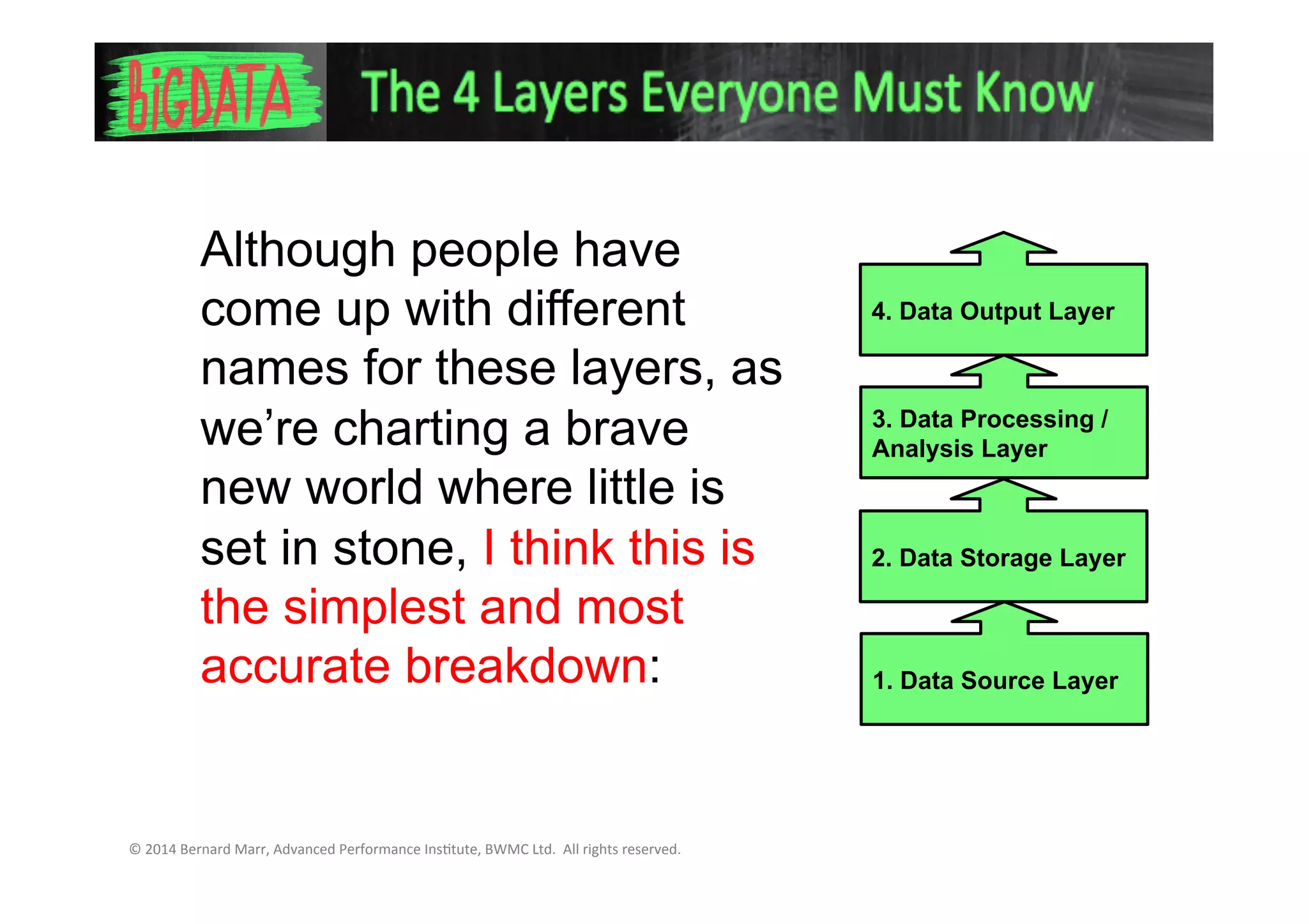
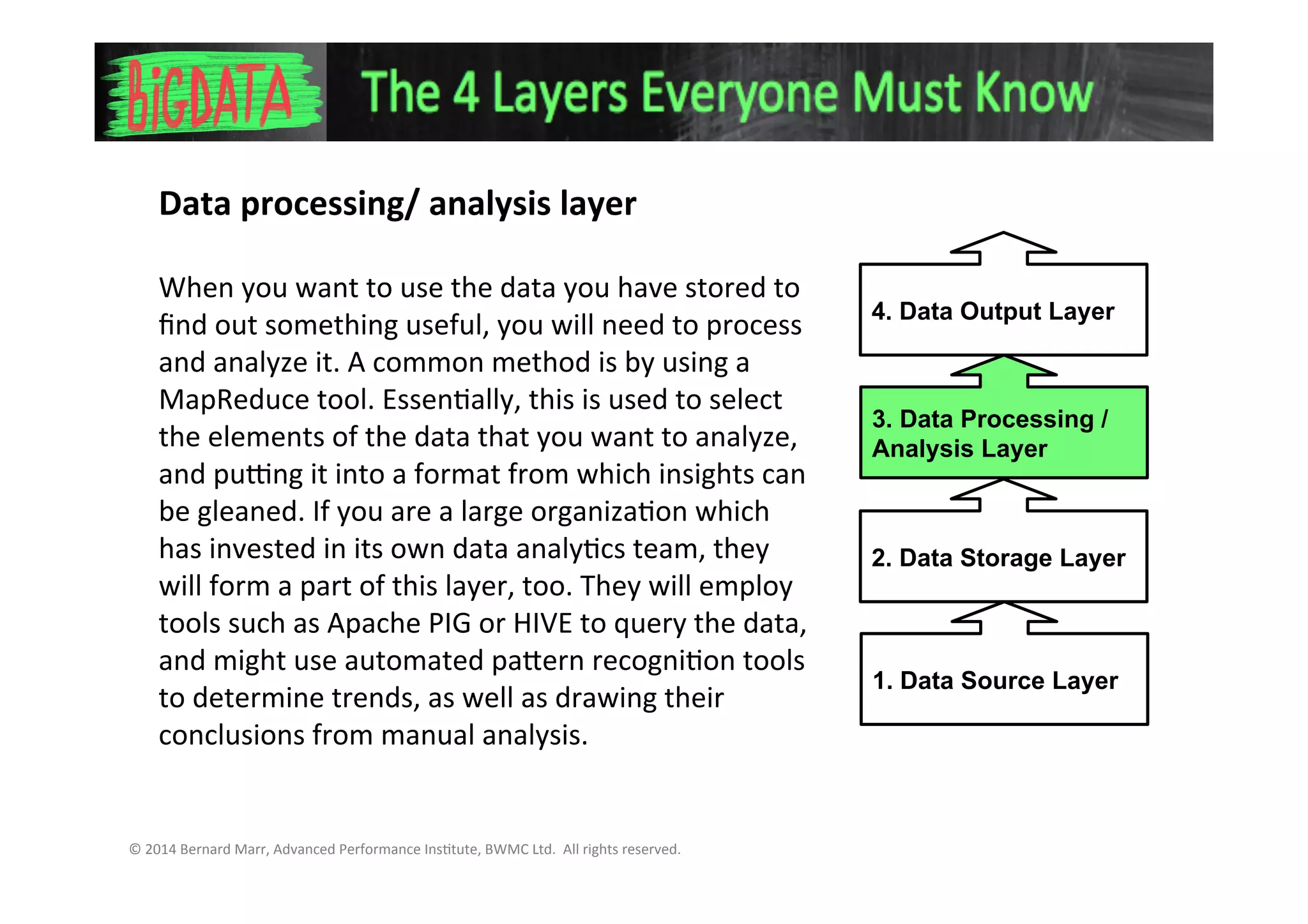
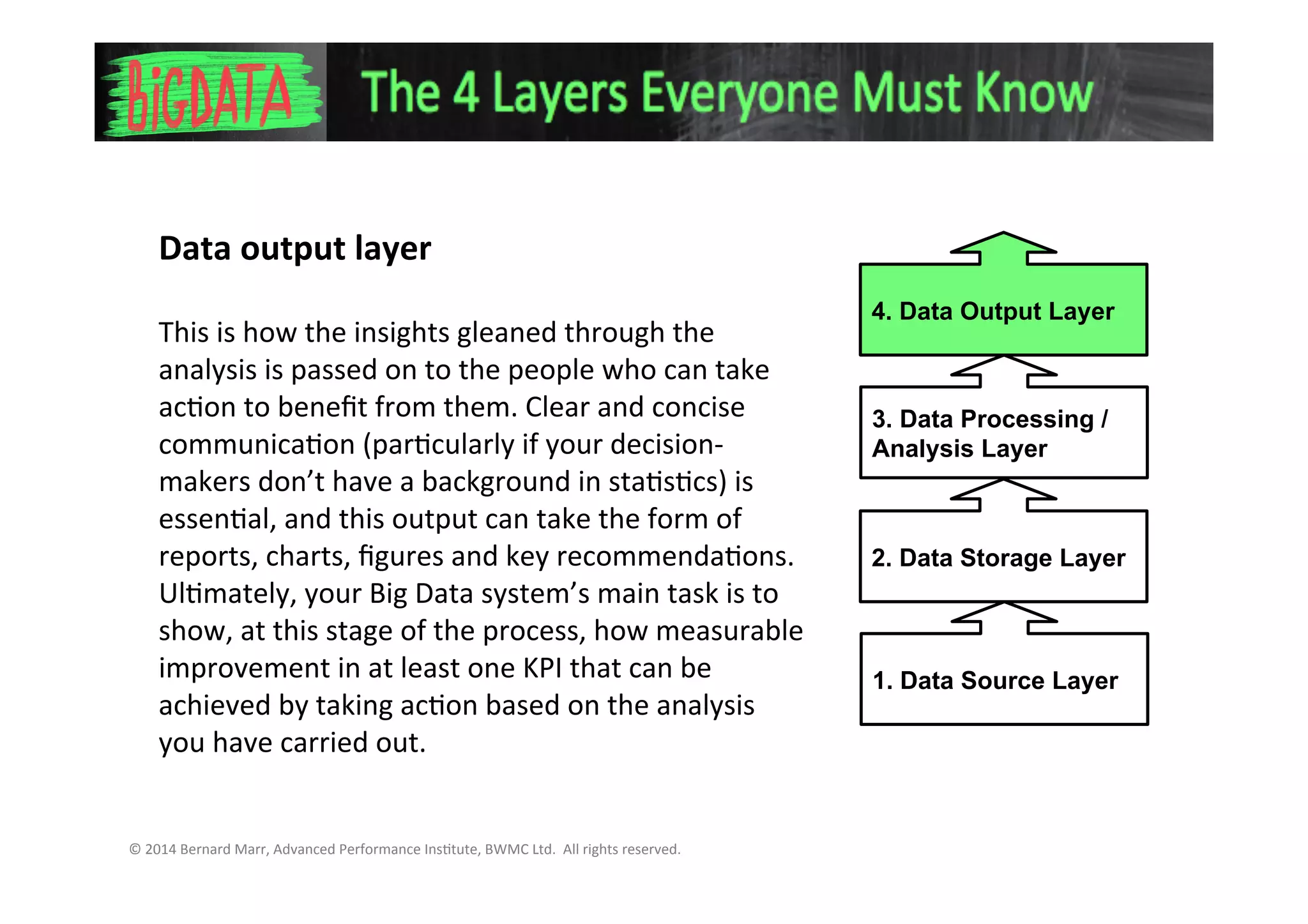
The document discusses the 4 key layers of a big data system:
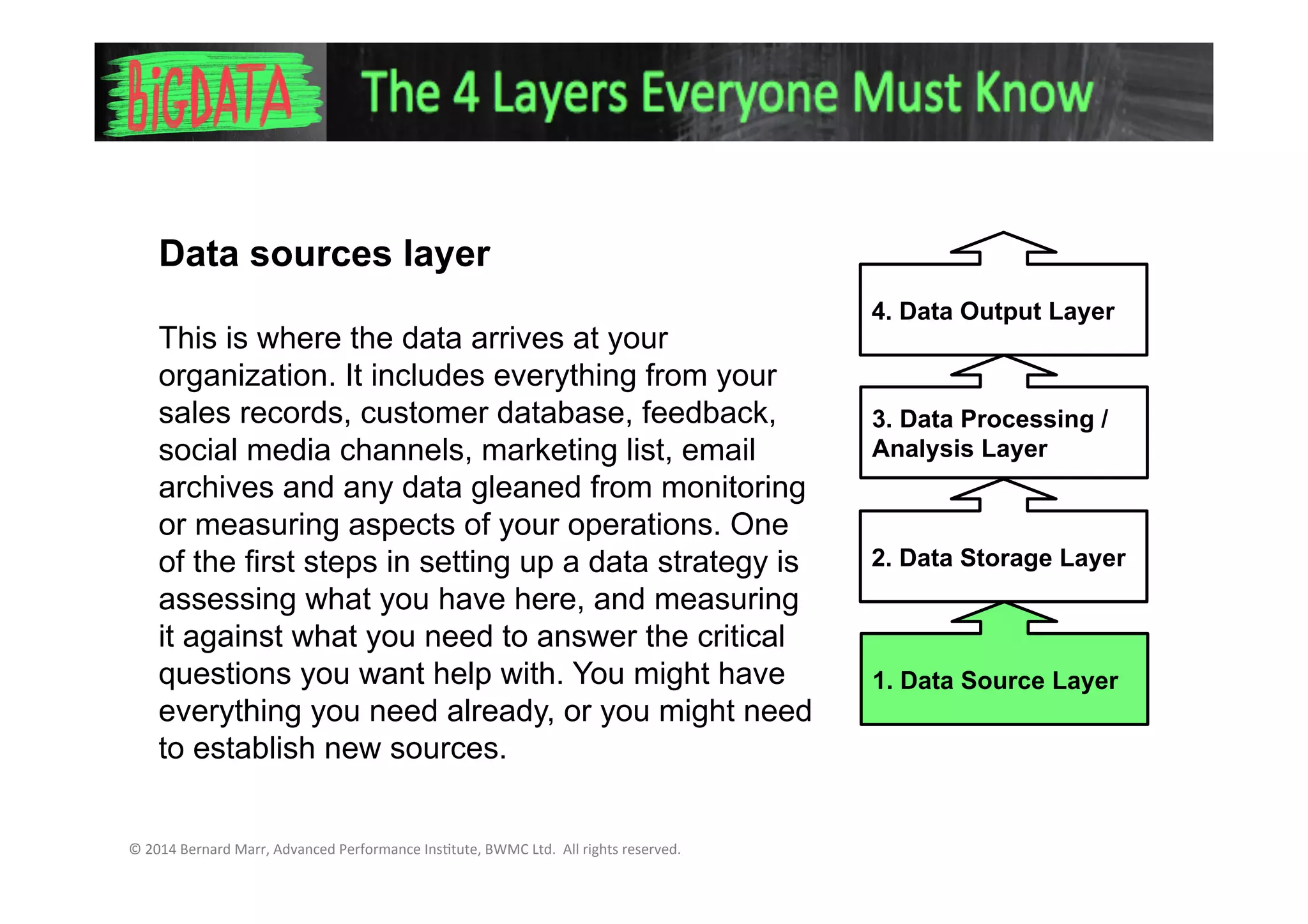
1. The data source layer where data arrives from various sources like sales records, social media, etc.
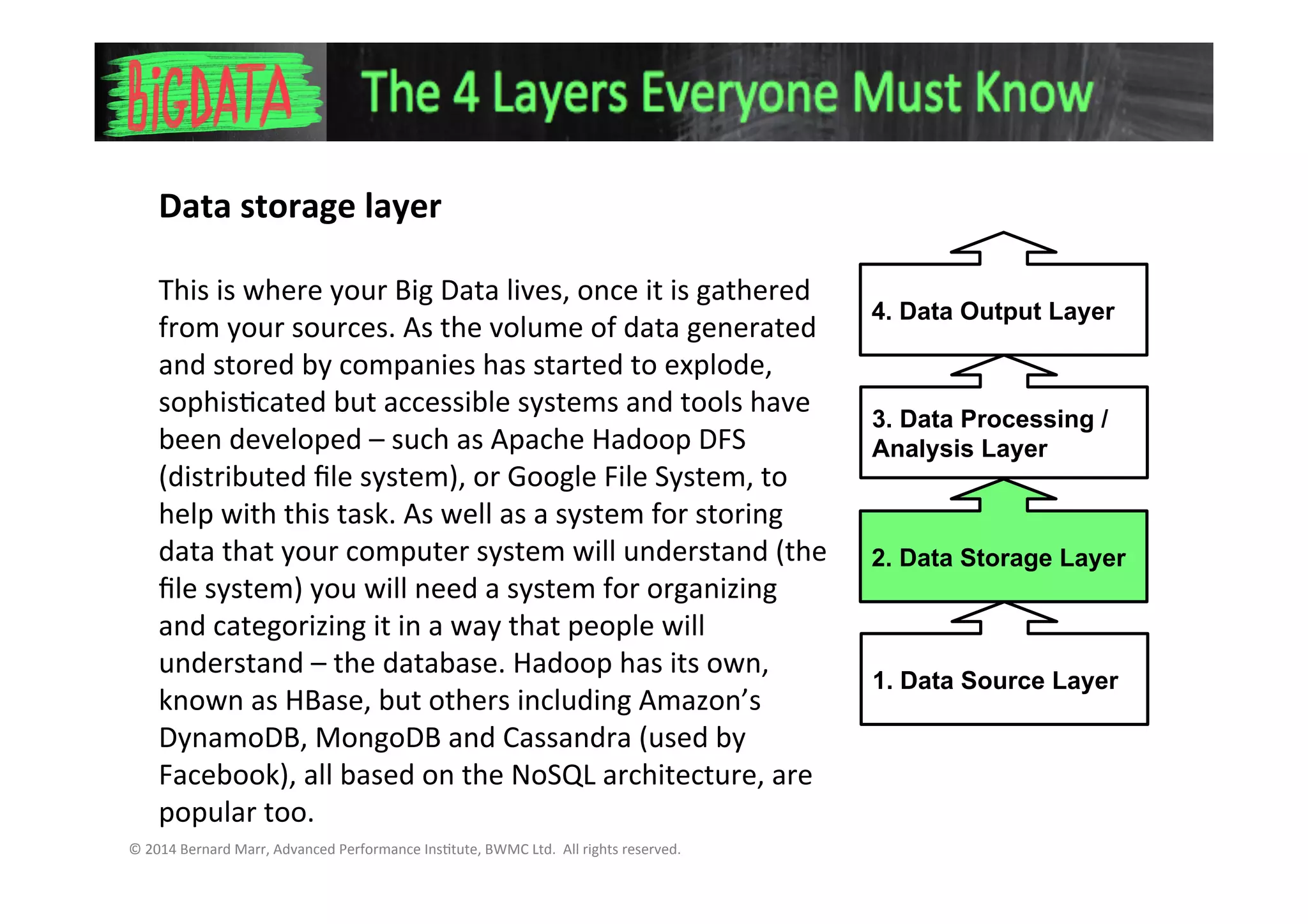
2. The data storage layer where big data is stored using systems like Hadoop or Google File System. It also requires a database system.
3. The data processing/analysis layer where tools like MapReduce are used to select, analyze, and format the data to glean insights.
4. The data output layer is how the insights are communicated to decision makers through reports, charts and recommendations to take action.