resolve
“www.oreilly.com.” This is successful.
• The browser then successfully connects to www.oreilly.com.
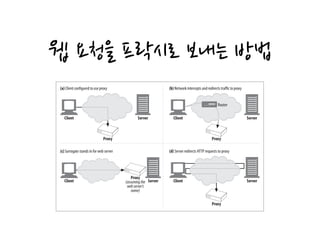
URI Resolution with an Explicit Proxy
When you use an explicit proxy the browser no longer performs any of these conve-
nience expansions, because the user’s URI is passed directly to the proxy.
As shown in Figure 6-17, the browser does not auto-expand the partial hostname
when there is an explicit proxy. As a result, when the user types “oreilly” into the
browser’s location window, the proxy is sent “http://oreilly/” (the browser adds the
default scheme and path but leaves the hostname as entered).
For this reason, some proxies attempt to mimic as much as possible of the browser’s
convenience services as they can, including “www...com” auto-expansion and addi-
Figure 6-17. Browser does not auto-expand partial hostnames when there is an explicit proxy
Client
(1) User types “oreilly”into
browser’s URI location window
(3a)The browser does auto-expansion,
converting“oreilly”into “www.oreilly.com”
DNS server
(2a) Proxy is explicitly configured,
so the browser looks up the address
of the proxy server using DNS
(2b) Success! Get proxy server
IP addresses
www.oreilly.com
(3a) Browser tries to connect to proxy
(3b) Success;connection established
(4a) Browser sends HTTP request
Proxy
GET http://oreilly/ HTTP/1.0
Proxy-connection: Keep-Alive
User-agent: Mozilla/4.72[en] (Win98:I)
Host: oreilly
Accept: */*
Accept-encoding: gzip
Accept-language: en
Accept-charset: iso-8859-1,*,utf-8
Requestmessage,assentin(4a)
(4b) Proxy gets a partial hostname
in the request,because the client
did not auto-expand it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpdefinitiveguidech6-160322084110/85/HTTP-6-22-320.jpg)


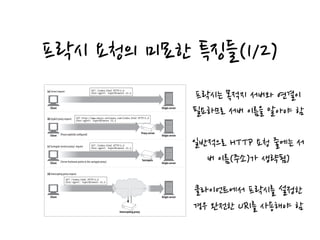
![메시지 추적:Via
Via 헤더 필드는 메시지가 지나가는 중간 노드의 정보를 나열
메시지가 노드를 지날때 해당 정보를 Via 목록의 끝에 반드시 추가되어야 함.
Via syntax
The Via header field contains a comma-separated list of waypoints. Each waypoint
represents an individual proxy server or gateway hop and contains information about
the protocol and address of that intermediate node. Here is an example of a Via
header with two waypoints:
Via = 1.1 cache.joes-hardware.com, 1.1 proxy.irenes-isp.net
Figure 6-20. Via header example
Client
proxy-62.irenes-isp.net
(HTTP/1.1) www.joes-hardware.com
cache.joes-hardware.com
(HTTP/1.0)
GET /index.html HTTP/1.0
Accept: text/html
Host: www.joes-hardware.com
Via: 1.1 proxy-62.irenes-isp.net, 1.0 cache.joes-hardware.com
Requestmessage(asreceivedbyserver)
[중개자가 받은 프로토콜 이름]/버전 노드 이름 노드 코멘트로 구성](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/httpdefinitiveguidech6-160322084110/85/HTTP-6-25-320.jpg)