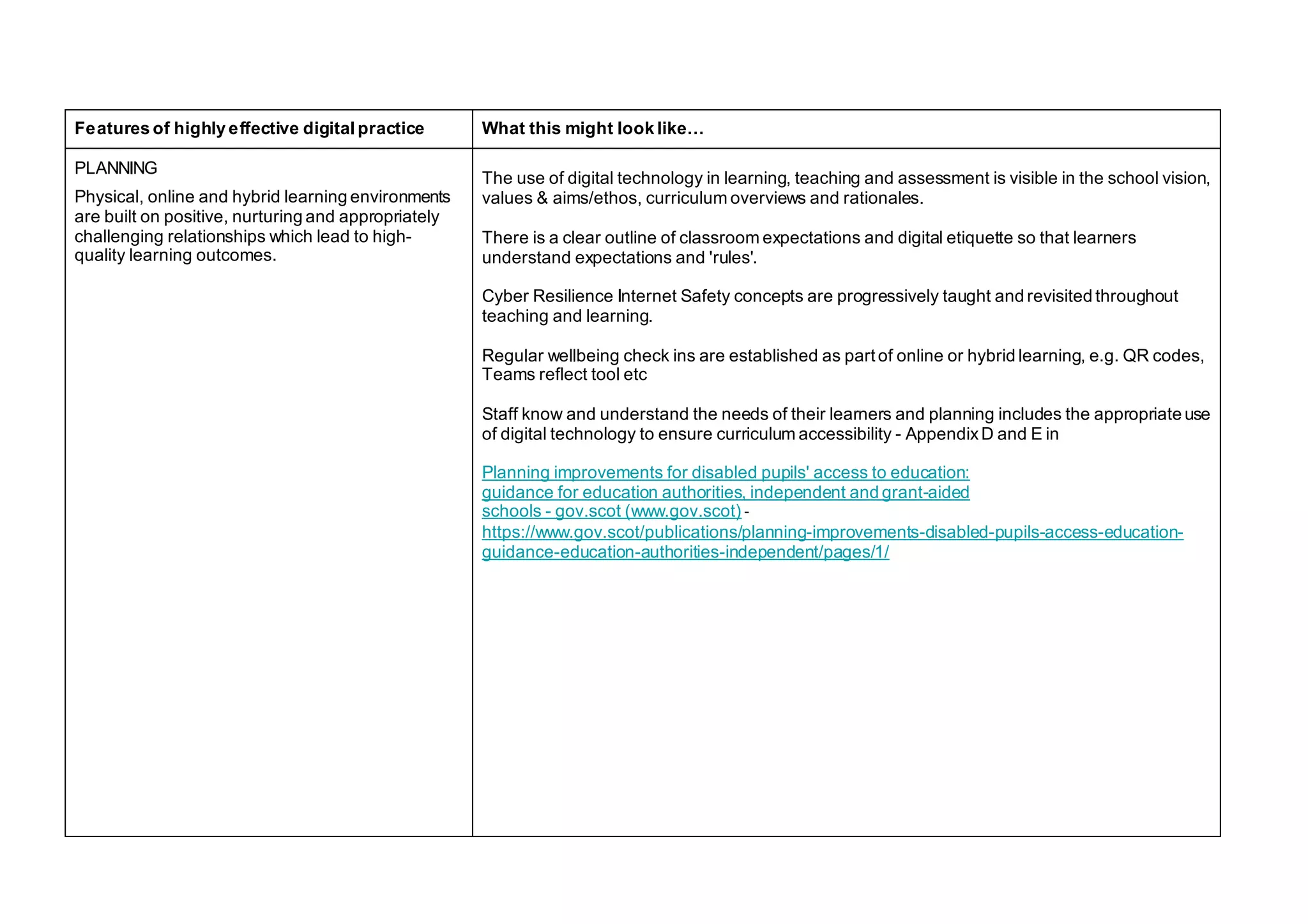
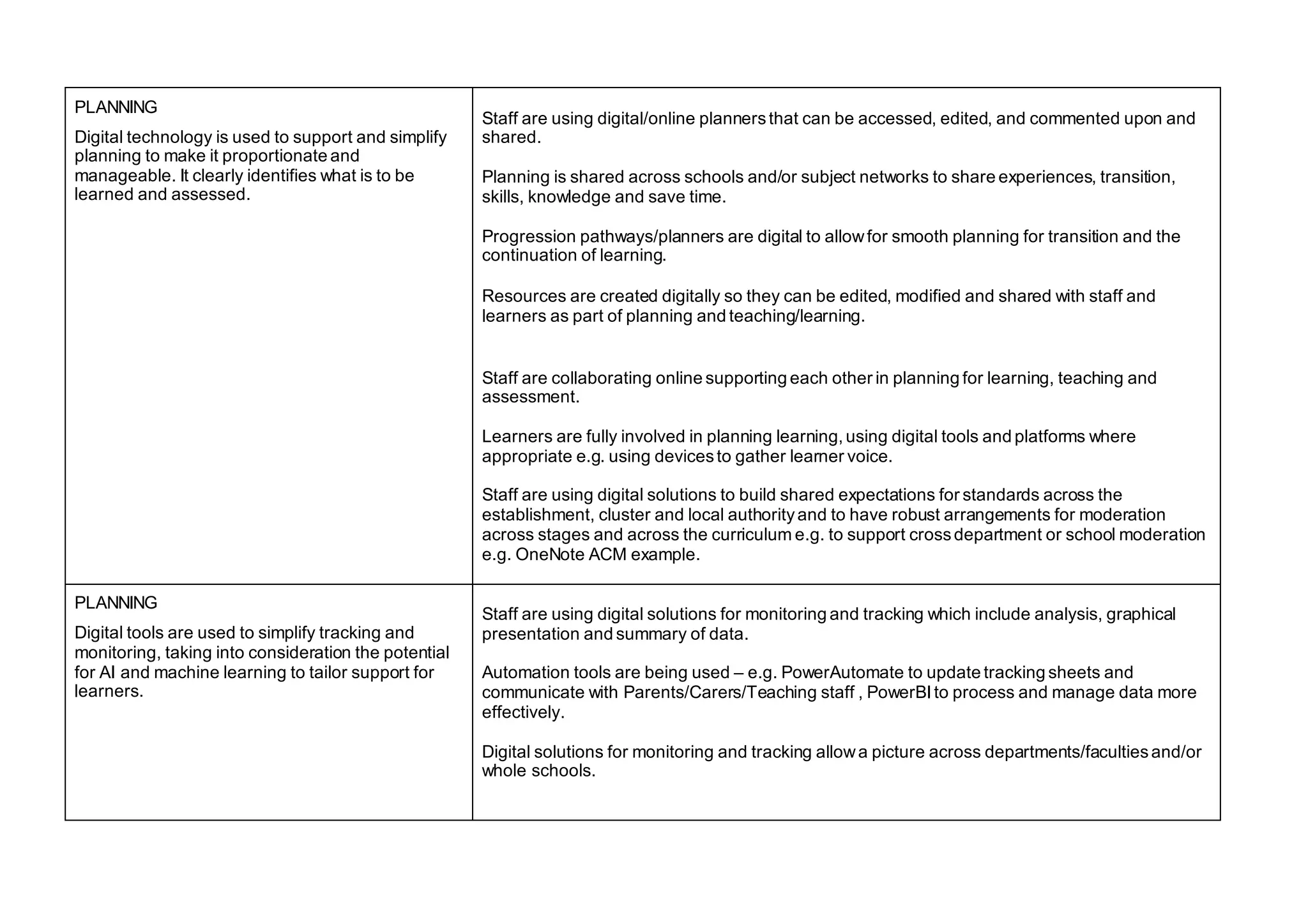
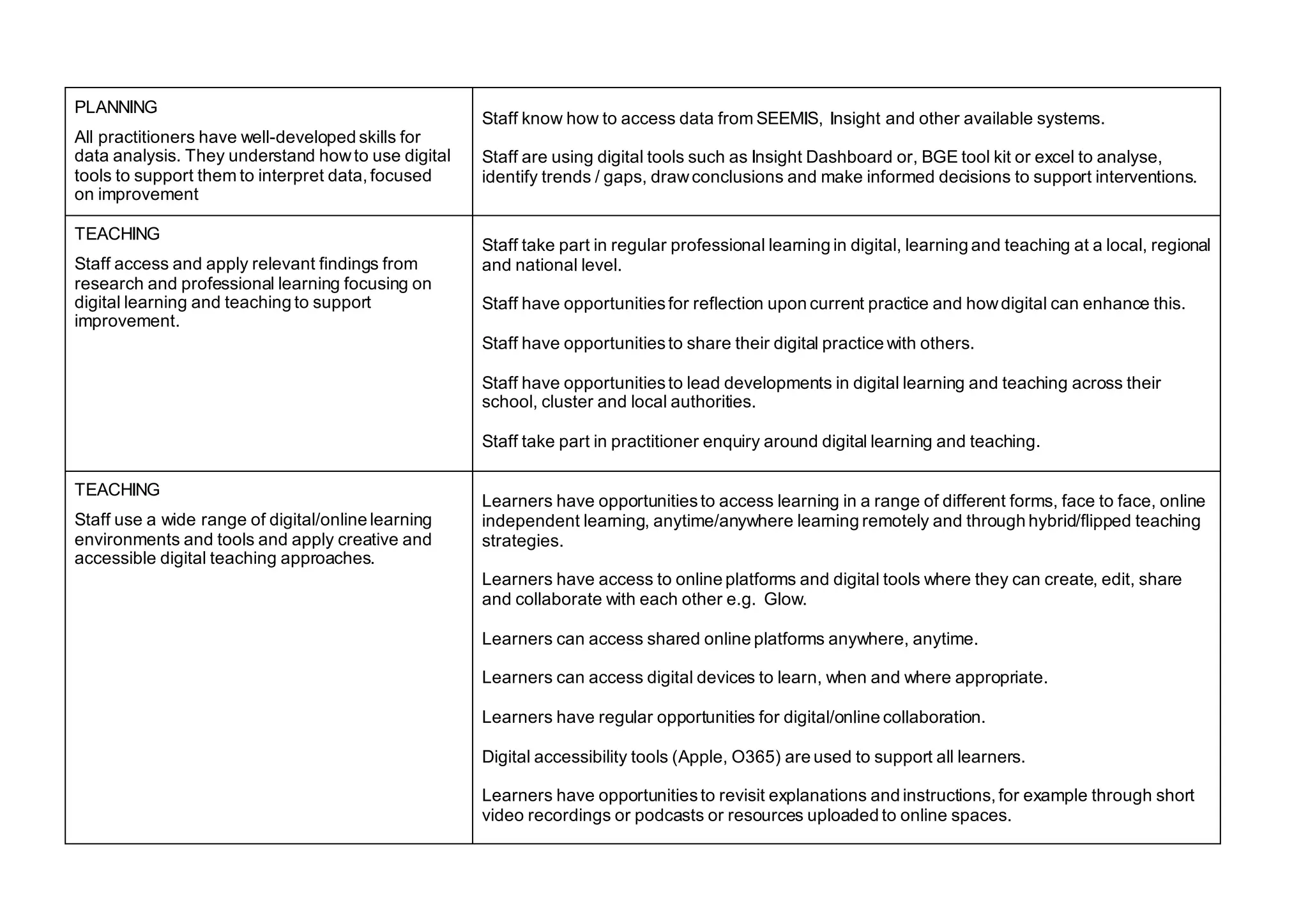
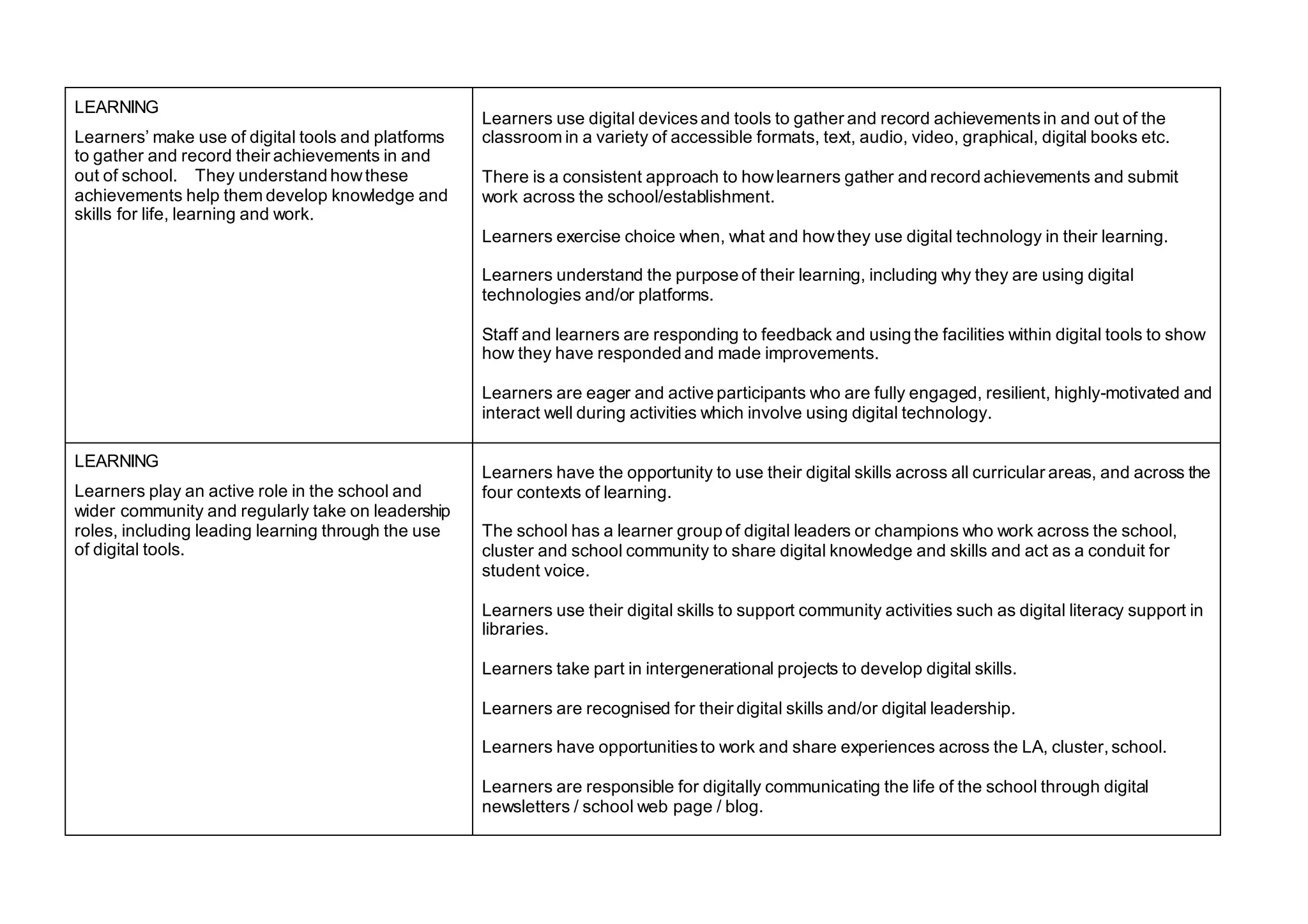
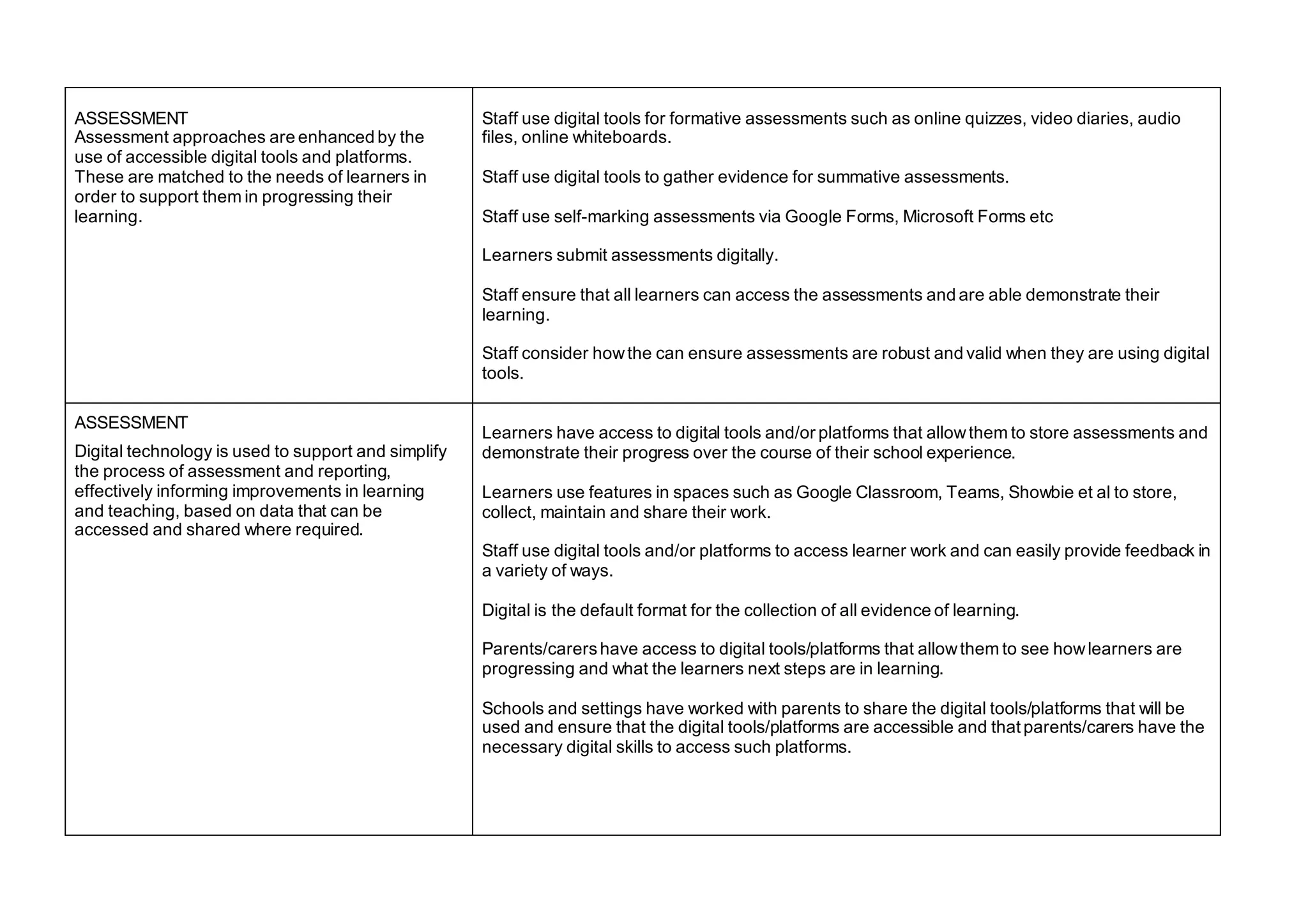
The document outlines the features of effective digital learning, teaching, and assessment in Scottish schools, emphasizing the role of digital technologies in educational improvement since the 2016 strategy. It specifies the essential qualities of digital practice in areas such as planning, teaching, learning, and assessment, aiming to enhance learning outcomes for all students. Additionally, it provides resources for evaluation and discussion among educators to foster continuous development in digital education practices.