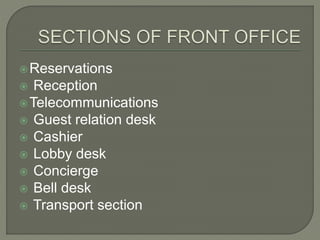
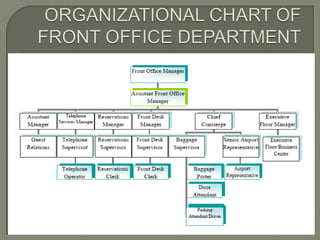
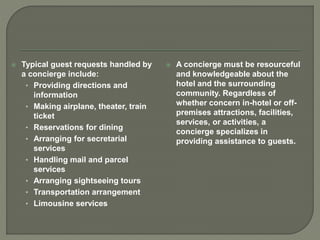
The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of a rooms division manager in a hotel. A rooms division manager supervises front office employees and coordinates with other departments to serve guests. Key duties include staffing, purchasing, budgeting, supervising payroll and availability controls, maximizing room rates and occupancy, handling customer issues, and staying up-to-date on market events and competition. The goal is to oversee smooth front office operations and guest services.