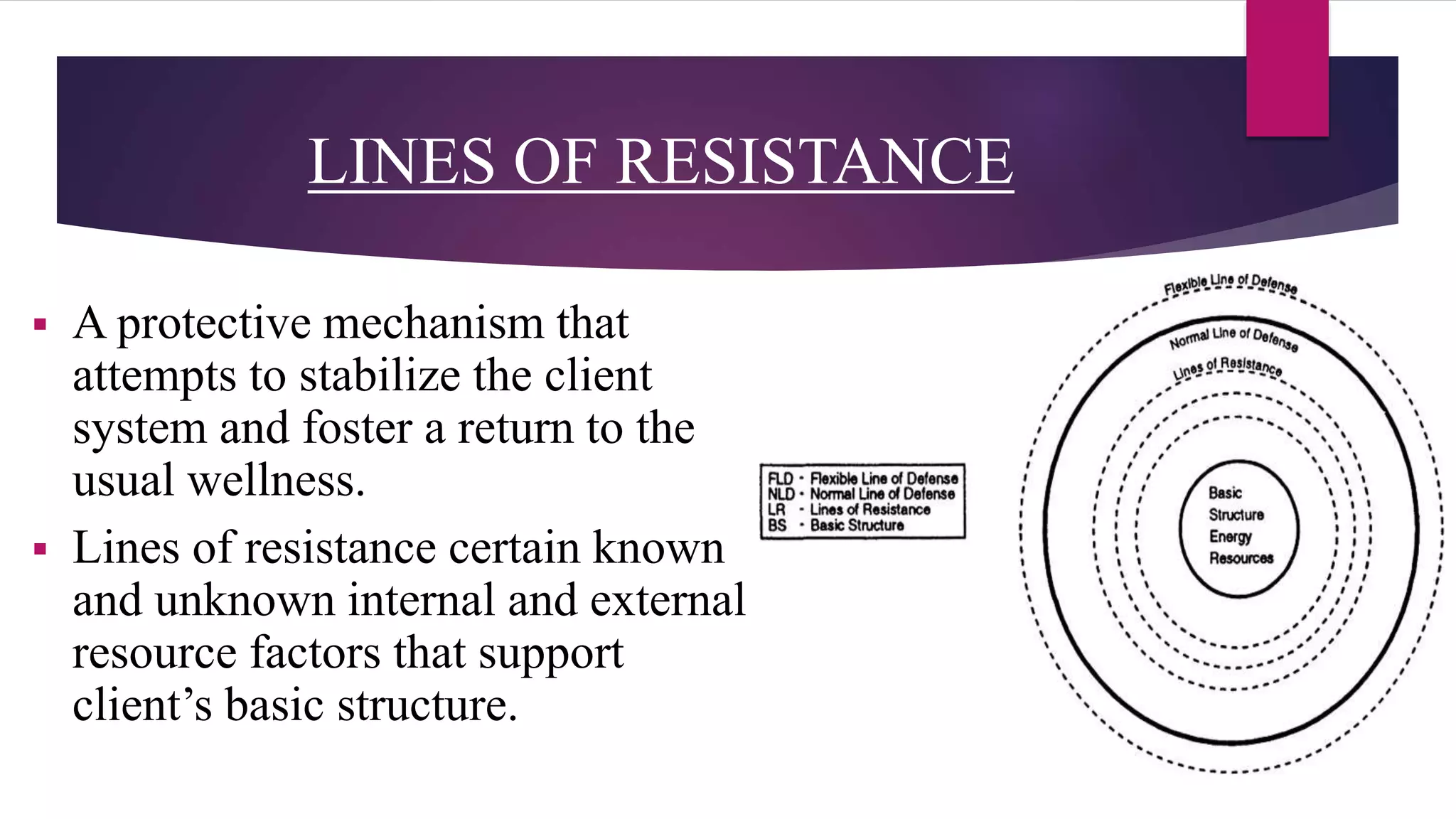
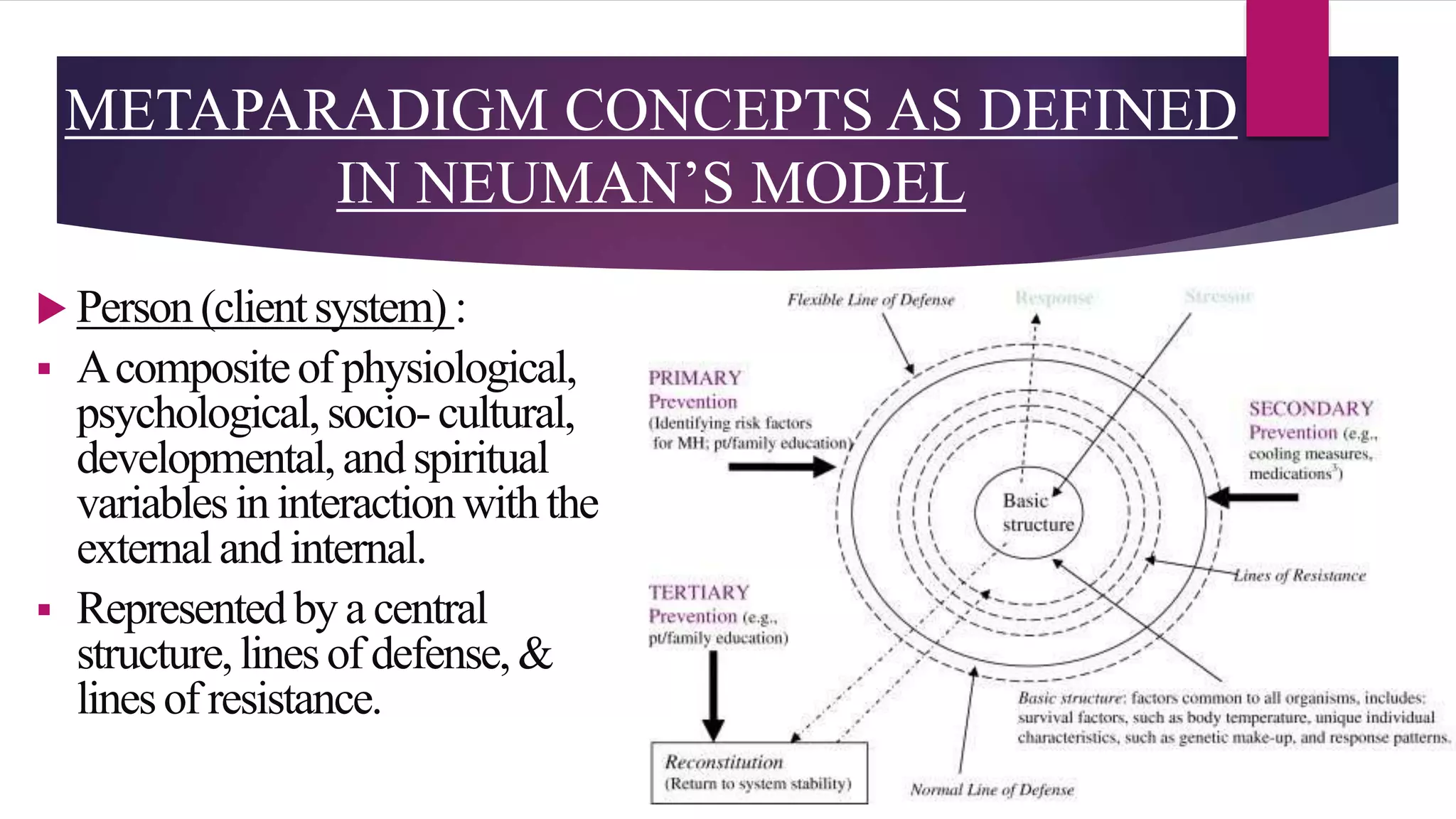
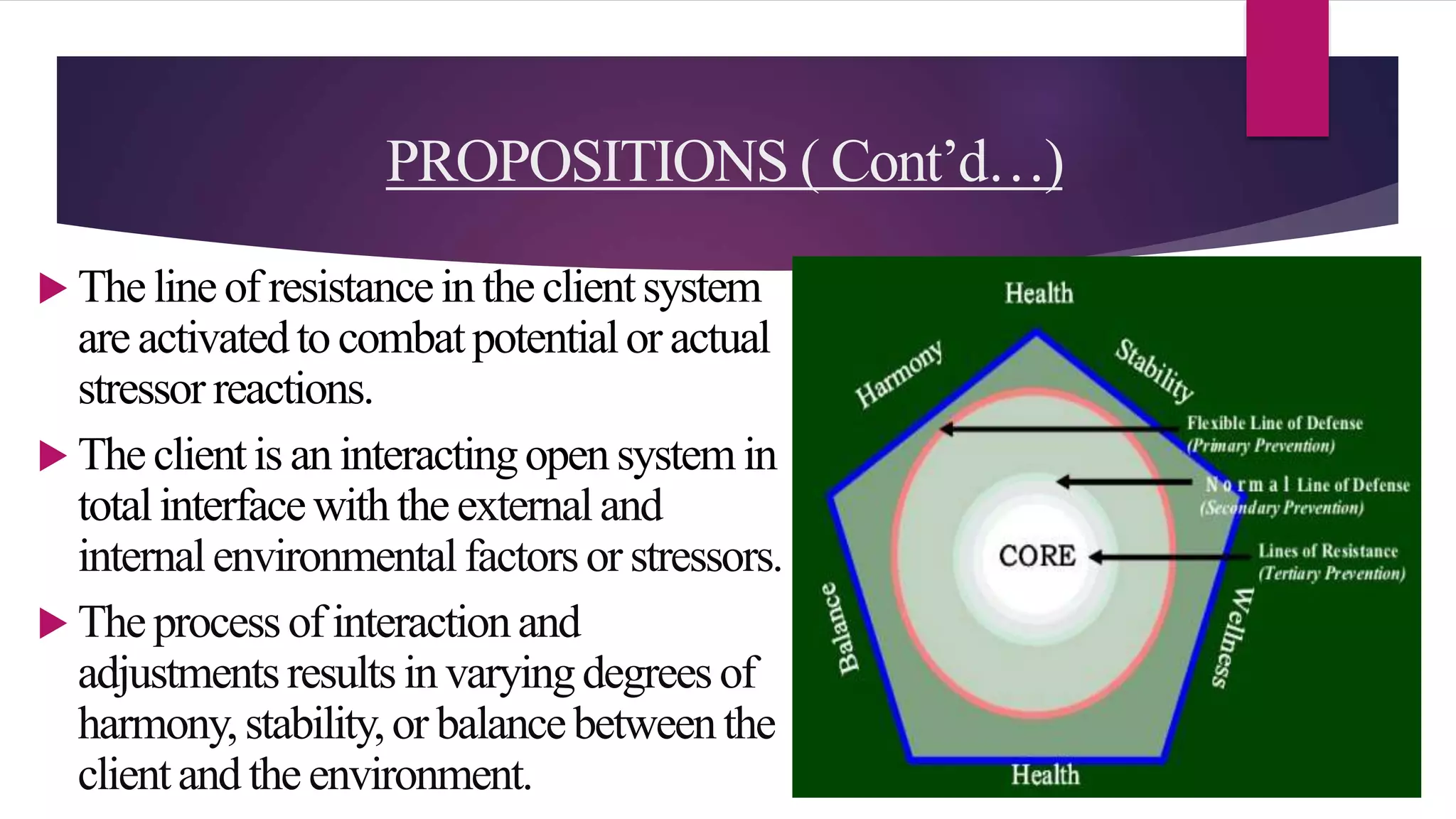
The document discusses Betty Neuman's Systems Model, which integrates various disciplines to provide a framework for nursing that focuses on the client system's interaction with environmental stressors. It outlines key components such as lines of defense to protect the client from stressors, methods of nursing interventions at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, and emphasizes the role of assessment and partnership in nursing practice. The model's applicability to various client systems and its comprehensive approach to health maintenance and wellness are also highlighted.