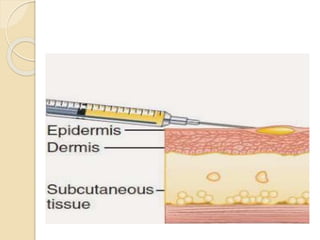
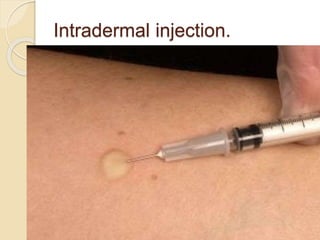
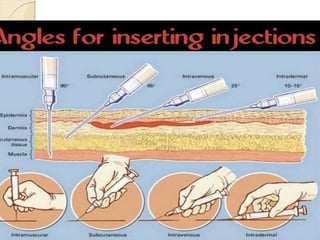
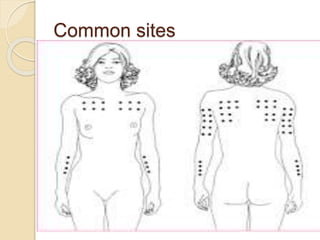
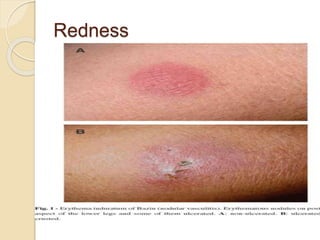
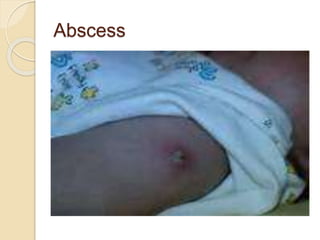
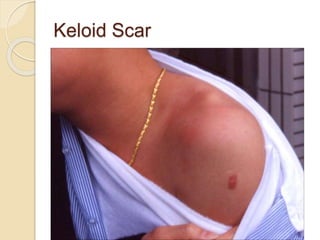
This document provides information about intradermal injections, including the purpose, common sites, required equipment, and procedure. An intradermal injection deposits medication into the dermis just below the epidermis, allowing for long absorption. Common sites are the inner forearm, upper arm, back, and chest. The procedure involves preparing the medication, cleaning the injection site, inserting the needle at a 5-15 degree angle just under the skin, injecting the medication to form a wheal, and properly disposing of supplies. Potential complications include redness, tenderness, abscess, and keloid scarring.