3 center 4 electrons bond By Malik Xufyan
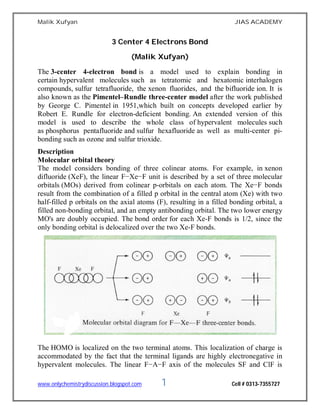
- 1. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 1 Cell # 0313-7355727 3 Center 4 Electrons Bond (Malik Xufyan) The 3-center 4-electron bond is a model used to explain bonding in certain hypervalent molecules such as tetratomic and hexatomic interhalogen compounds, sulfur tetrafluoride, the xenon fluorides, and the bifluoride ion. It is also known as the Pimentel–Rundle three-center model after the work published by George C. Pimentel in 1951,which built on concepts developed earlier by Robert E. Rundle for electron-deficient bonding. An extended version of this model is used to describe the whole class of hypervalent molecules such as phosphorus pentafluoride and sulfur hexafluoride as well as multi-center pi- bonding such as ozone and sulfur trioxide. Description Molecular orbital theory The model considers bonding of three colinear atoms. For example, in xenon difluoride (XeF), the linear F−Xe−F unit is described by a set of three molecular orbitals (MOs) derived from colinear p-orbitals on each atom. The Xe−F bonds result from the combination of a filled p orbital in the central atom (Xe) with two half-filled p orbitals on the axial atoms (F), resulting in a filled bonding orbital, a filled non-bonding orbital, and an empty antibonding orbital. The two lower energy MO's are doubly occupied. The bond order for each Xe-F bonds is 1/2, since the only bonding orbital is delocalized over the two Xe-F bonds. The HOMO is localized on the two terminal atoms. This localization of charge is accommodated by the fact that the terminal ligands are highly electronegative in hypervalent molecules. The linear F−A−F axis of the molecules SF and ClF is
- 2. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 2 Cell # 0313-7355727 described as a 3-center 4-electron bond. In the xenon fluorides, all bonds are described with the 3-center 4-electron model. Molecules without an s-orbital lone pair such as PF and SF are described by an extended version of the 3-center 4- electron model (See hypervalent molecule). Valence bond theory The bonding in XeF can also be shown qualitatively using resonant Lewis structures: In this representation, the octet rule is not broken, the bond orders are 1/2, and there is increased electron density in the fluorine atoms. These results are consistent with the molecular orbital picture discussed above. Hypervalent description with d orbitals Older models for explaining hypervalency invoked d orbitals. As of 2010, these models still appear in some beginning-level college texts;[6] however, quantum chemical calculations suggest that d-orbital participation is negligible due to the large energy difference between the relevant p (filled) and d (empty) orbitals. Furthermore, a distinction should be made between "d orbitals" in the valence bond sense and "d functions" that are included in the QM calculation aspolarization functions. The 3-center-4-electron bonding model has the advantage of dispensing with the need for d orbitals, which has led to its acceptance. Other systems Three-center four-electron interactions can also be considered in the transition state of S2 reactions and in some (resonant) hydrogen bonding (as in the bifluoride anion) Explanation with examples: The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model has long been used successfully to predict the geometry of various main group molecules. Hexa coordinated AB6-type main group molecules belong to an important class of compounds. This type of molecule possesses six electron pairs in the central atom. Similarly the penta coordinated AB5-type molecules possessing five electron pairs are predicted to have trigonal bipyramidal structure. Previous Knowledge About AB6-type Molecules
- 3. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 3 Cell # 0313-7355727 According VSEPR model hexa coordinated AB6-type molecules have Octahedral structure. Coordinated by six ligands. Two d orbitals are required to participate in bonding. As a result, two electrons in the s and p subshells are promoted to higher-level d orbitals forming six sp3 d2 hybrid orbitals in the central atom. According VSEPR model penta coordinated AB5-type molecules possess ◦ Five electron pairs ◦ Trigonal bipyramidal structure ◦ Central atom coordinated by five ligands ◦ One d orbital is required to participate in bonding. ◦ As a result, one electron in the s or p subshell is promoted to a higher- level d orbital forming five sp3 d hybrid orbitals in the central atom. Factors which disfavor the utilization of d orbitals Two factors which disfavor the utilization of d orbitals and have made d- orbital participation in bonding in main group compounds a controversial issue. 1. Energetically unfavorable s2 pn d0 → s1 pn-1 d2 [n = 3(P), 4(S), or 5(Cl, Br. I)] excitation, which requires a large promotion energy. 2. d orbitals in nonmetals are heavily shielded by the more penetrating s and p electrons and extremely diffuse. As a result, they have poor overlap with the orbitals of neighboring atoms. Bonding in the AB6-type Molecules
- 4. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 4 Cell # 0313-7355727 SF6 and PF6 - anion are often chosen as representatives of AB6-type main group molecules. Six fluorine ligands approach to the central sulfur or phosphorus atom along the x, y, and z axes forming an octahedral structure. Electronic Configuration of S,P and F Electronic Configuration of Sulphur is 1s2 ,2s2 ,2p6 ,3s2 ,3px 2 ,3py 1 ,3pz 1 Electronic Configuration of Phosphorus is 1s2 ,2s2 ,2p6 ,3s2 ,3px 1 ,3py 1 ,3pz 1 Electronic Configuration of Florine is 1s2 ,2s2 , 2px 2 ,2py 2 ,2pz 1 Ligand’s p orbitals have effective overlap with all the orthogonal sulfur or phosphorus 3p (3px, 3py, 3pz) orbitals in six orientations (±x, ±y, ±z). A filled 3p subshell in the central atom (achieved readily by s-p transition) is required, because the entire S.F or P.F bond distances in SF6 or PF6 . are equal. Six S.F bonds in SF6 result from the overlap of F(p1 ).S(3px 2 ).F(p1 ) F(p1 ).S(3py 2 ).F(p1 ) F(p1 ).S(3pz 2 ).F(p1 )
- 5. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 5 Cell # 0313-7355727 Six P.F bonds in PF6 - are formed by the overlap of F(p1 ).P(3px 2 ).F(p1 ) F(p1 ).P(3py 2 ).F(p1 ) F(p1 ).P(3pz 2 ).F(p1 )
- 6. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 6 Cell # 0313-7355727 Bonding in the AB5E-type Molecules The halogen pentafluoride XF5 (X = Cl, Br, or I) belongs to the AB5E type molecule. A square pyramidal structure with a lone pair in the central halogen atom. In all the XF5 molecules the basal X.Fb bonds (all are equivalent) are about 0.1 Å longer than the axial X.Fa bond. This shows that bonding in basal and axial positions must be different. Electronic Configuration of Chlorine is 1s2 ,2s2 ,2p6 ,3s2 ,3px 2 ,3py 2 ,3pz 1 Two sp hybrid orbitals could form on the central halogen atom pointing toward the axial positions.
- 7. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 7 Cell # 0313-7355727 The shorter axial X.Fa bond is reasonably formed by the overlap of an sp orbital with the fluorine p orbital. The lone pair resides in another sp orbital in the opposite axial position. Two sets of the longer, linear basal Fb.X.Fb bonds are reasonably formed by the overlap of the unhybridized, orthogonal px and py orbitals, respectively, with the terminal fluorine p orbitals leading to a three-center, four-electron bond. Bonding in the AB4E2-type Molecules Xenon tetrafluoride XeF4 is an example of AB4E2-type molecules. A square planar structure with two lone pairs in the central xenon atom. In XeF4 two sp hybrid orbitals could reasonably form on Xe pointing toward the axial positions and holding a lone pair in each of them. The two sets of linear F.Xe.F bonds are formed as three-center, four-electron bonds, the same as formation of the basal Fb.X.Fb bonds in the above- discussed halogen pentafluorides XF5.
- 8. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 8 Cell # 0313-7355727 Bonding in the AB5-type Molecules An alternative model that does not involve d orbitals in bonding in the pentacoordinated AB5-type molecules such as phosphorus pentahalides PX5 (X = F, Cl). Instead, three sp2 hybrid orbitals (each contains a single electron) are formed on the central atom overlapping with ligand orbitals in the equatorial positions Longer axial bonds are formed via the overlap of the unhybridized p orbital (containing two electrons) on the central atom and the two terminal ligand orbitals, resulting in a three-center, four-electron bond.
- 9. Malik Xufyan JIAS ACADEMY www.onlychemistrydiscussion.blogspot.com 9 Cell # 0313-7355727 Malik Xufyan M.Sc. Chemistry, B.Ed. JIAS ACADEMY JHANG SADAR CELL # 0313-7355727
