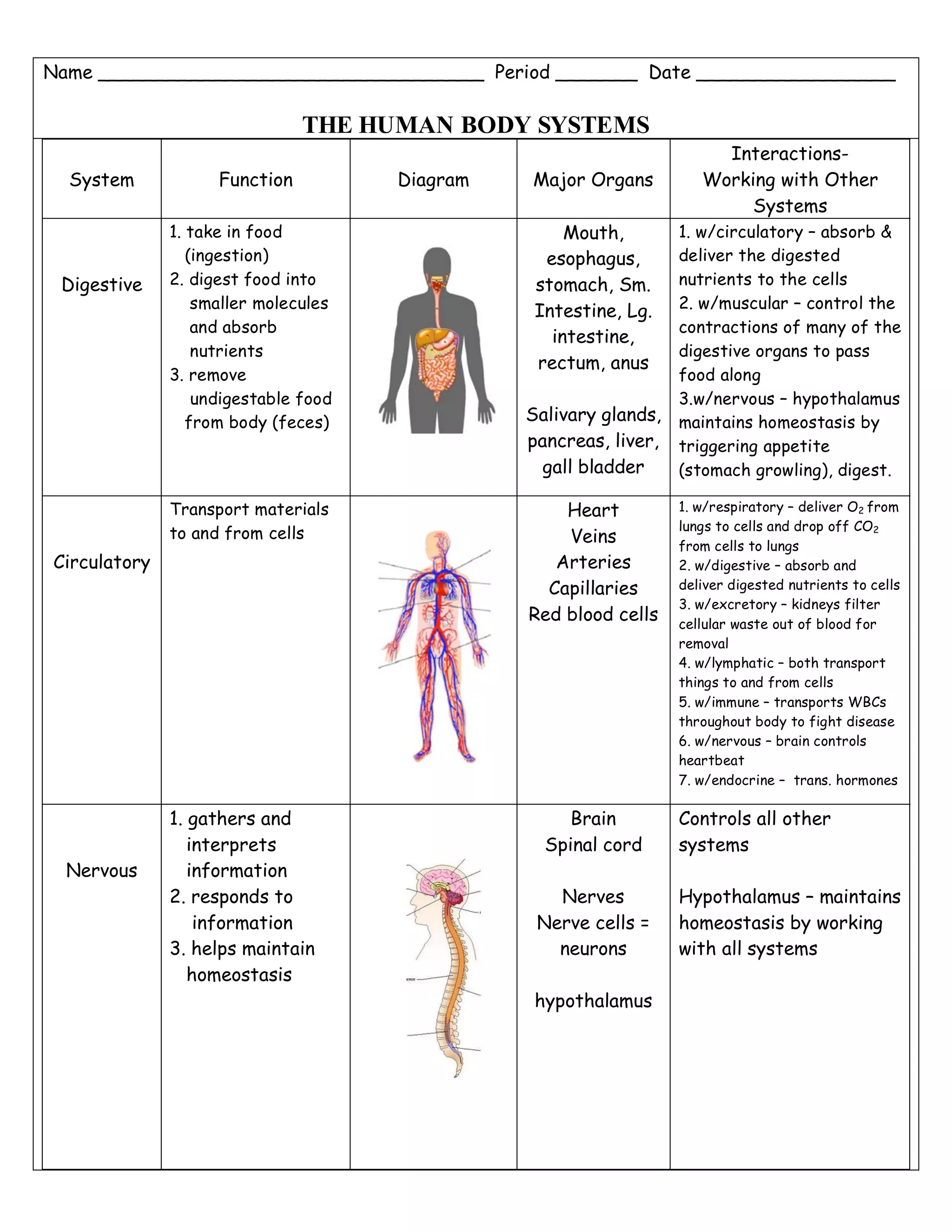
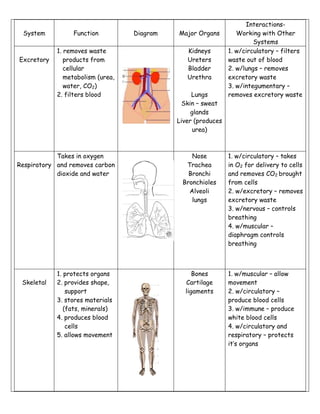
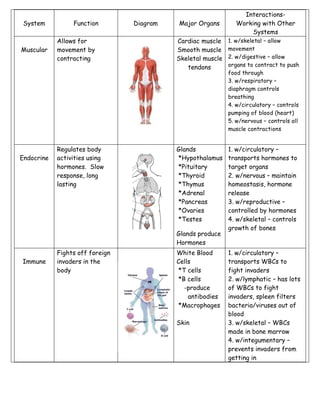
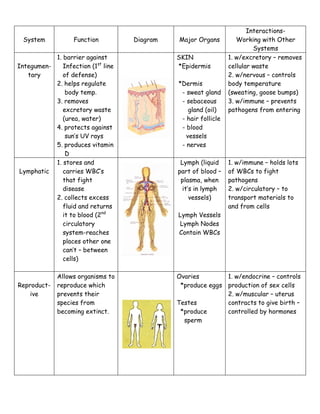
The document describes the major human body systems, including their functions, main organs, and interactions with other systems. It lists the 11 main systems as digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, endocrine, immune, integumentary, and lymphatic. For each system it provides a brief description of its function, diagrams of major organs, and notes on how it interacts with other body systems to maintain homeostasis.