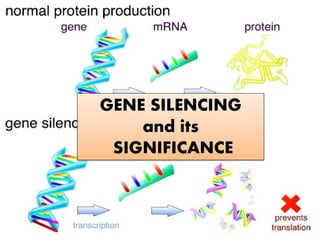
Gene silencing and its significance
- 2. • defined as a molecular process involved in the down regulation of specific genes. • Interruption or suppression of the expression of a gene at transcriptional or translational levels. • “switching off” • Gene silencing is same as gene knock down but is totally different from gene knock out. • When genes are knock down ,there expression is reduced by at least 70% , where in contrast when genes are knocked out, they are completely eliminate from organism’s genome. • allow researchers to study essential genes that are required for the animal models to survive and cannot be removed. • they provide a more complete view on the development of diseases since diseases are generally associated with genes that have a reduced expression. • probably evolved as a genetic defense system against viruses and invading nucleic acids (Brigneti et al., 1998; Voinnet et al., 2000; Waterhouse et al., 2001; Wassenegger, 2002)
- 4. GENE “SILENCING” BY MODIFICATION OF HISTONES AND DNA
- 5. Silencing is a position effect---a gene is silenced because of where it is located, not in response to a specific environmental signal. Also, silencing can “spread” over large stretches of DNA ,switching off multiple genes, even ones quite distant from the initiating event. The most common form of silencing is associated with a dense form of chromatin called heterochromatin. Both activation and repression of transcription often involve modification of nucleosomes to alter the accessibility of a gene to the transcriptional machinery and other regulatory proteins. Transcription can also be silence by methylation of DNA by enzymes called DNA methylases.
- 7. Rap1 recruits SIR complex to the telomere. SIR2, a component of that complex, deacetylates nearby nucleosomes. The unacetylated tails themselves then bind Sir3 and SIR4, recruiting more SIR complex, allowing the SIR2 within it to act on nucleosomes further away, and so on. This explains the spreading of the silencing effect produced by deacetylation. The telomeres, the silent mating-type locus, and the rDNA genes are all “silent” regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Silencing in Yeast Is Mediated by Deacetylation and Methylation of Histones.
- 8. Consider the telomere as an example. •The final 1-5 kb of each chromosome is found in a folded , dense structure. •Genes taken from other chromosomal locations and moved to this region are often silenced, particularly if they are only weakly expressed in their usual location. •Mutations have been done , in which a gene placed at the telomere is expressed at higher levels. •These studies implicate three genes encoding regulators of silencing: Silent information regulator(SIR)2,3 and 4. The three proteins encoded by these genes form a complex that associates with silent chromatin, and Sir2 is a histone deacetylase. •The silencing complex is recruited to the telomere by a DNA- binding protein(RAP1) that recognizes the telomere’s repeated sequences. •Histone methyl transferases attach methyl groups to histone tails. •Just as acetylated residues within histones are recognized by proteins bearing bromodomains, methylated residues bind proteins with chromodomains.
- 9. Position effect • Position effect is the effect on the expression of a gene when its location in a chromosome is changed, often by translocation. • described in Drosophila with respect to eye colour and is known as position effect variegation (PEV).
- 11. Repression by polycomb also uses histone methylation Polycomb repressive complex 1 Polycomb Response Elements (PREs) DNA binding subunit (PHO or PHOL - Repressive Complex ) Polycomb protein (PHO) = Protein pleiohomeotic
- 12. Switching a gene off through DNA methylation and histone midification
- 13. DNA Methylation Is Associated with Silenced Genes in Mammalian Cells Some mammalian genes are kept silent by methylation of nearby DNA sequences. Methylation of DNA can mark sites where heterochromatin subsequently forms. DNA methylation lies at the heart of a phenomenon called imprinting. Two regulatory sequences are critical for the differential expression of the human H19 and Igf2 genes: An enhancer and an insulator.
- 14. Imprinting Two examples of genes controlled by imprinting- the mammalian Igf2 and H19 genes. The H19 genes is expressed from only the matermal chromosome, Igf2 from the paternal chromosome. The methylation state of the insulator element determines whether or not the insulator binding protein( CTCF) can bind and block activation of the H19 gene from the downstream enhancer.
- 15. Some States of Gene Expression Are Inherited through Cell Division even when the Initiating Signal Is No Longer Present Patterns of DNA methylation can be maintained through cell division
- 17. Paramutation : • In epigenetics, a paramutation is an interaction between two alleles at a single locus, whereby one allele induces a heritable change in the other allele. • The change may be in the pattern of DNA methylation or histone modifications. • For example – Anthocyanin pigment in corn plant • B allele – Anthocyanin pigment coded • Paramutagenic allele at this locus(B’) cause reduced pigment production • B allele is silenced by the B’ allele in the first generation • In next generation, the newly silence B allele is paramutagenic and silence.
- 18. Transposon silencing: • is a product of histone modification that prevent the transcription of that area of DNA. • The “jumping” of transposon generates the genomic instability and cause the extremely deleterious mutations.
- 19. Transgene silencing: • insertion of transgene in to a transcriptionally inactive part of genome. When an insertion of any transgene it does not show activity as per desire and this is because of it’s instability. • The lose of transgene stability is because of gene silencing. • E.g. slow fruit softening tomato, by reducing expression of polygalactouronase enzyme.
- 20. RNA Directed DNA Methylation: • an epigenetic process first elucidated in plants where by small double- stranded RNAs (dsRNA's) are processed to guide methylation to complementary DNA loci. • In Arabidopsis thaliana
- 23. RNA i (RNA interference): • it is a post transcriptional process triggered by the introduction of double stranded RNA (ds RNA) which leads to the gene silencing in a sequence specific manner. • It is also known as post transcriptional gene silencing / co suppression and quelling.
- 26. Non sense Mediated Decay: • is a cellular mechanism of mRNA surveillance that functions to detect nonsense mutations and prevent the expression of truncated or erroneous proteins. • NMD is triggered by exon junction complexes (EJCs) (components of the assembled RNP) that are deposited during pre- mRNA processing.
- 27. Anti sense RNA technology: • It blocks the activity of the mRNA in a stoichiometric manner. • Antisense RNA has the opposite sense to m RNA. • The presence of complimentary sense and antisense RNA in the in the same cell can lead to the formation of a stable duplex which interferes with gene expression at the level of RNA processing or possible translation. • This technology widely used in plants for gene inhibition.
- 28. Strategies for G S in research
- 30. GENE SILENCING IN PLANTS Currently, there are several routes of GS identified in plants, such as: • transcriptional gene silencing (Vaucheret & Fagard, 2001), • post-transcriptional gene silencing or RNA interference (PTGS or RNAi) (Vaucheret et al., 2001), • microRNA silencing (Bartel, 2004), • and virus induced gene silencing (Burch-Smith et al., 2004). • All these pathways play an important role at the cellular level, affecting differentiation, gene regulation (Bartel, 2004), and protection against viruses and transposons (Waterhouse et al., 2001).
- 33. Applications for GS in plants • the production of virus resistant plants through genetic transformation. • used in food quality modification such as the reduction of caffeine levels in coffee beans and to increase the nutritional value of corn protein and tomato. • Research on forest tree yield and quality has included the study of GS related to lignin synthesis. • research on fruit crops has targeted applications of GS on viral and bacterial resistance, and physiological aspects such as self fertility.
- 34. Advantages of gene silencing: • Downregulation of gene expression simplifies "knockout" analysis. • Easier than use of antisense oligonucleotides. Si RNA more effective and sensitive at lower concentration. • Cost effective • Can be labelled Ease of transfection by use of vector • blocking expression of unwanted genes and undesirable substances. • Inducing viral resistance • Powerful tool for analysing unknown genes in sequenced genomes. • Useful approach in future gene therapy. • Oligonucleotides can be manufactured quickly, some within one week; the sequence of the mRNA is all that is needed. • Cancer treatments • Modulation of HIV-I replication by RNA i. • Small RNA and it’s application in andrology and urology.
- 35. Disadvantages of gene silencing: • ”High pressure injection” and electroporation can cause significant damage to the integrity of the normal tissues and organs and thus preclude the utilisation in a clinical set-up. • Liposomes/cationic encapsulated Si RNA may also be toxic to the host and may cause severe host immune responses. • Other emerging strategies includes chemical modification of Si RNA molecules and encapsulated with different molecules are still in their infancy and need to be thoroughly investigated before used in therapeutic applications.
