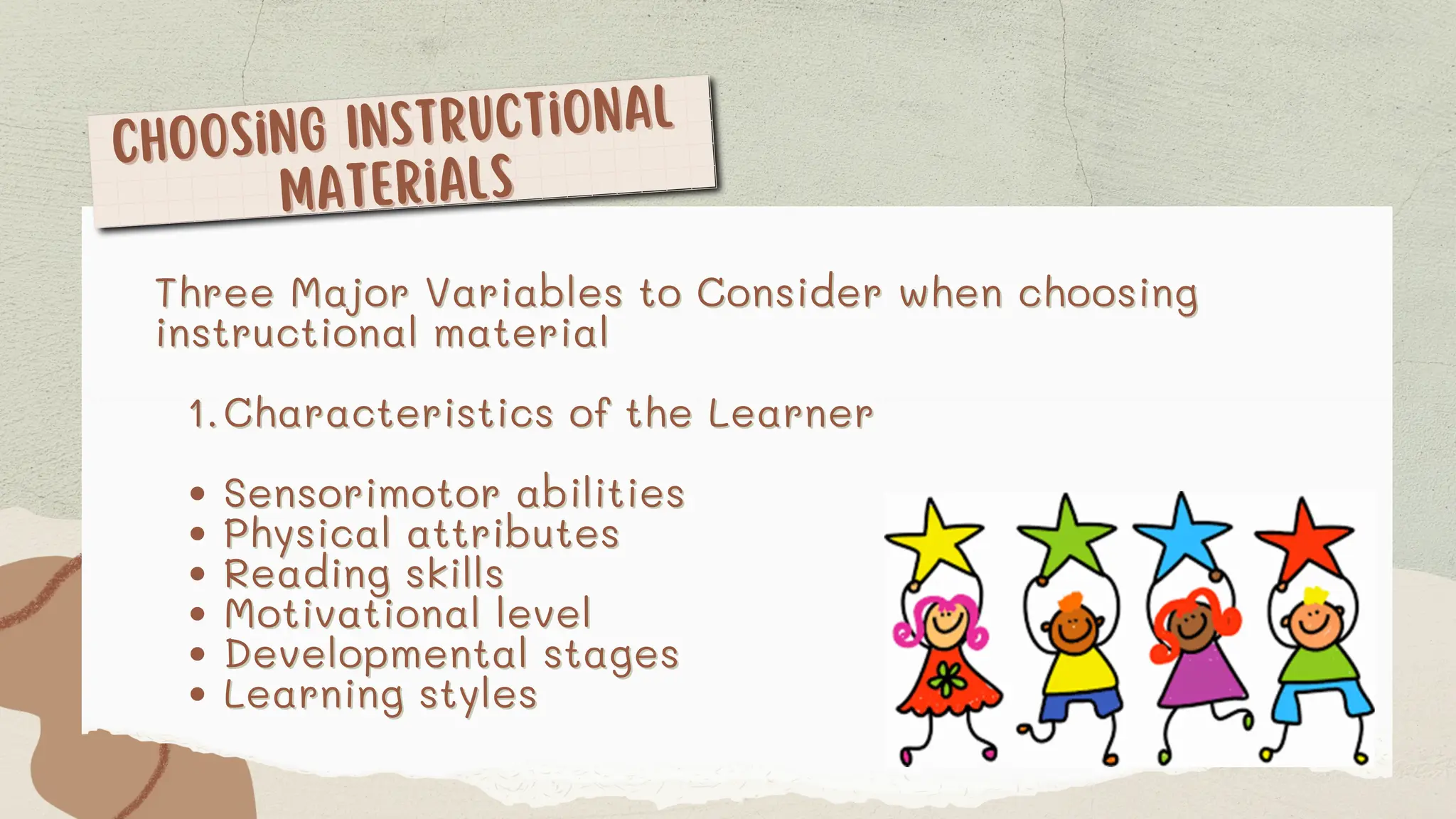
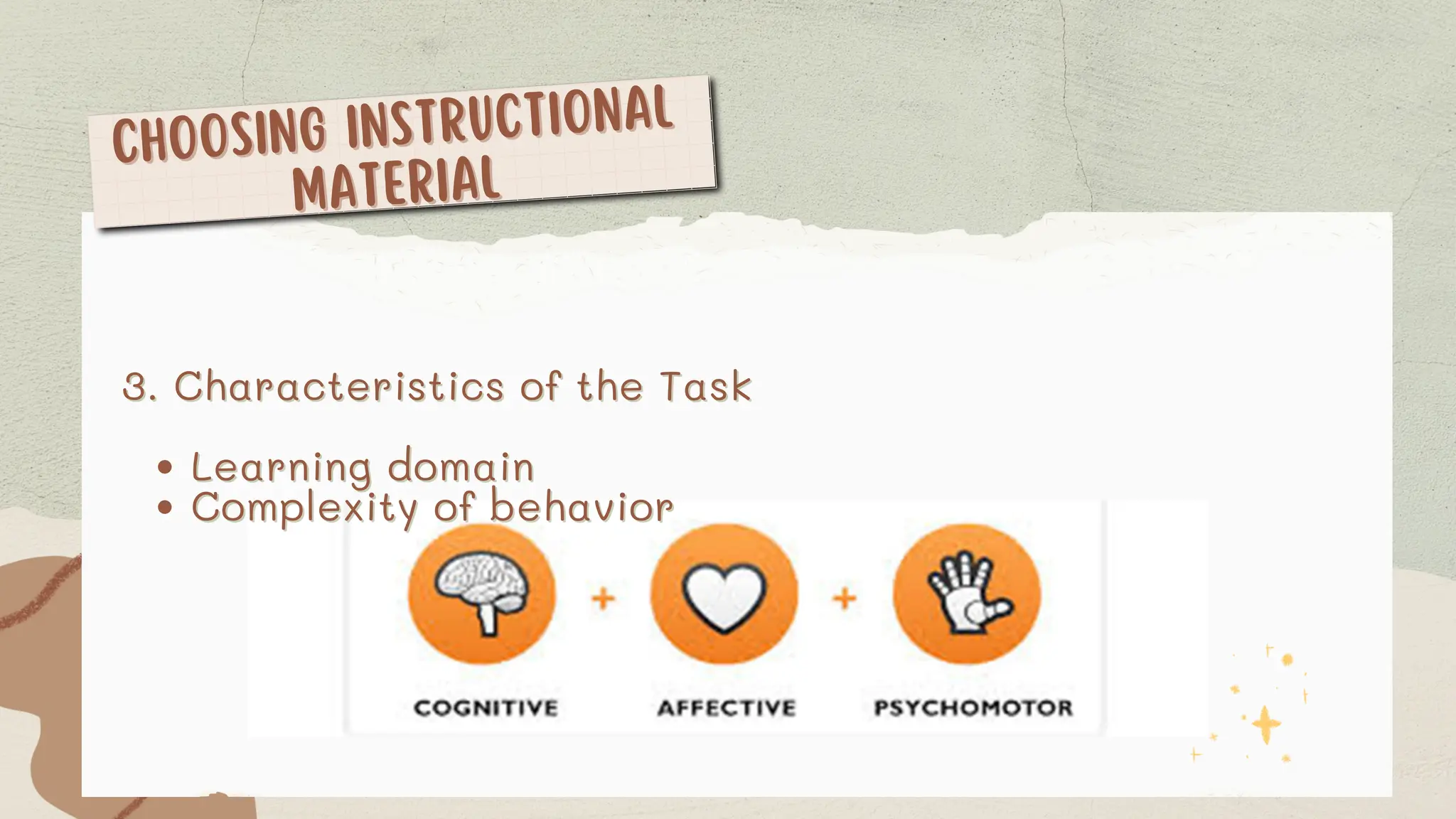
The document discusses the differences between instructional methods and materials. It provides examples of various types of instructional materials including written materials like printed texts and instructor-composed materials. Demonstration materials such as models, displays, posters and diagrams are also covered. The document concludes with sections on audiovisual materials which are categorized into projected resources, audio resources, video resources, telecommunications resources and computer resources. Key factors to consider when selecting instructional materials include learner characteristics, the learning task, and available media options.