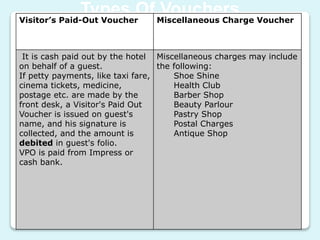
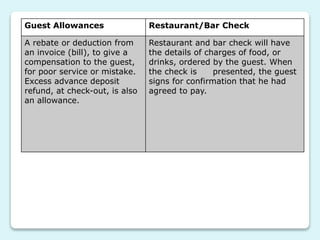
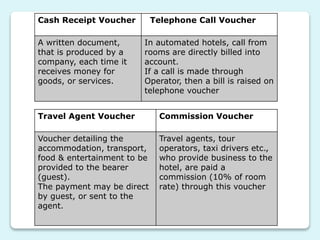
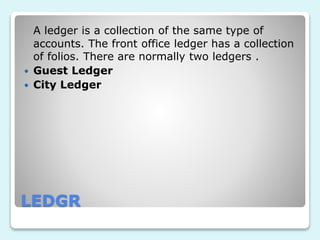
Front office accounting involves creating and maintaining guest and non-guest accounts, tracking financial transactions, monitoring credit limits, and providing management reports. It uses various types of accounts and vouchers to record transactions between guests, non-guests, and the hotel. Key functions include maintaining folios for individual and group accounts, as well as ledgers organized by guest and city accounts to collect the folios. Cash banks are also used to provide cash for transactions during shifts.