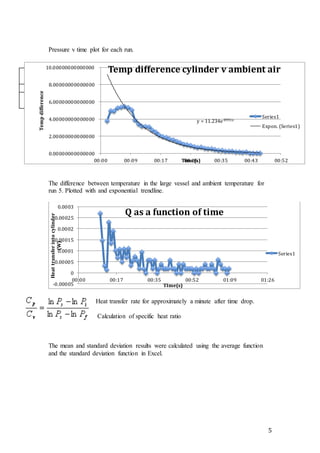
This document reports on two experiments conducted to determine thermodynamic properties of air. Experiment A involved simulating an adiabatic expansion of air in a vessel to calculate the adiabatic index. The average value obtained was 1.7, close to the expected value of 1.4. Experiment B used an isothermal expansion process to determine the ratio of volumes between two vessels, obtaining a value near the actual ratio of 2.43. Sources of error are discussed, and improvements like automated data logging are suggested to increase accuracy and consistency.