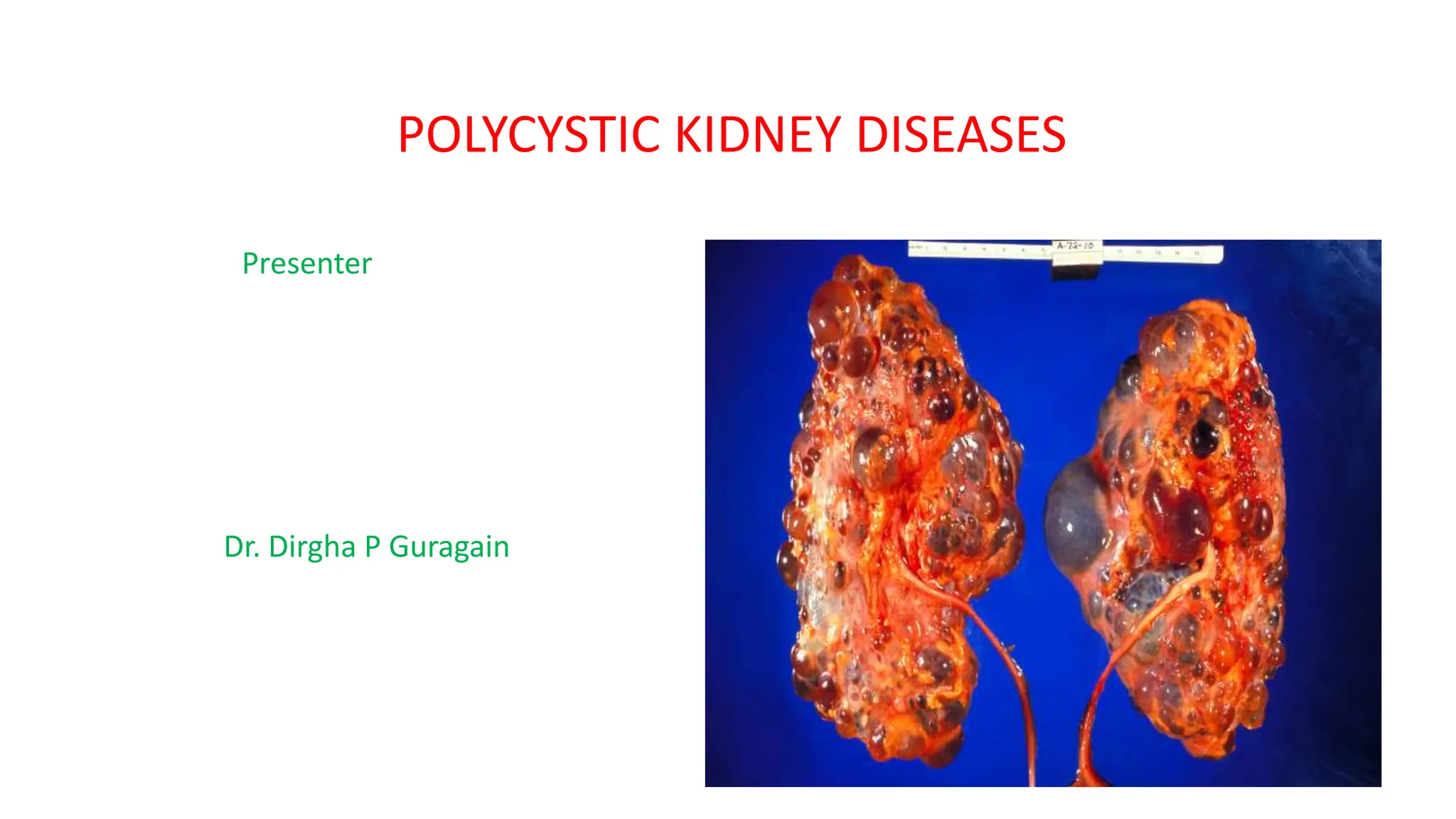
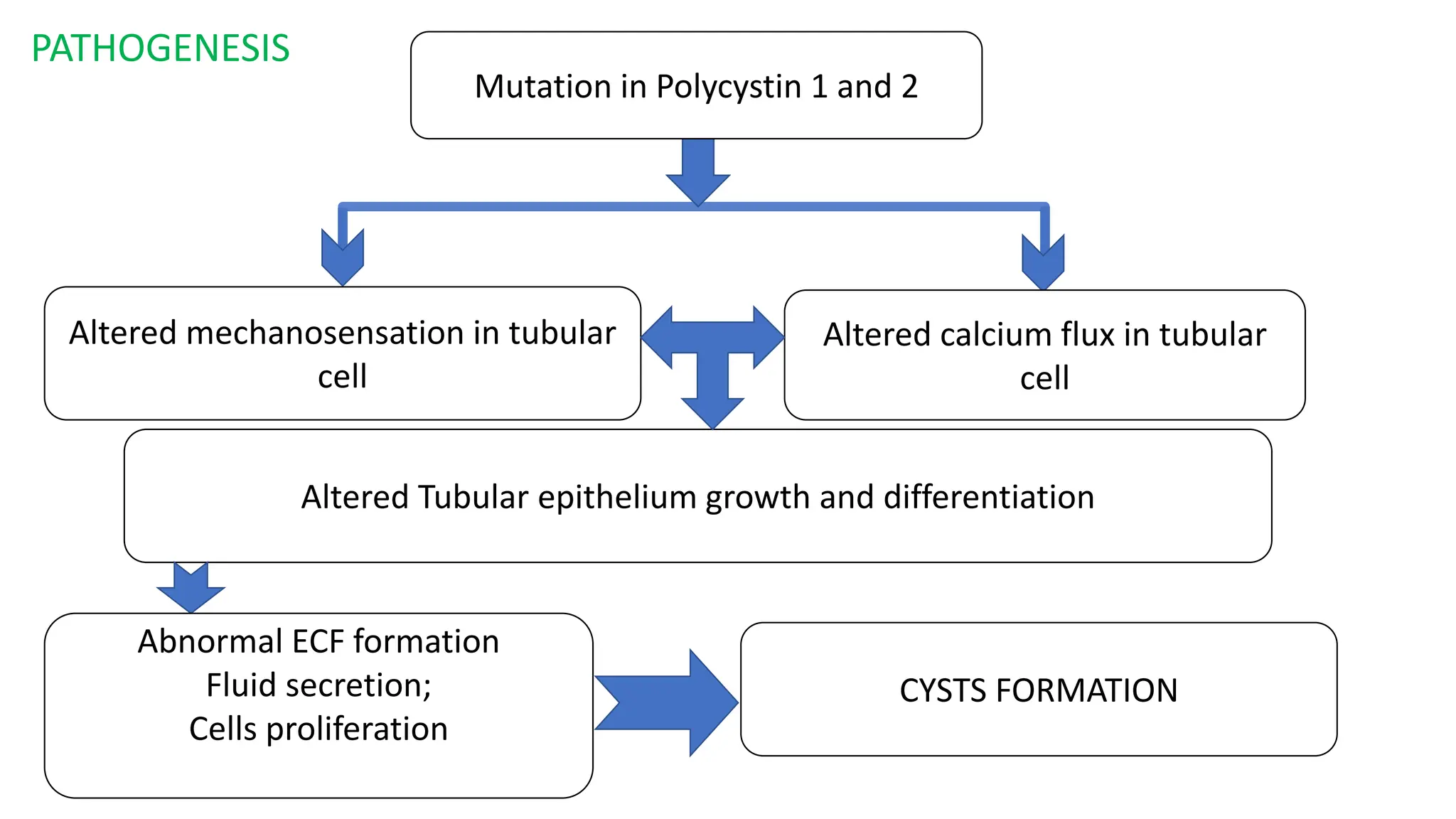
Polycystic kidney diseases (PKD) are inherited disorders characterized by bilateral kidney cyst formation, primarily including autosomal dominant (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive (ARPKD) varieties. ADPKD is associated with mutations in PKD1 and PKD2 genes, leading to progressive kidney damage and associated complications, which can result in end-stage renal disease by age 52 for PKD1 and 70 for PKD2. Diagnosis typically involves family history, ultrasound findings, and blood tests, while management focuses on blood pressure control, progression slowing, and treatment of renal complications.