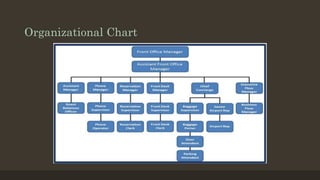
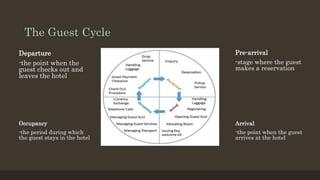
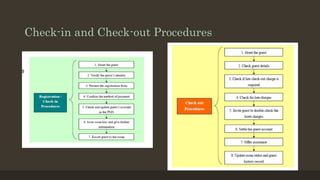
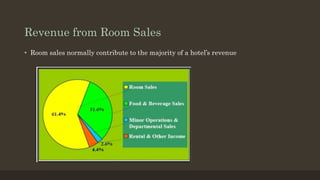
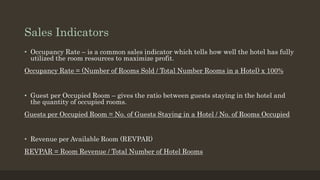
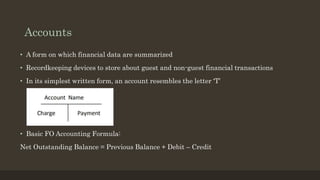
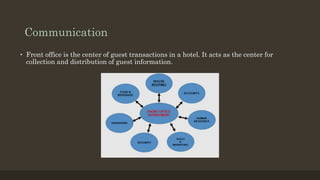
The document details the roles and organizational structure of the housekeeping and front office departments in a hotel, emphasizing their importance in enhancing guest experiences. It outlines key positions, responsibilities, and procedures for managing reservations, guest check-in/check-out processes, and maintaining financial transactions. It also discusses the methods used for ensuring efficient operations and communication within these departments.