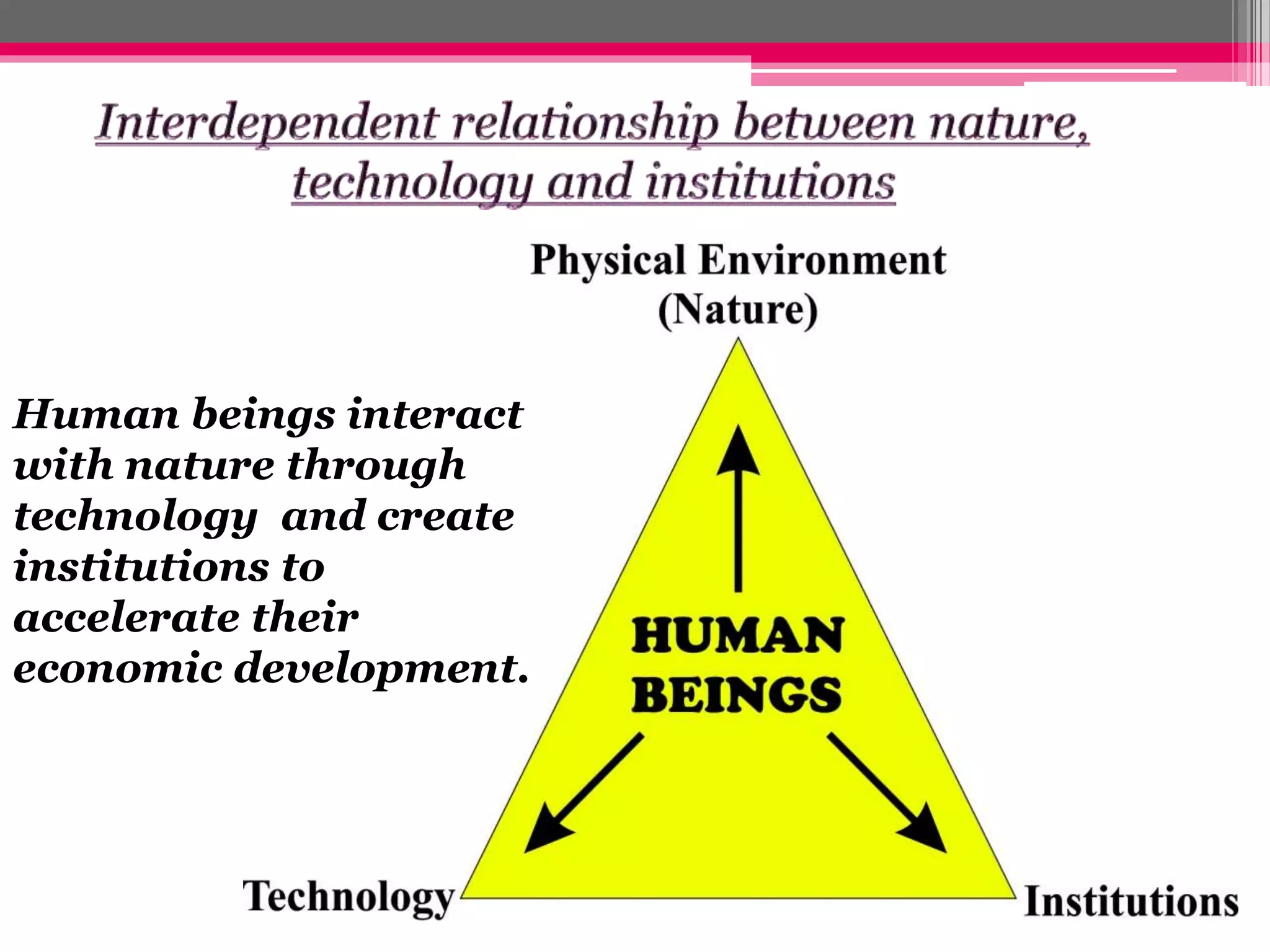
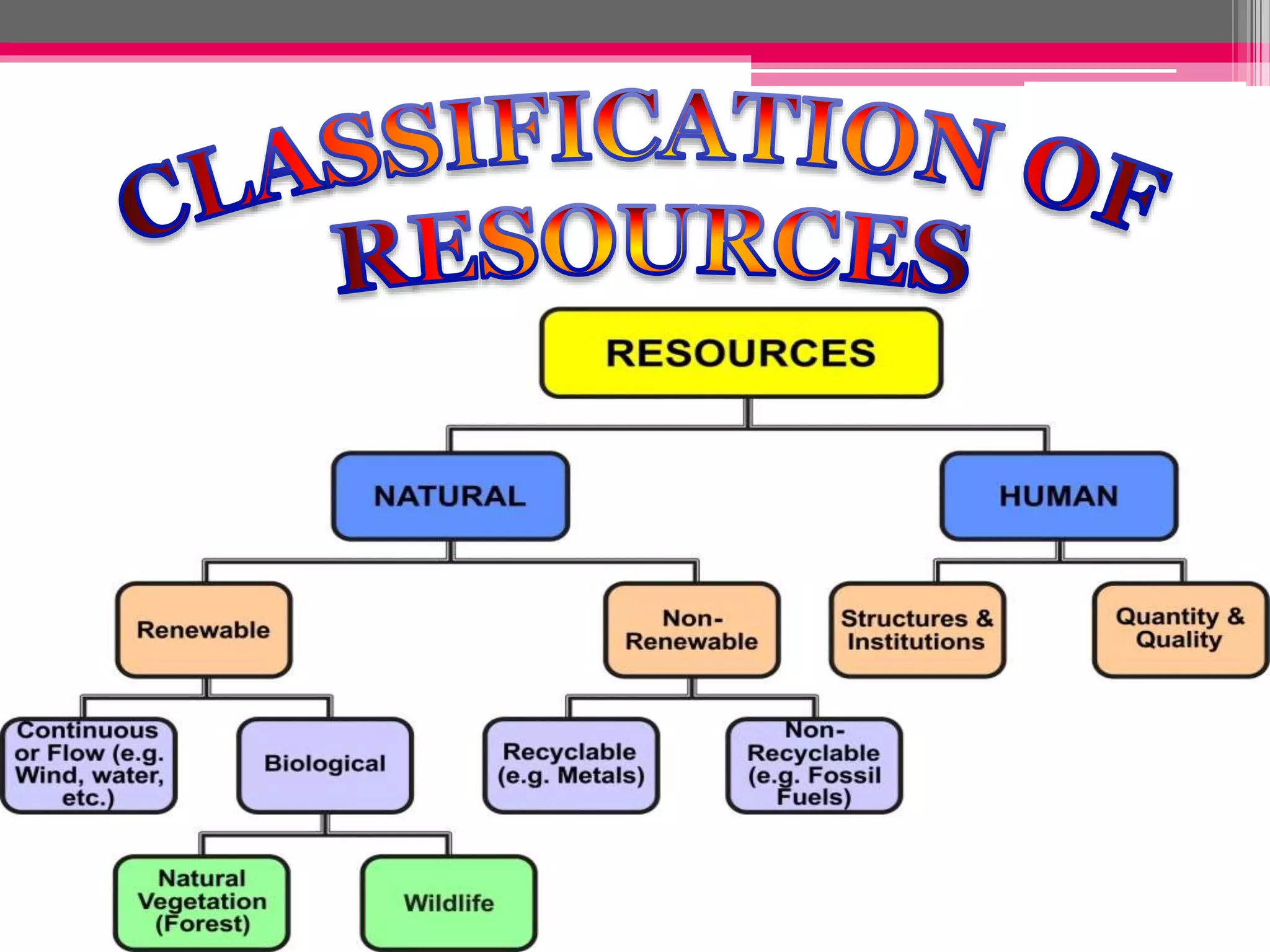
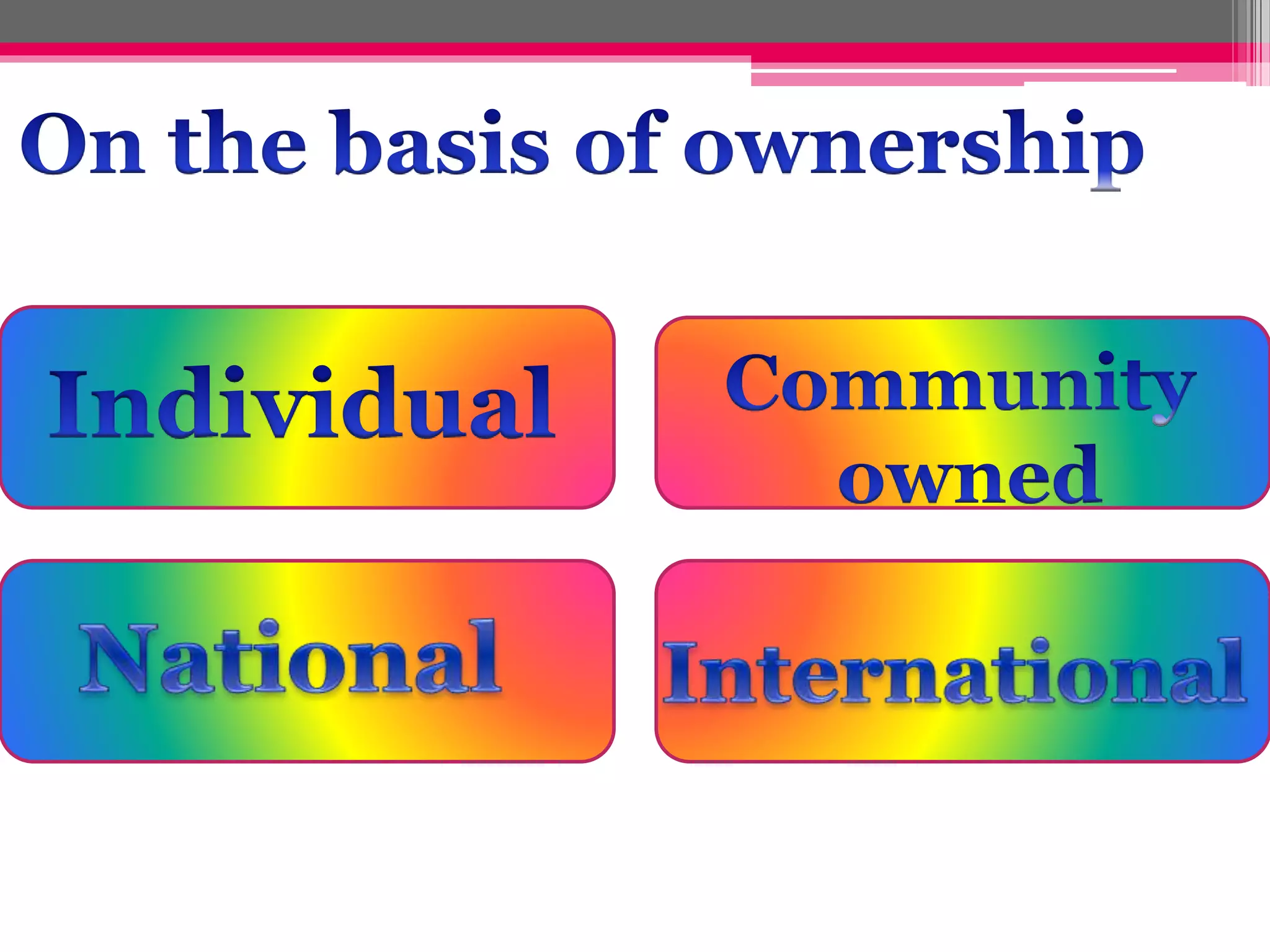
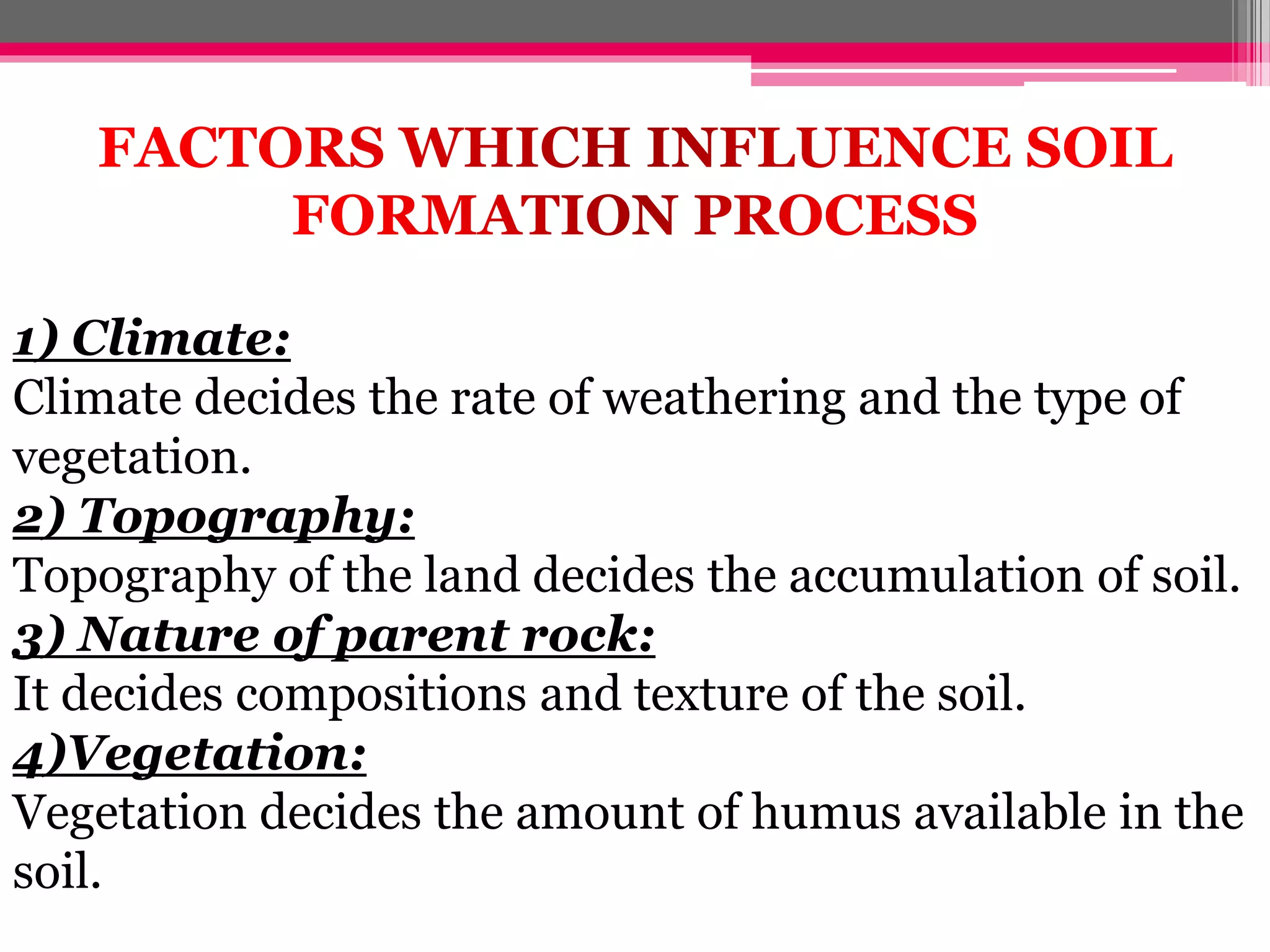
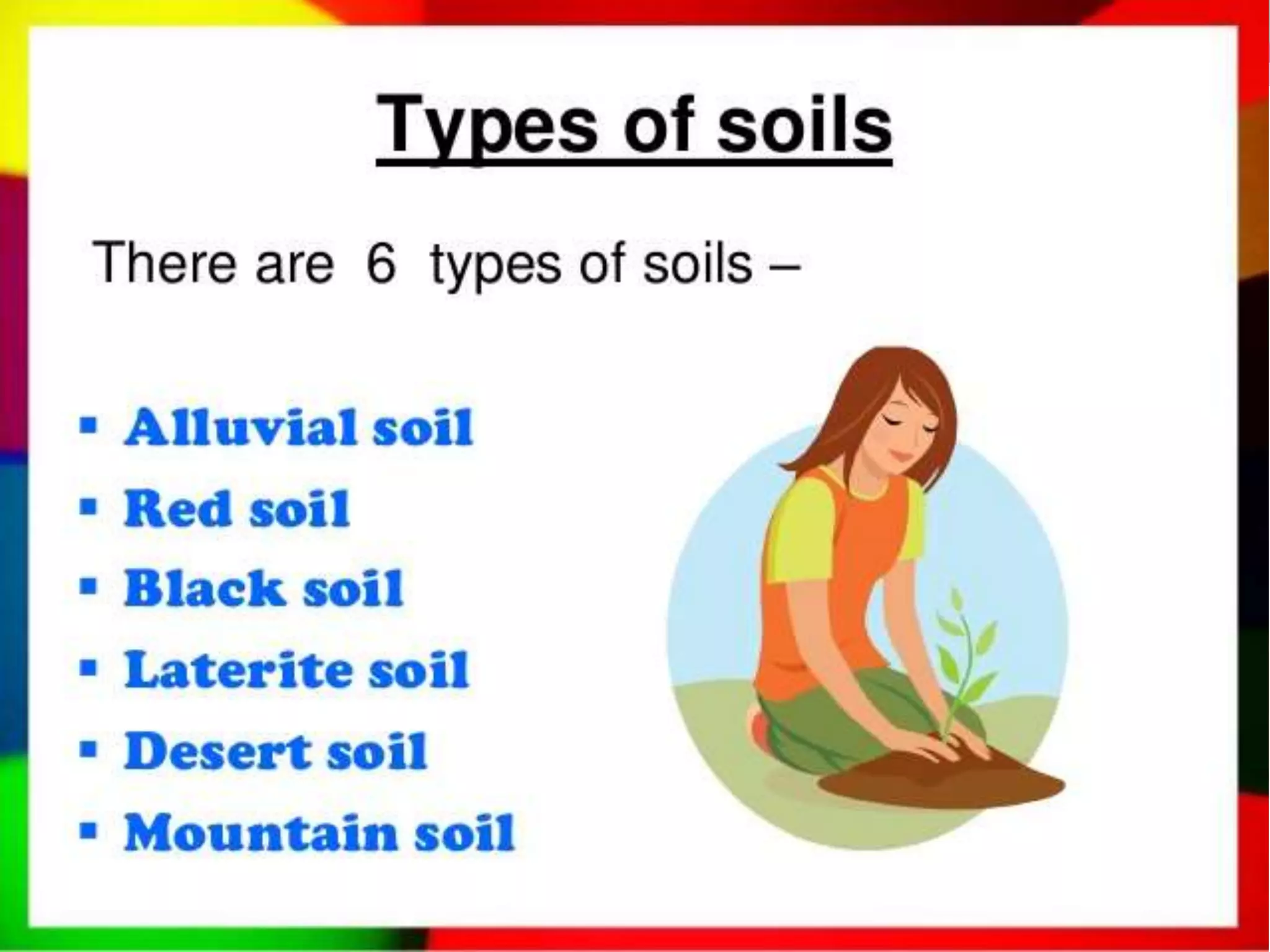
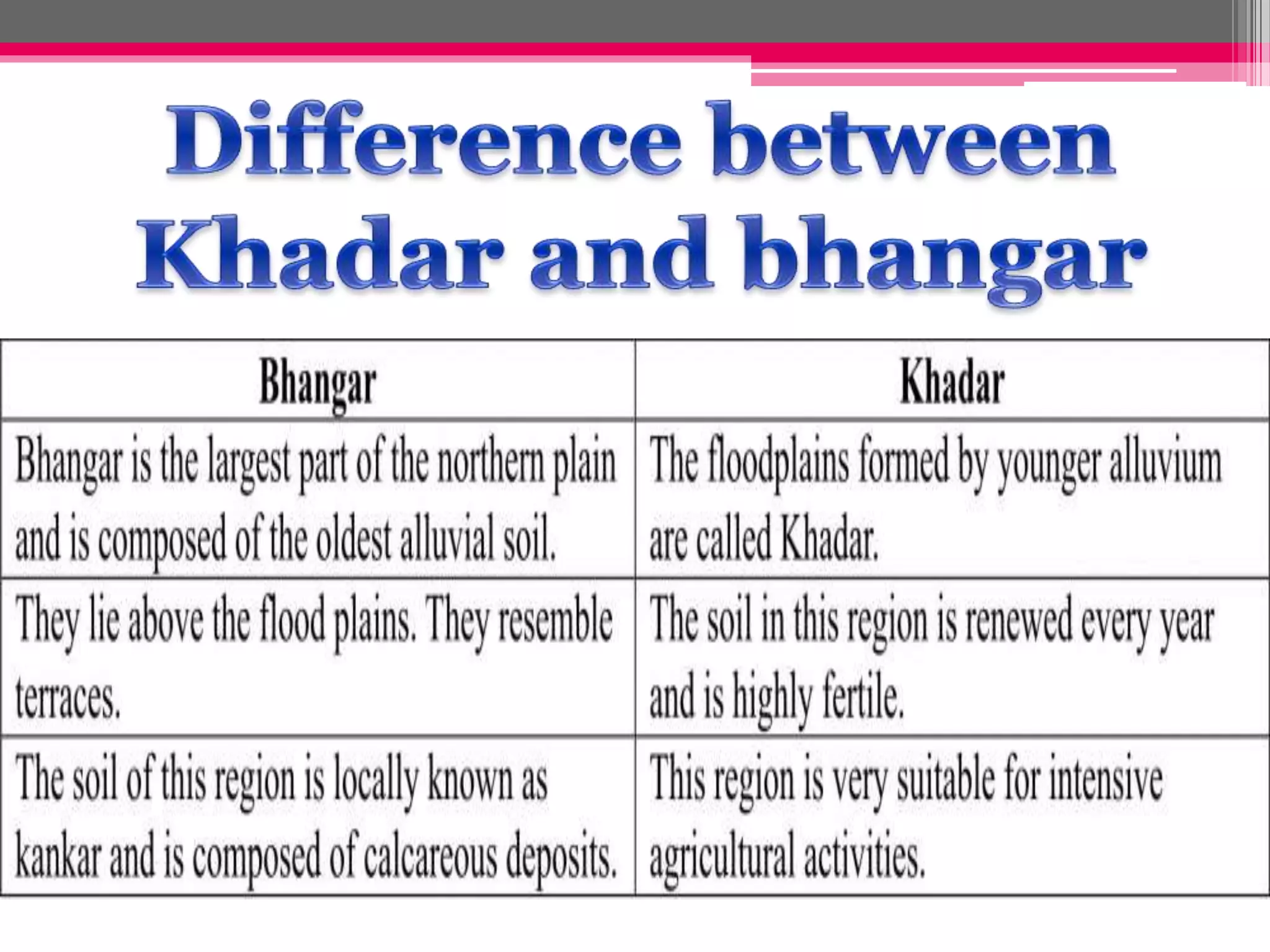
Human interaction with nature through technology has led to resource depletion and environmental issues such as global warming and pollution. Sustainable development aims to utilize resources responsibly for current and future generations, necessitating planning and conservation efforts to prevent over-exploitation. Measures such as terrace cultivation and strip cropping are recommended to combat soil erosion and promote resource conservation.