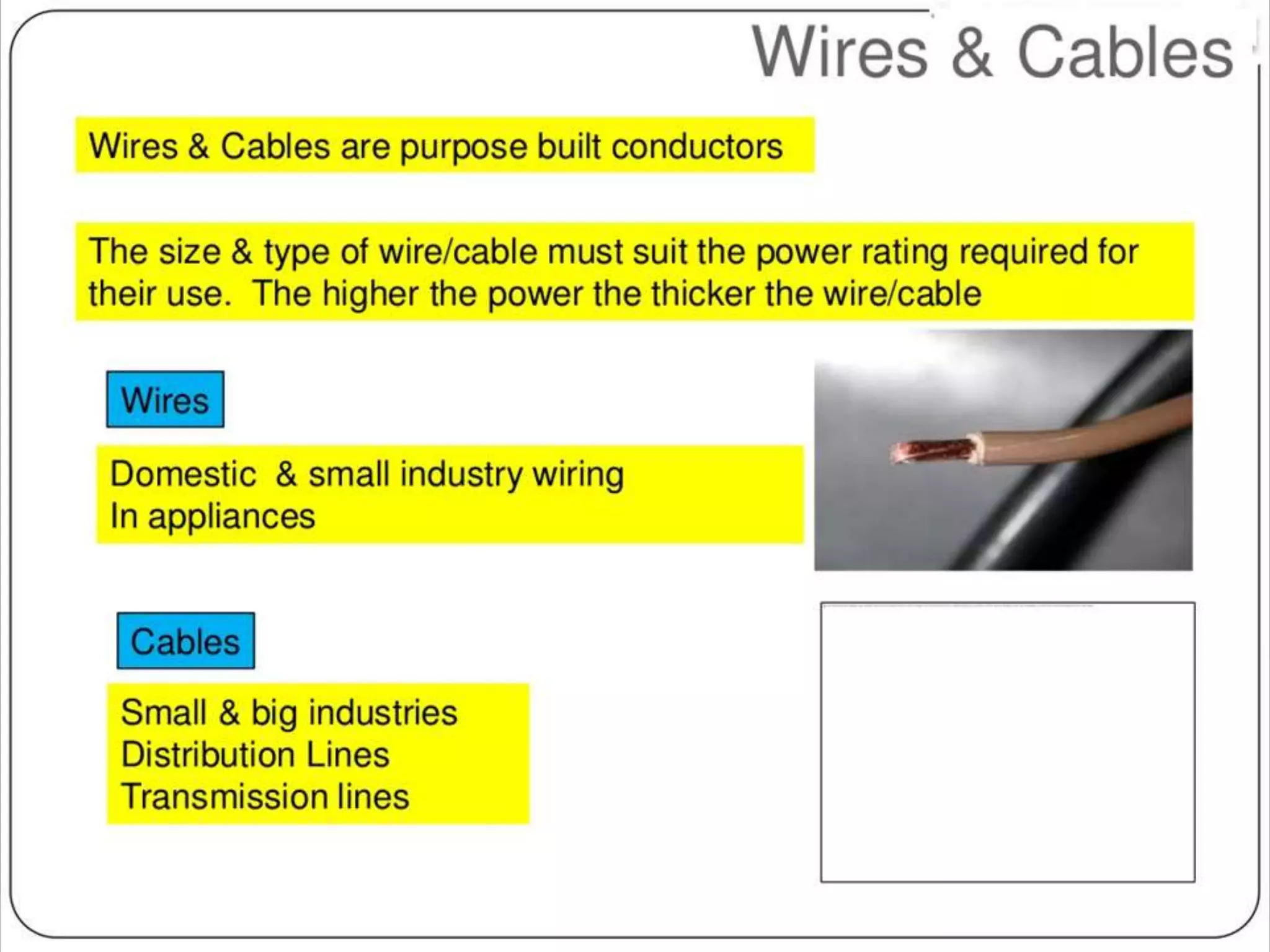
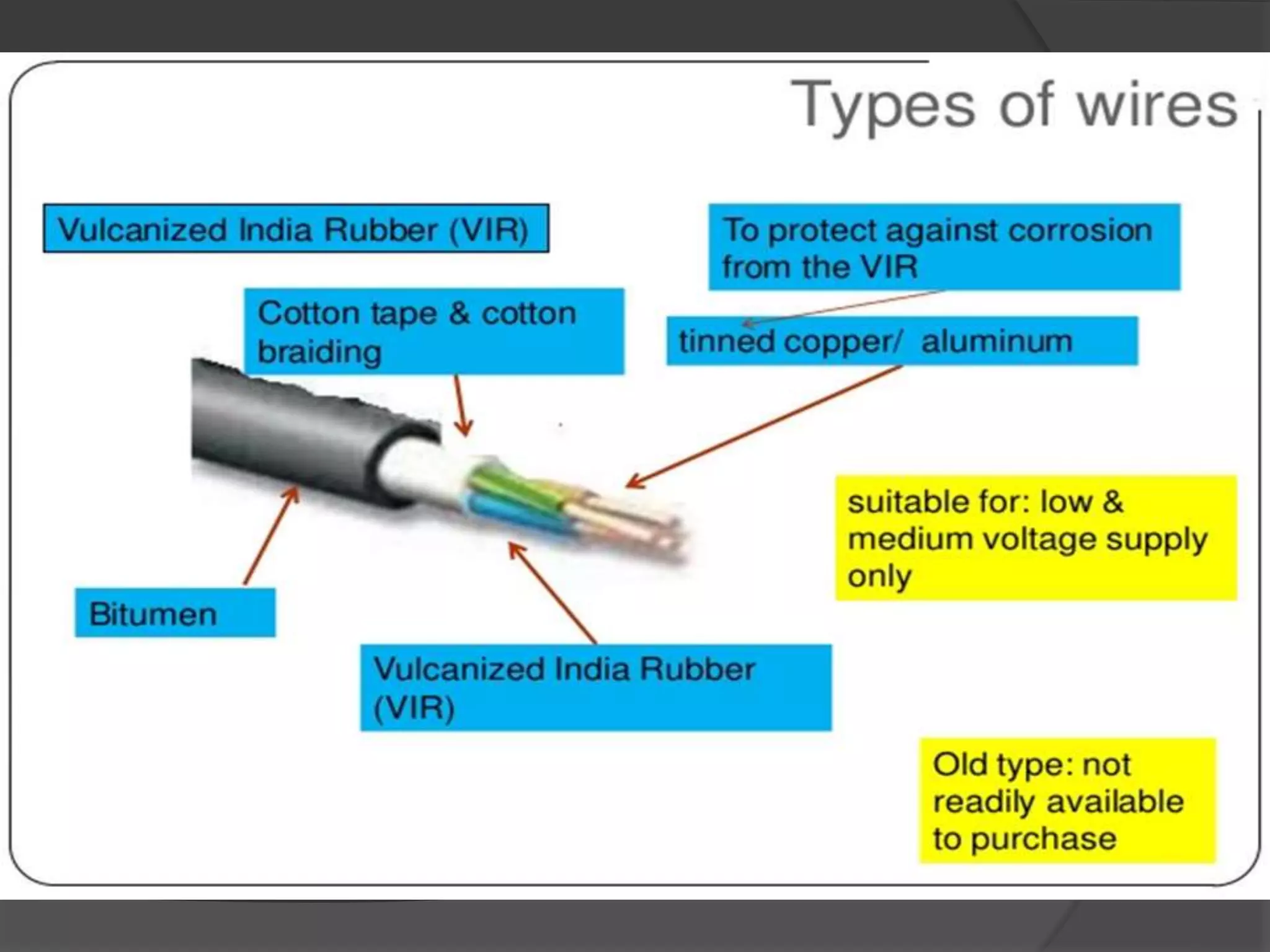
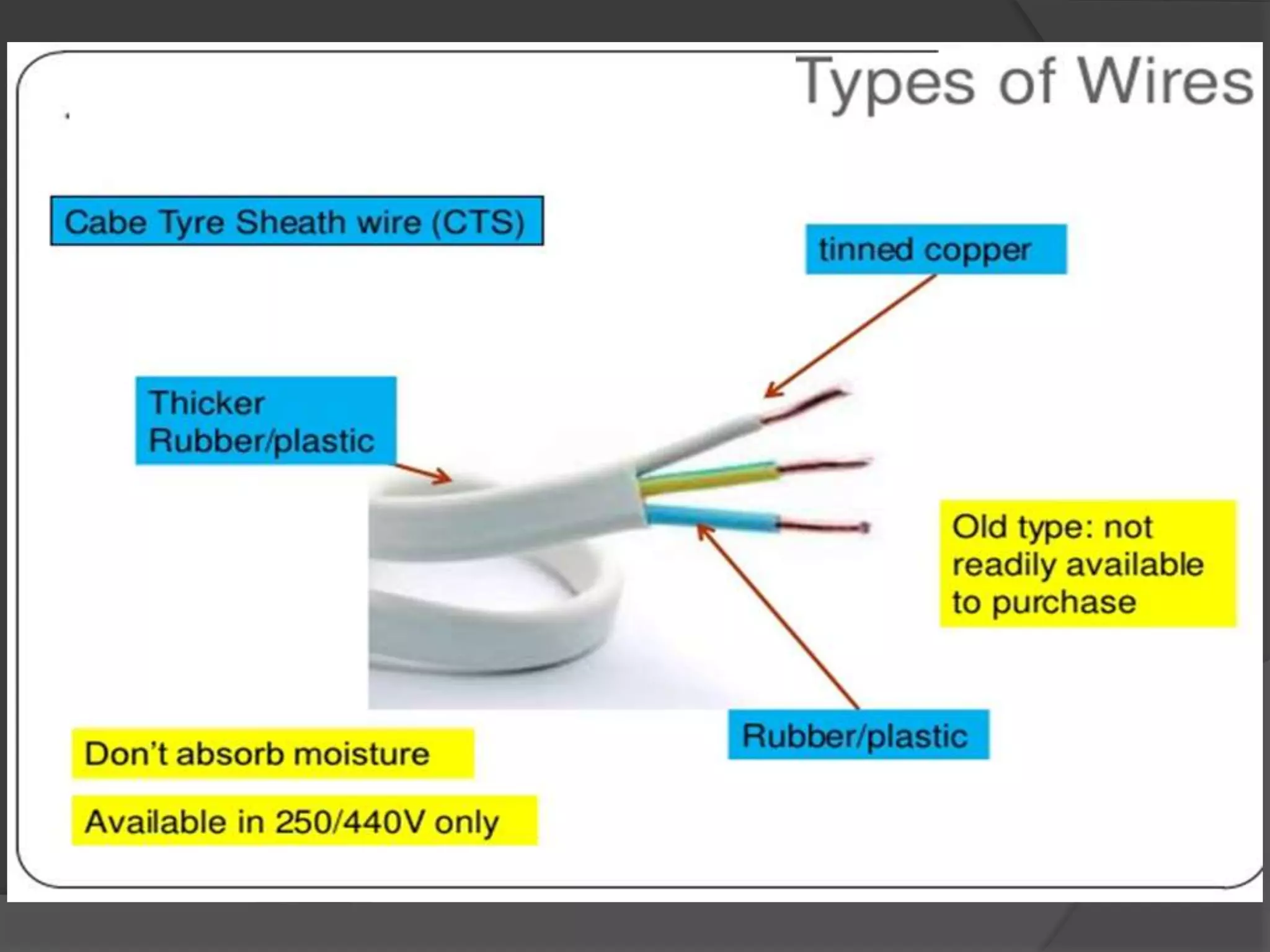
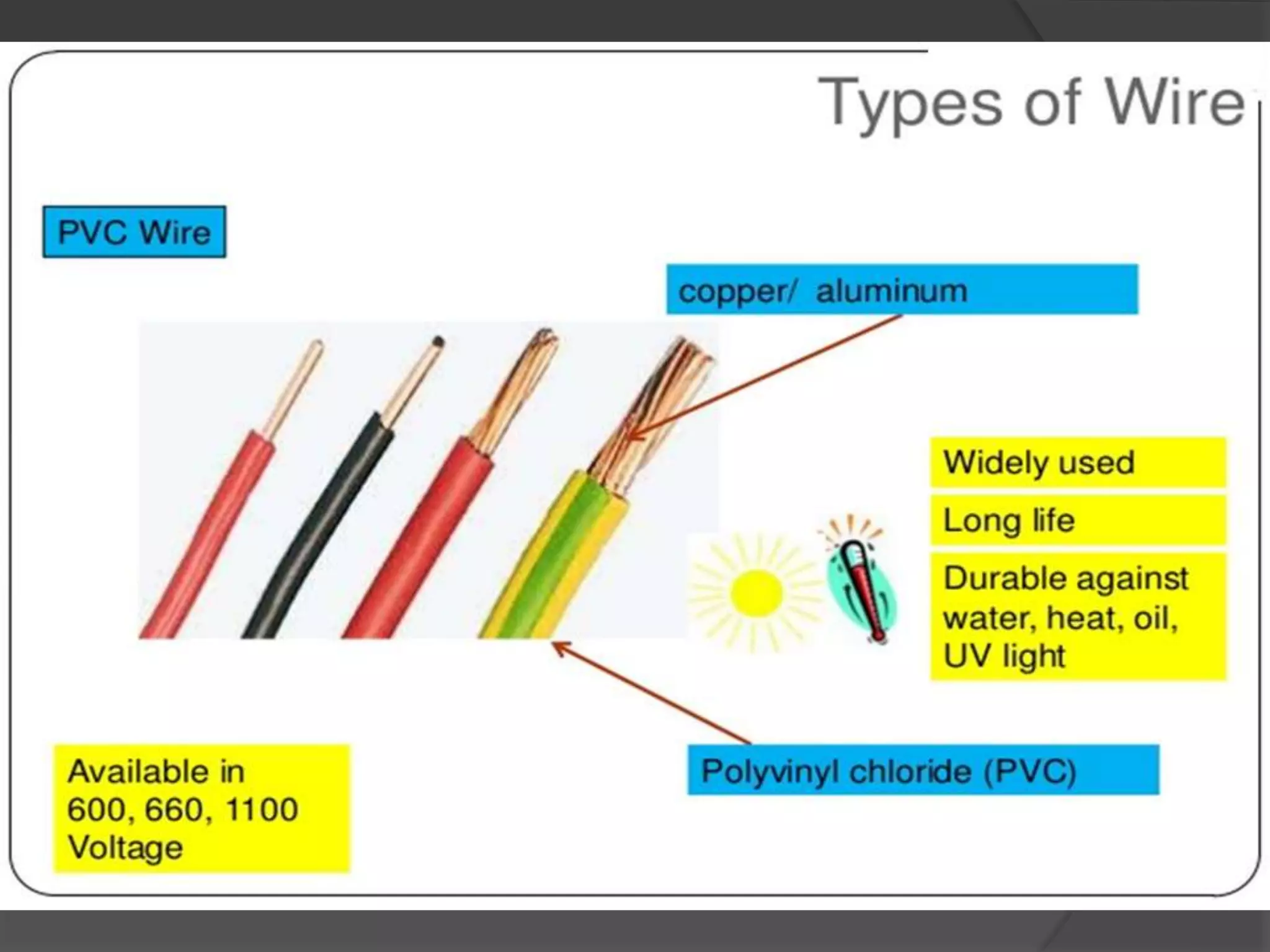
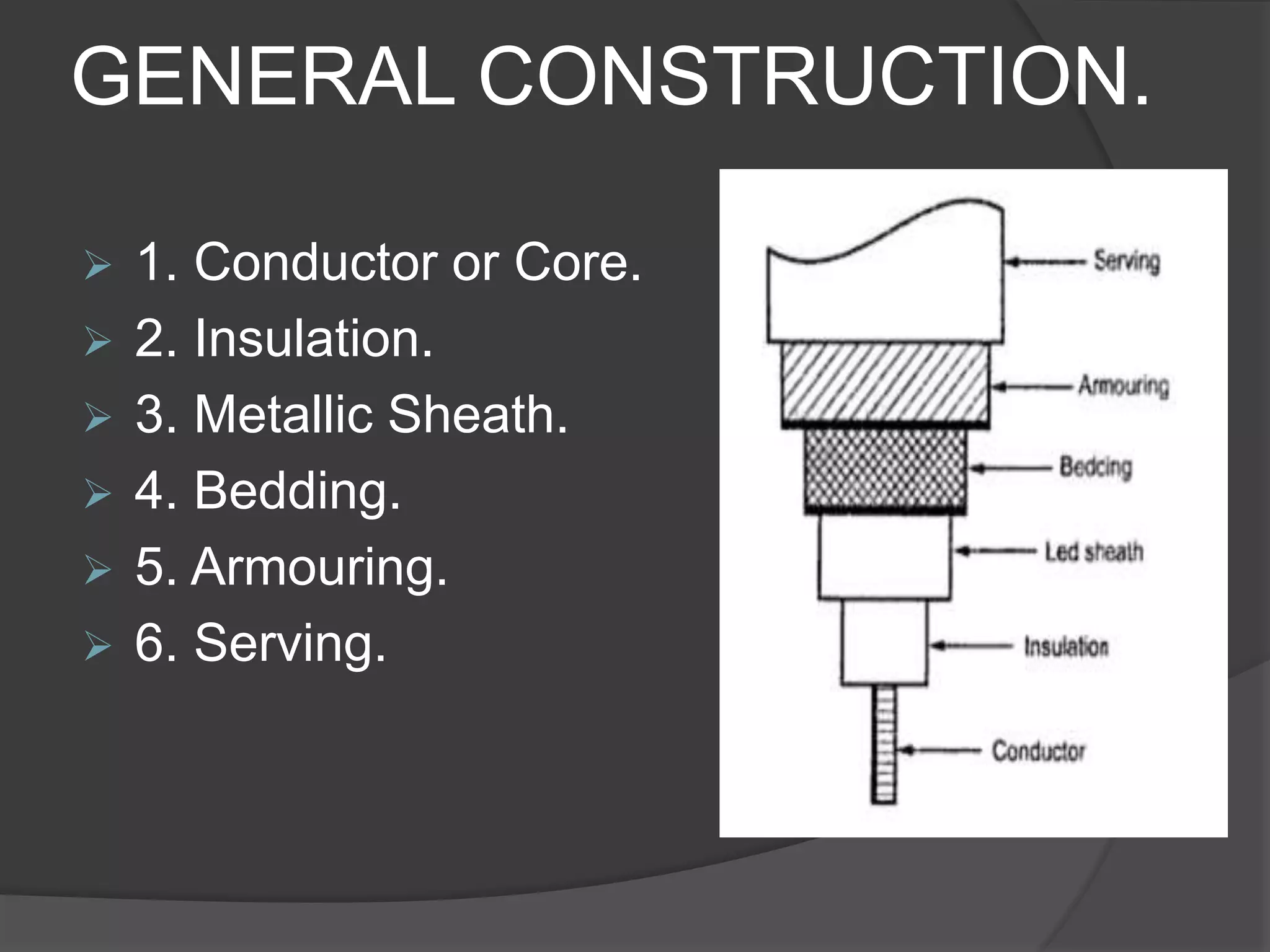
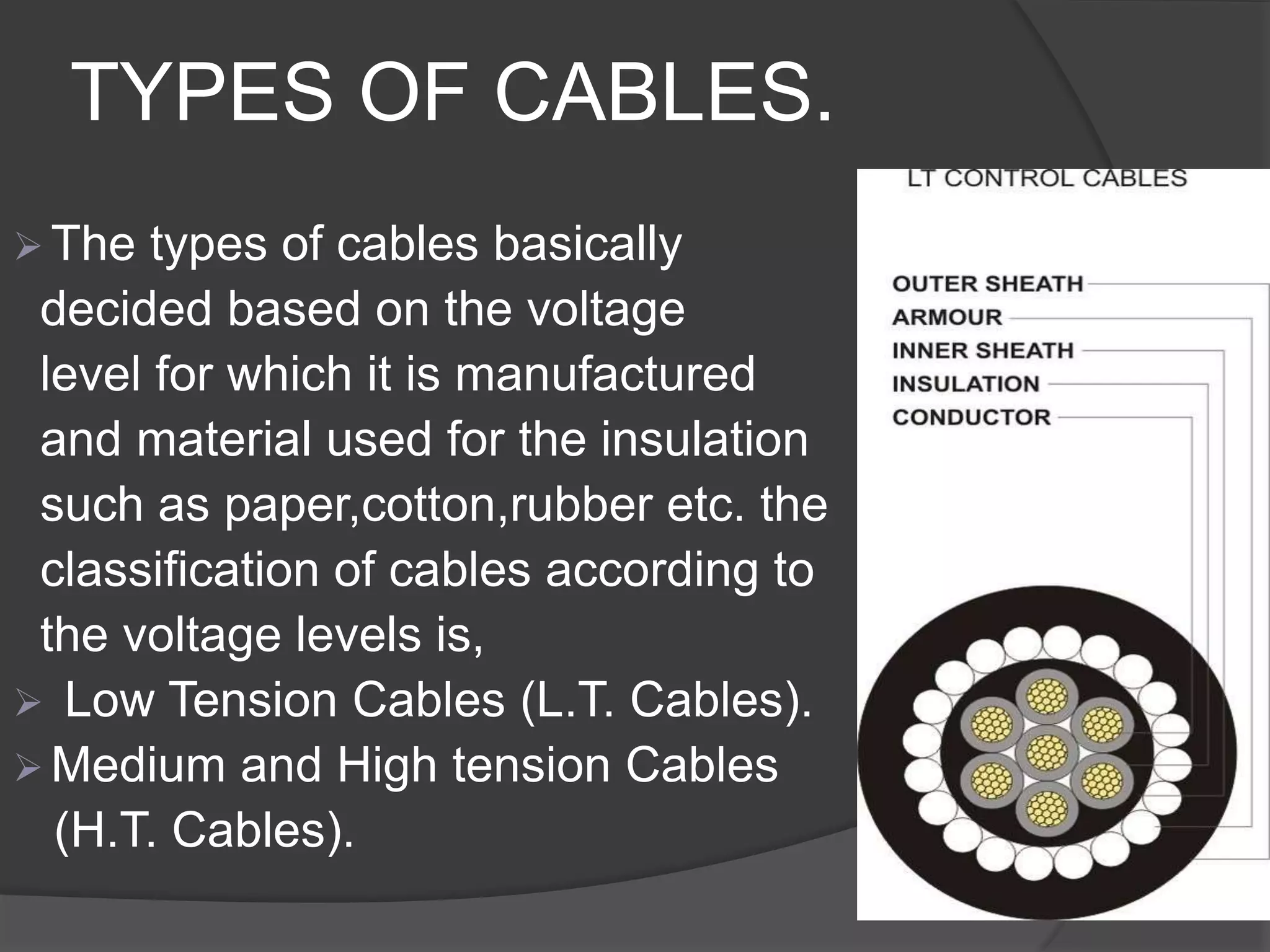
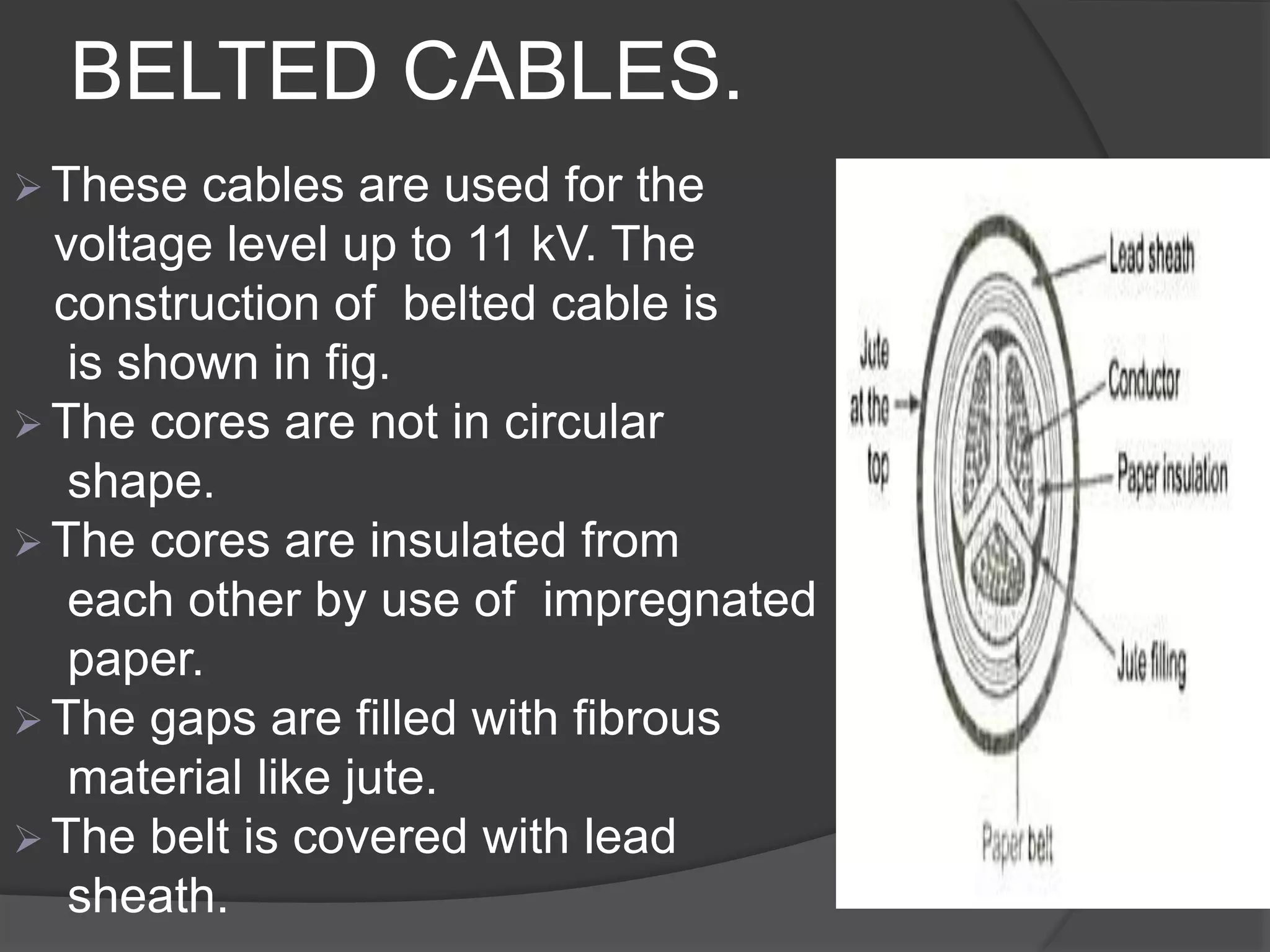
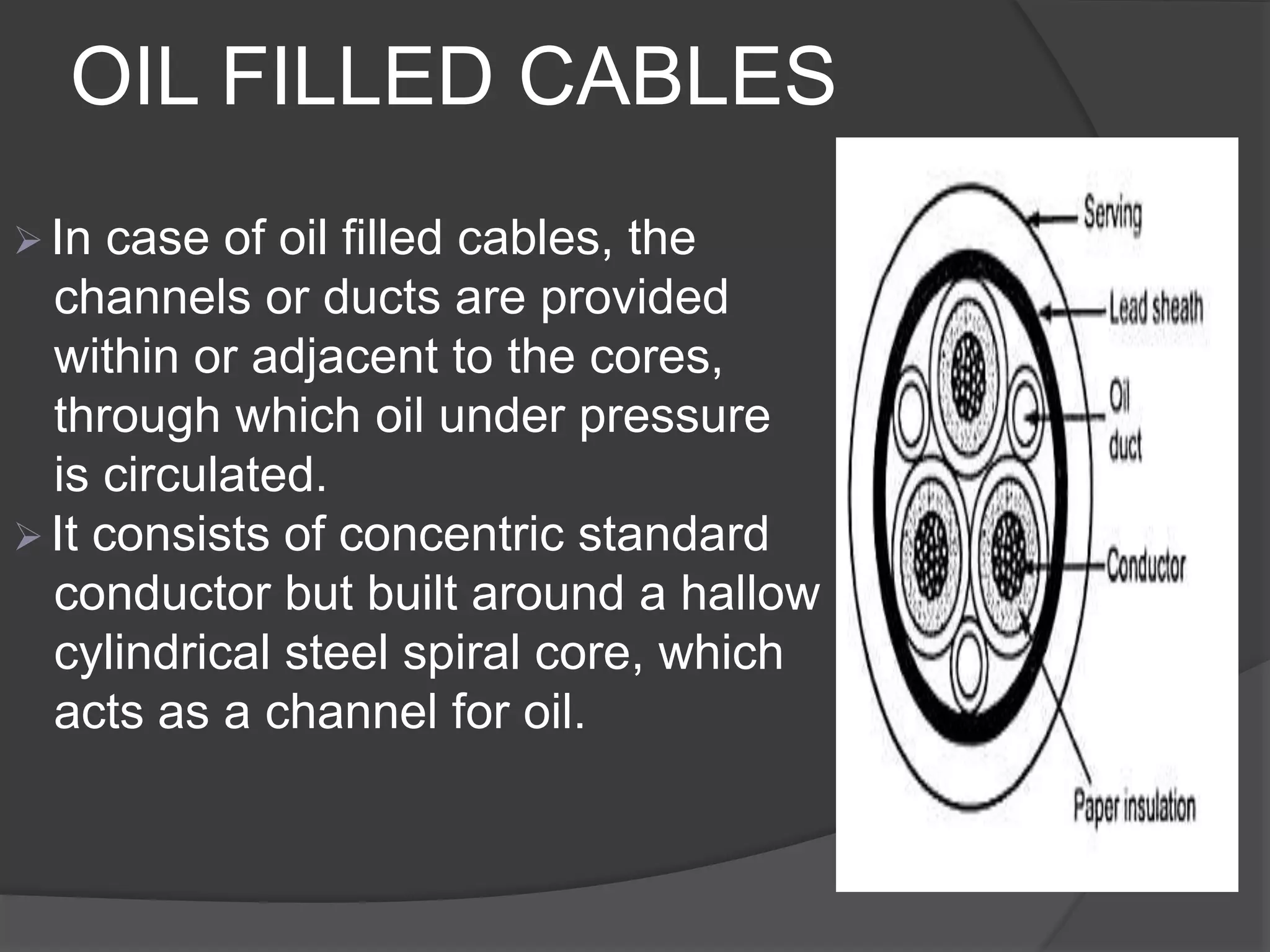
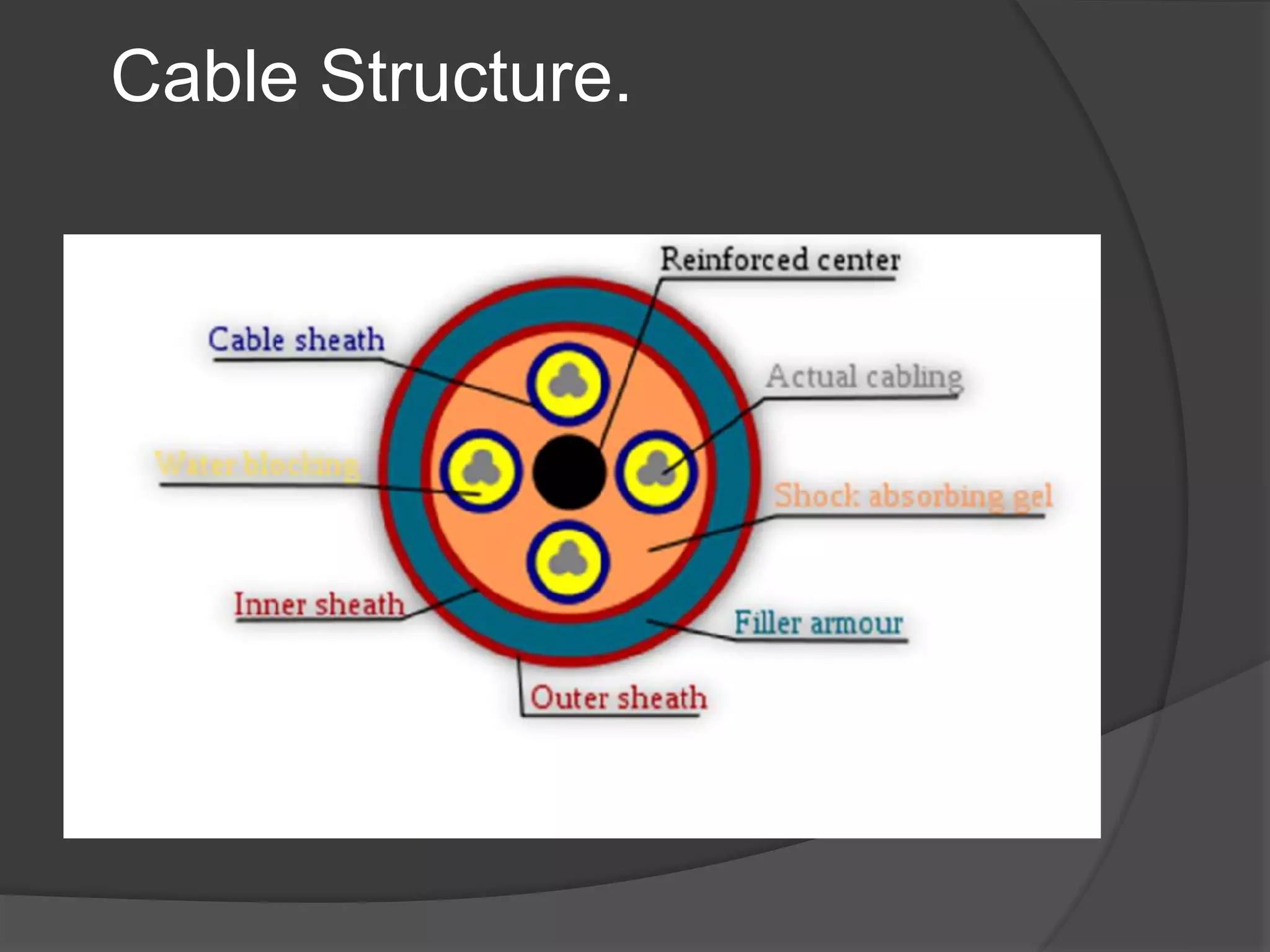
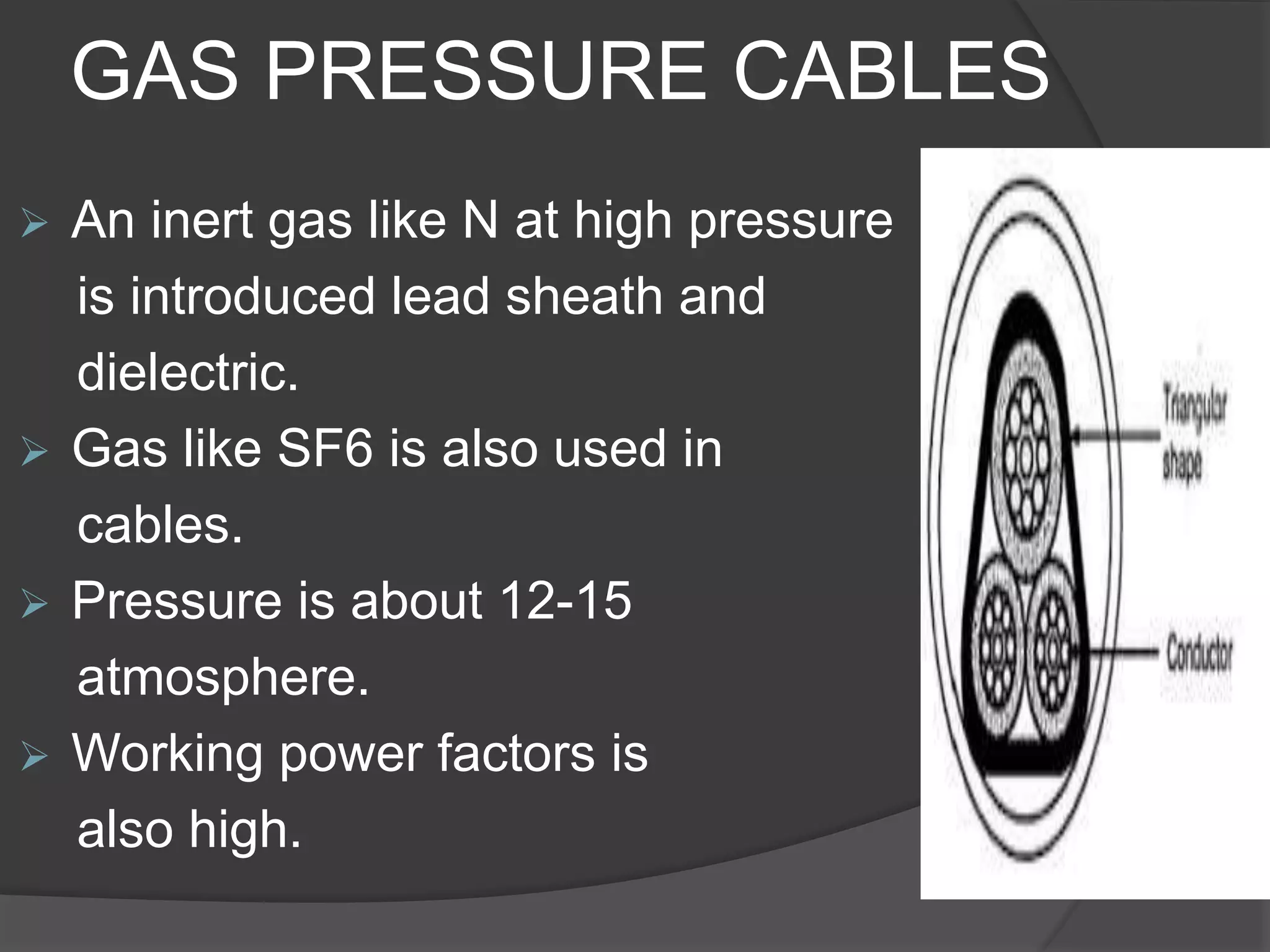
The document provides an overview of various types of electrical wires and cables, including their construction and applications. It discusses six types of wires, such as vulcanised Indian rubber wire and tough rubber sheathed wire, and outlines the general construction and types of power cables based on voltage levels. Additionally, it describes special cable types like belted, super tension, oil-filled, and gas pressure cables for high-voltage applications.