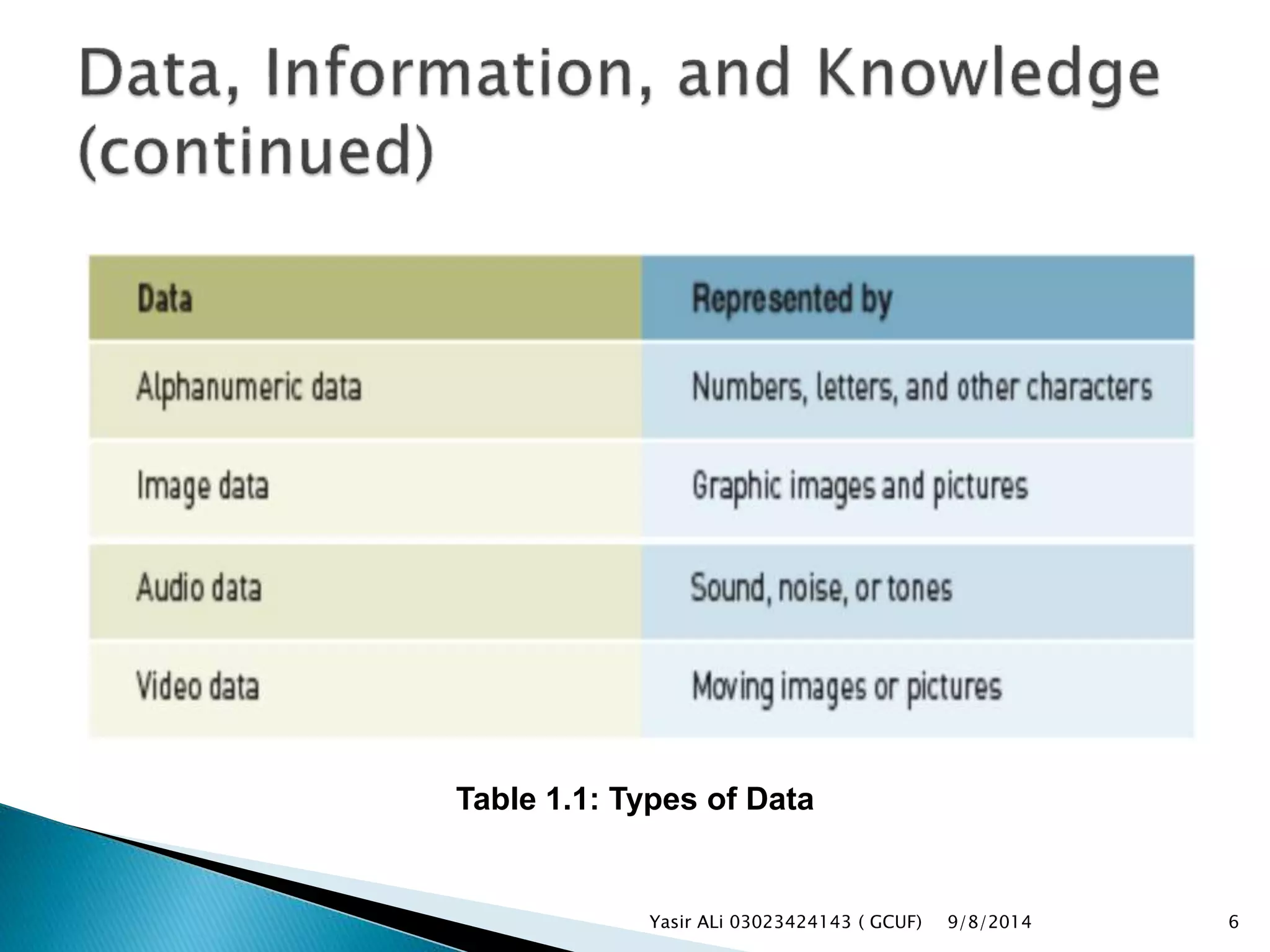
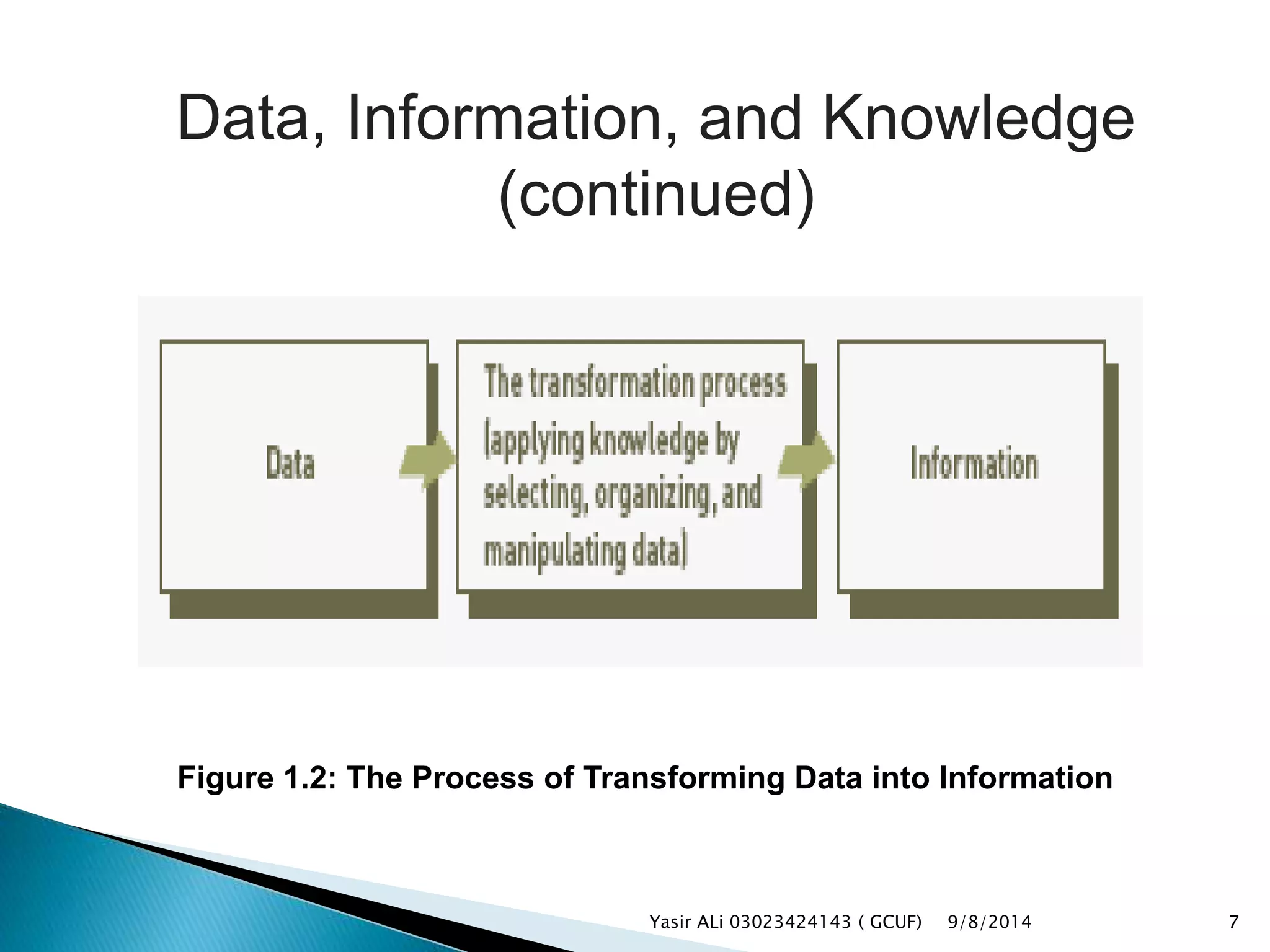
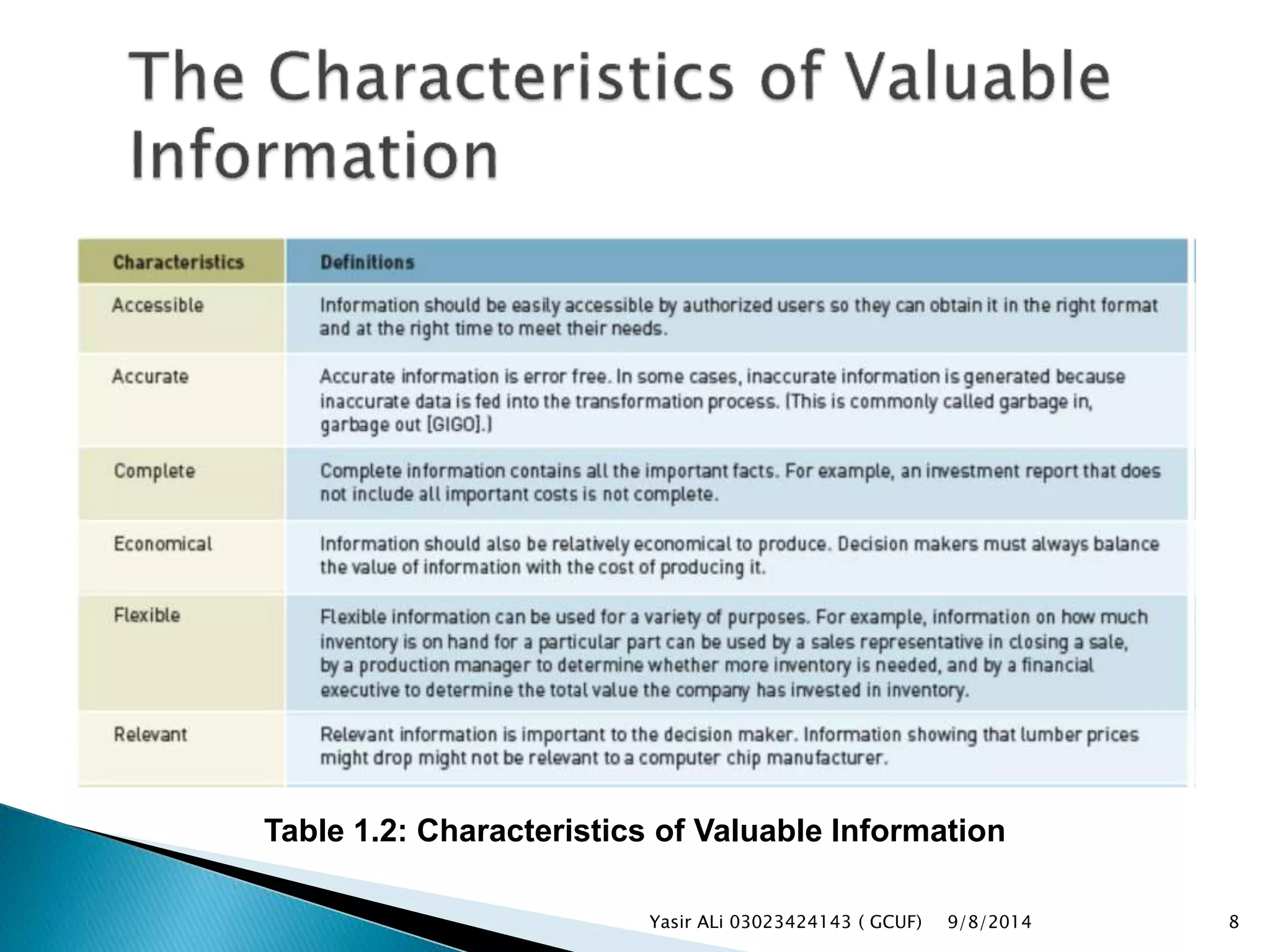
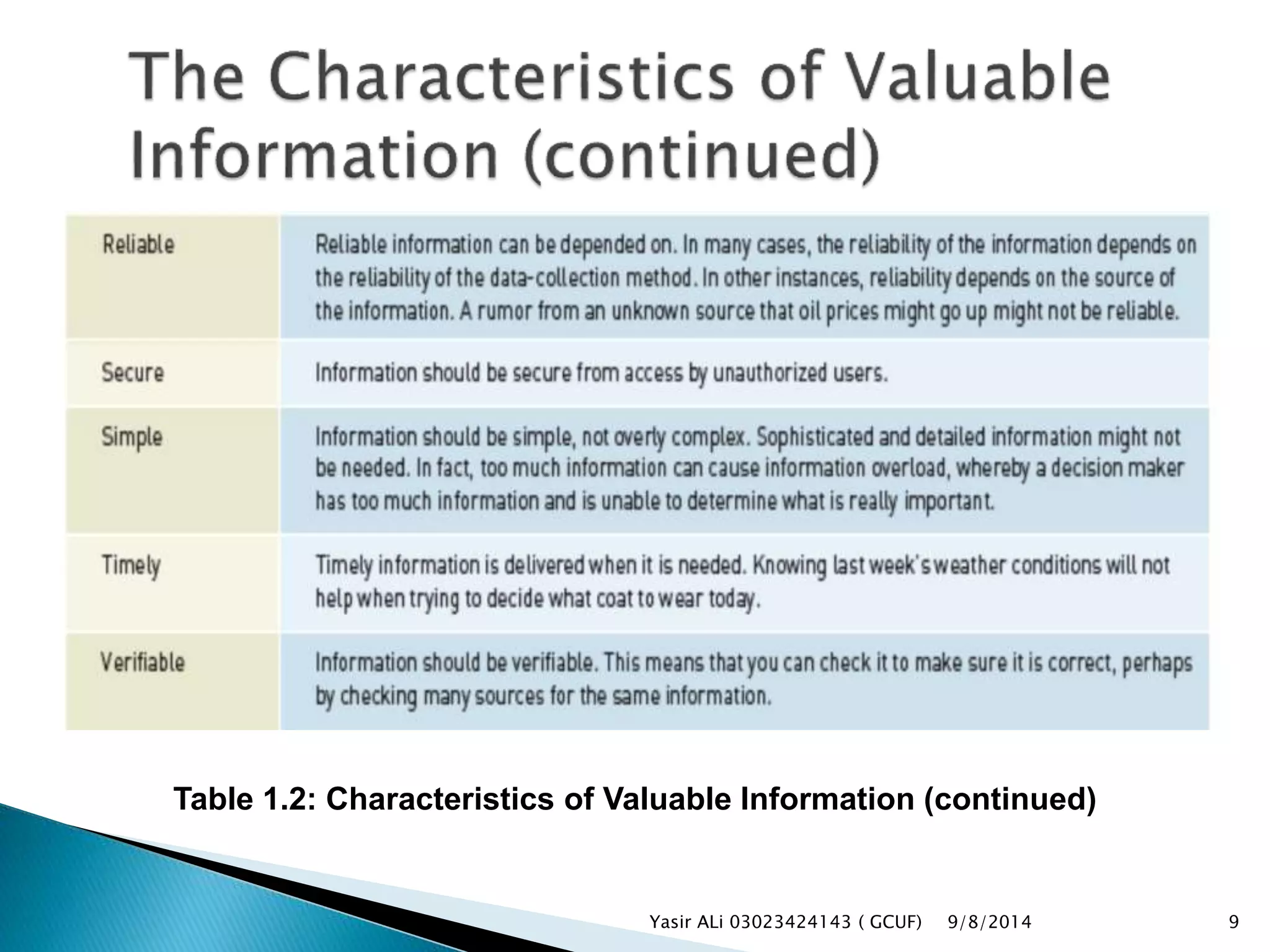
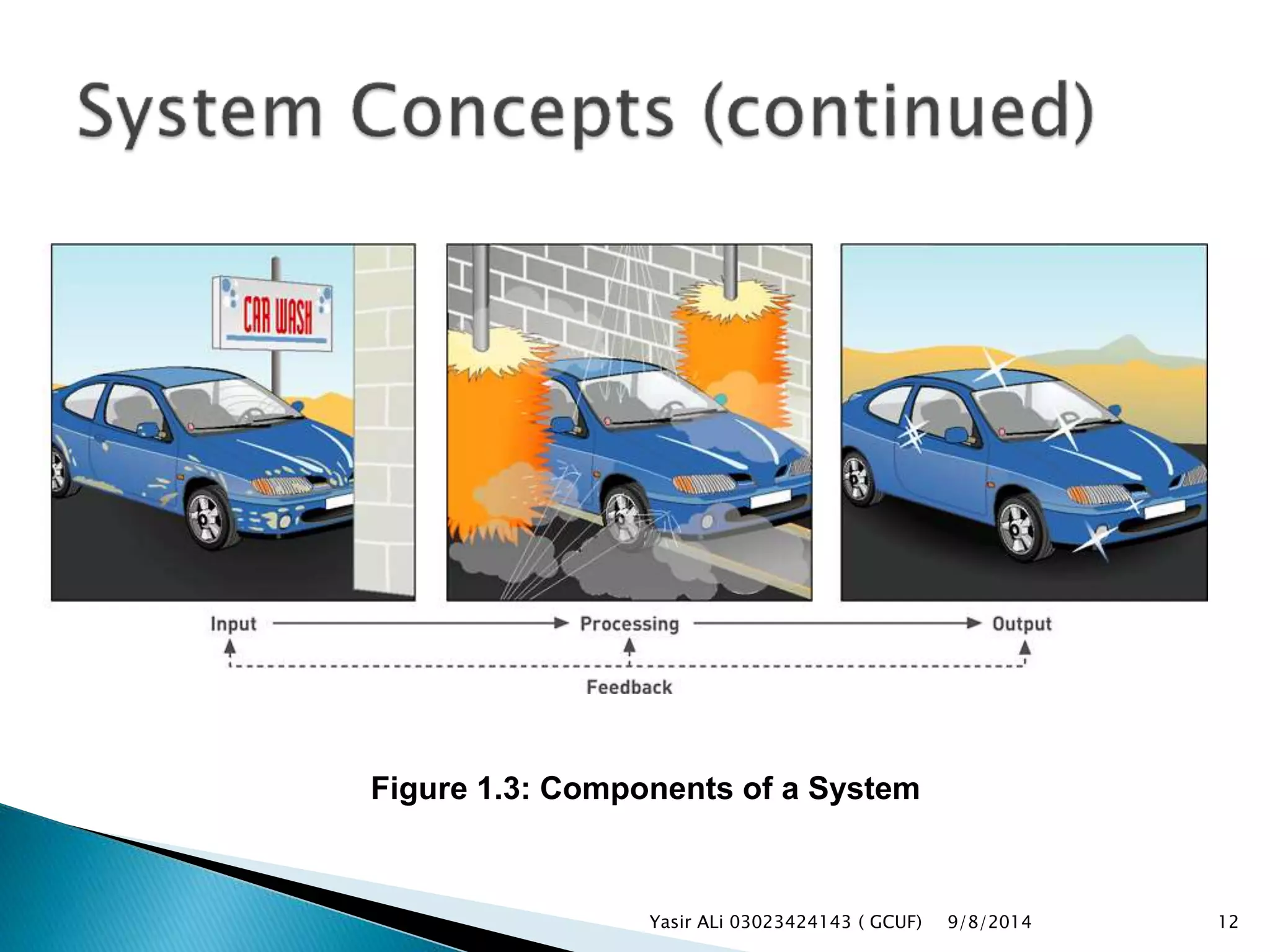
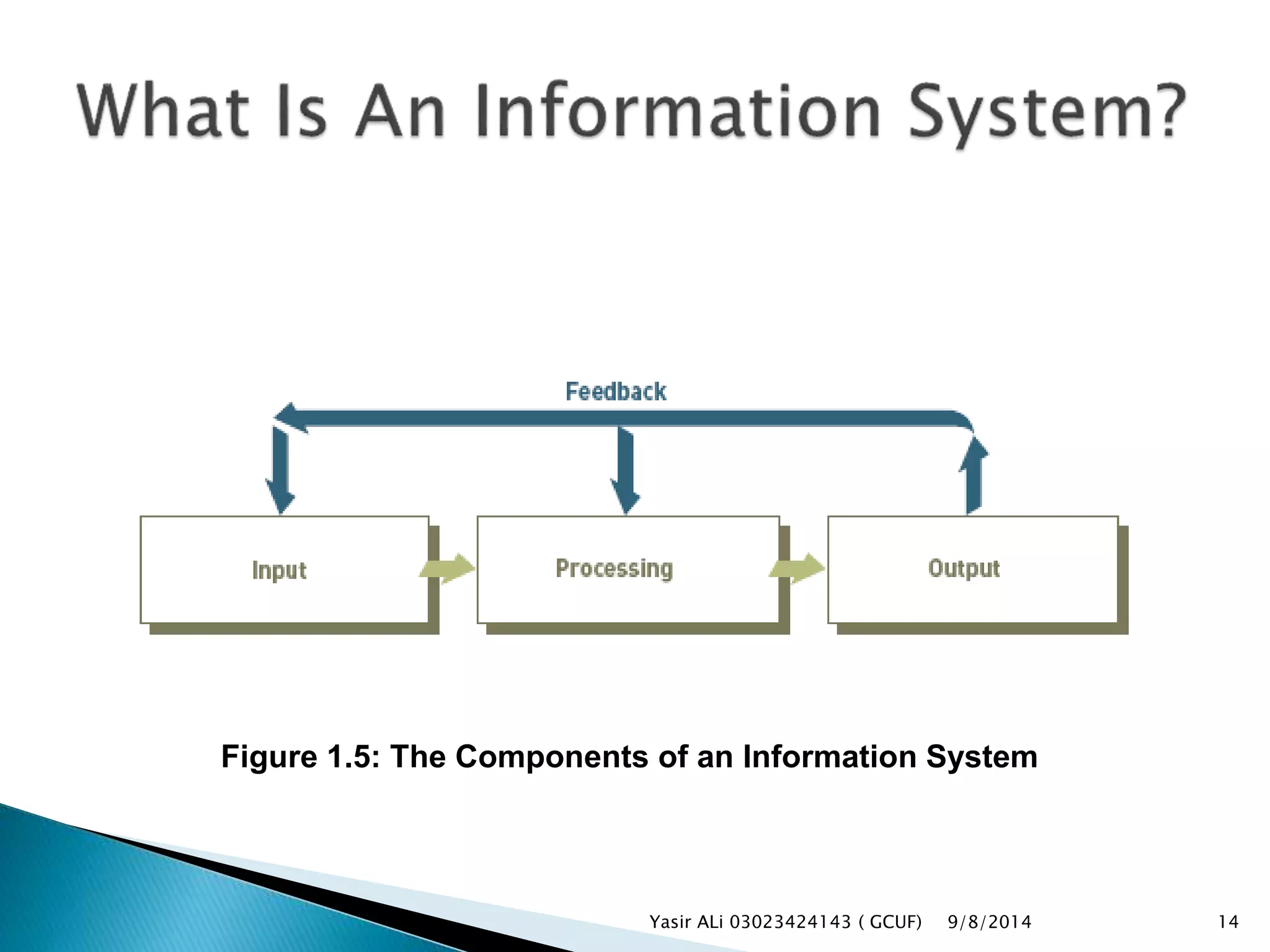
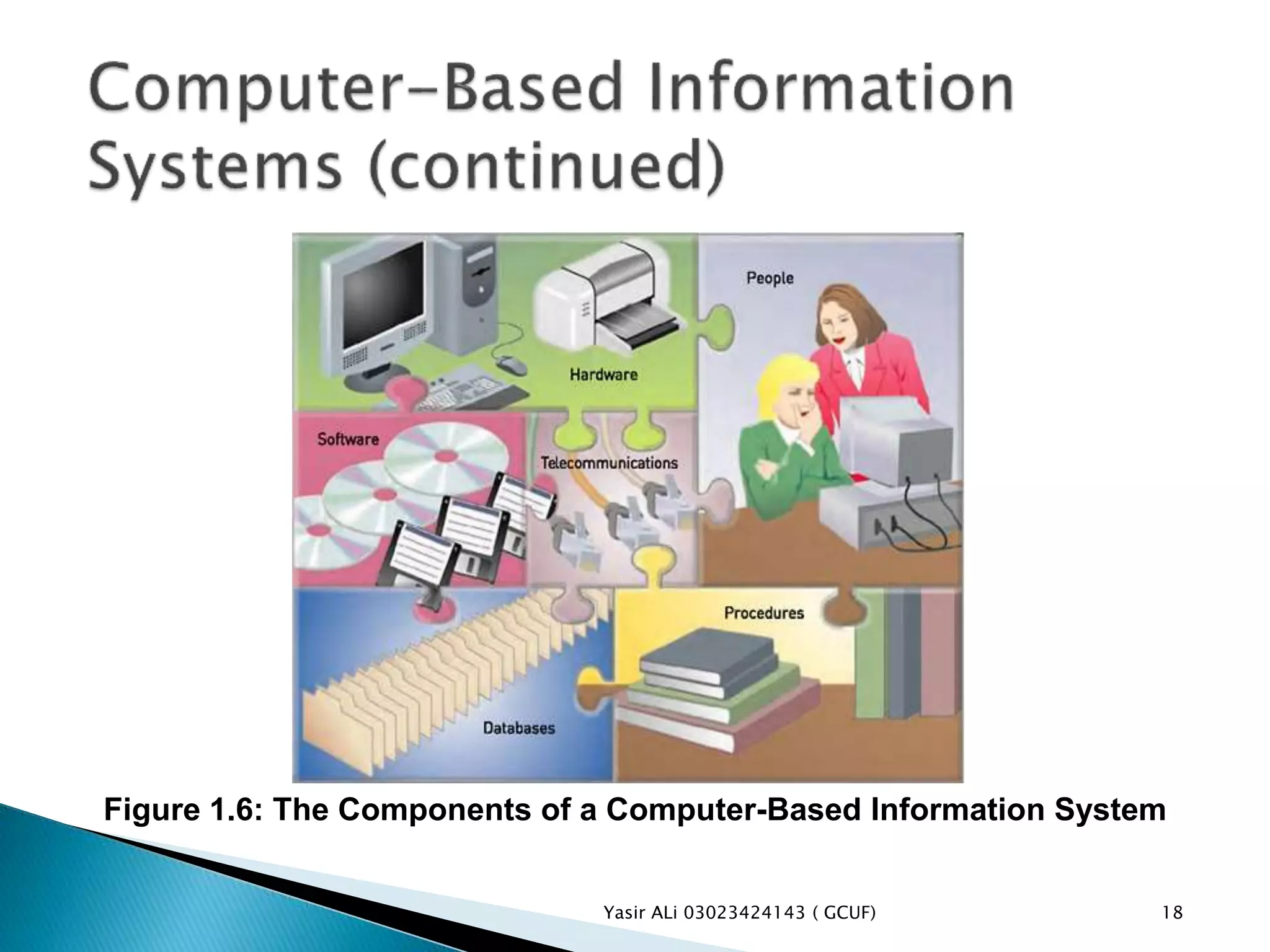
This document defines key concepts related to management, information systems, and computer-based information systems. It explains that management involves planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling an organization to accomplish goals. An information system is defined as a set of components that collect, manipulate and disseminate data and information to meet objectives. The document also distinguishes between data, information and knowledge, and describes the components and goals of information systems.