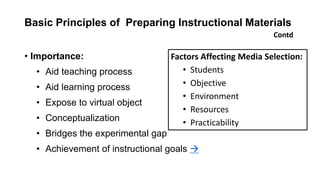
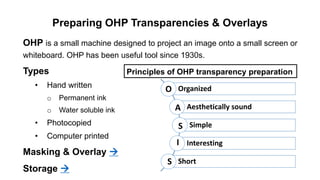
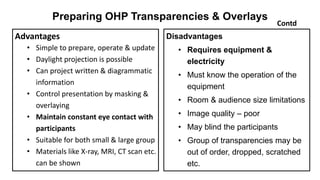
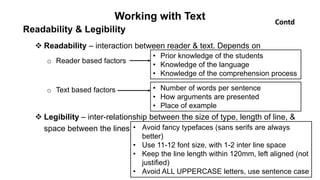
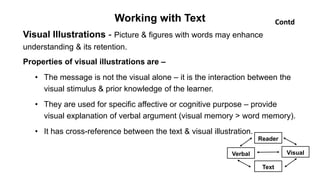
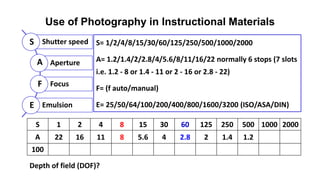
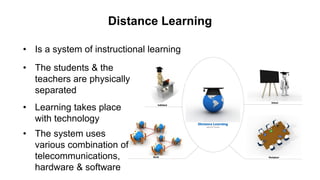
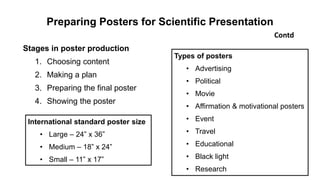
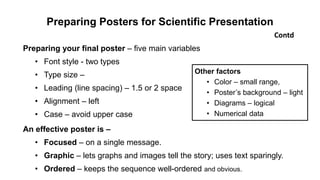
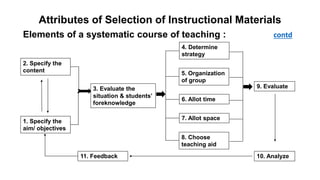
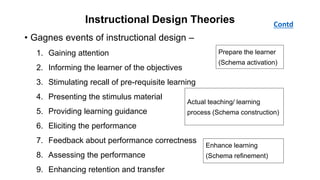
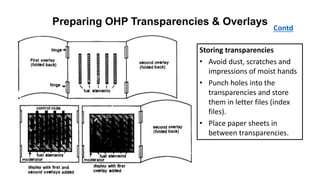
The document outlines the development of instructional materials, emphasizing a student-centered approach and detailing the types, characteristics, and practical application of various media used in teaching. It highlights the principles for creating effective instructional materials, evaluation strategies, and the role of technology in enhancing learning experiences. Furthermore, it addresses the importance of instructional design methodologies and offers guidelines for preparing various learning aids, such as handouts and presentations.