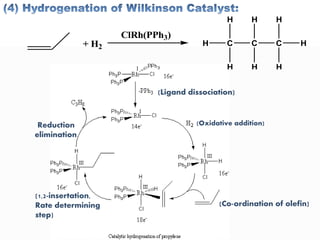
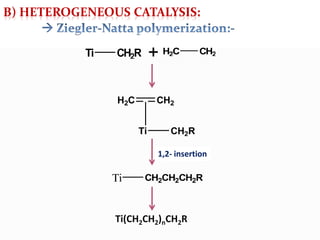
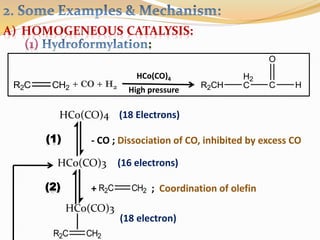
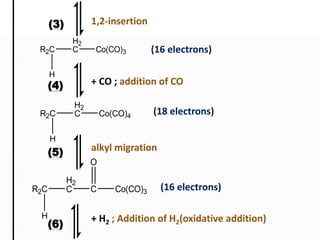
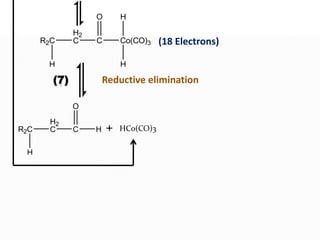
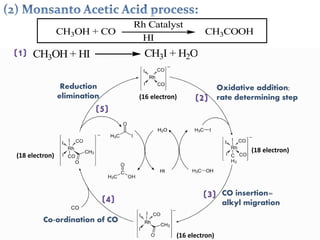
This document discusses organometallic compounds and their uses as catalysts in homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions. It provides examples of homogeneous catalysis using organometallic compounds like cobalt carbonyl and rhodium complexes. The mechanisms involve steps like oxidative addition, CO insertion, 1,2-insertion, and reductive elimination. Examples of heterogeneous catalysis on titanium surfaces are also provided. Finally, the document lists references used.



![H2C CH2
[PdCl4]2-
H2O
H3C C
O
H
Pd
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Pd
Cl
Cl
Cl
CH2
H2C
+ Cl-
H2C CH2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organometalliccatalysis-180525181928/85/Organometallic-catalysis-8-320.jpg)
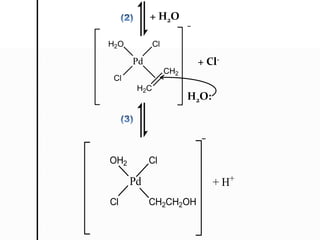
![Details: Pd
Cl OH2
Cl
HO:
H
C
H2
H
H3C C
OH
H
+ Pd[0]
+ 2Cl- + H2O
H3C C
OH
H + Pd[0] + 2Cl-
Catalyst
regenerated
by reaction
with CuCl2
H3C C
O
H + H+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organometalliccatalysis-180525181928/85/Organometallic-catalysis-10-320.jpg)