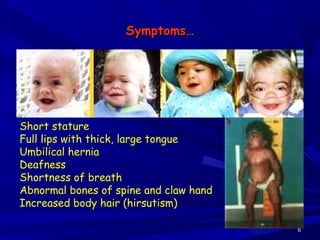
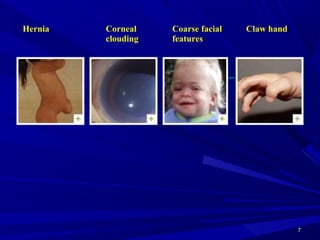
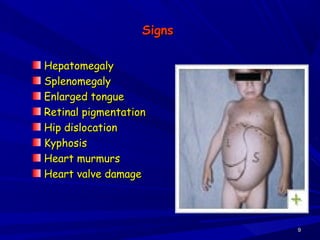
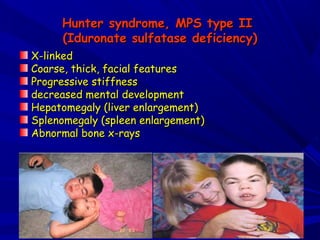
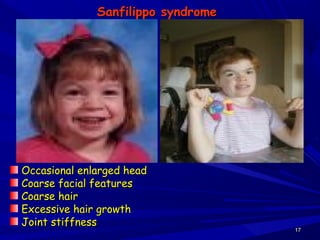
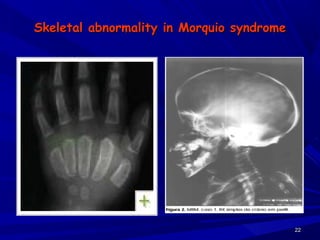
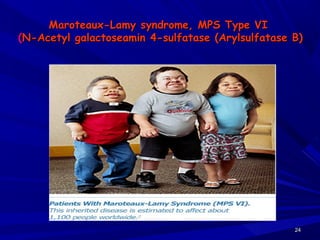
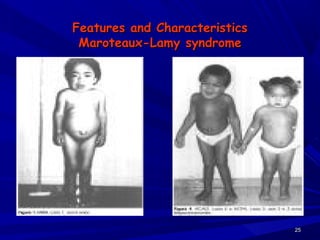
This document discusses various types of mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS), which are genetic disorders caused by deficiencies of enzymes needed to break down mucopolysaccharides. This leads to excessive accumulation of these substances in tissues. The document describes several specific types of MPS (e.g. Hurler syndrome, Hunter syndrome, Sanfilippo syndrome), their signs and symptoms, inheritance patterns, and diagnostic testing. It provides details on clinical manifestations, skeletal abnormalities, and treatments currently available which aim to cure MPS disorders through enzyme replacement therapy or gene therapy.