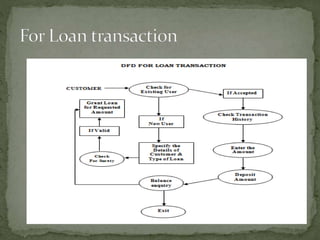
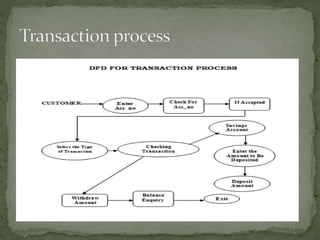
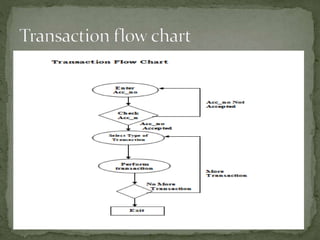
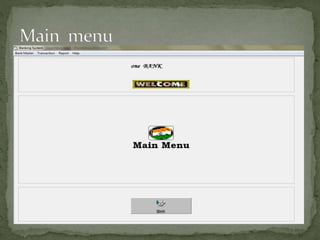
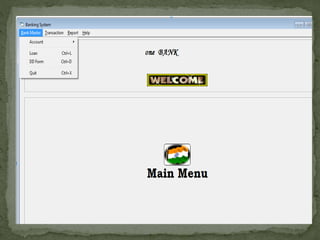
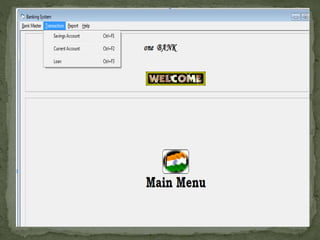
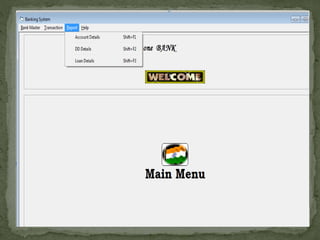
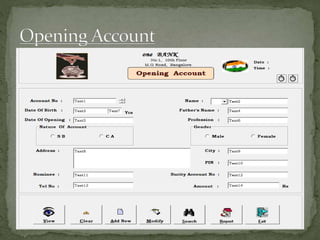
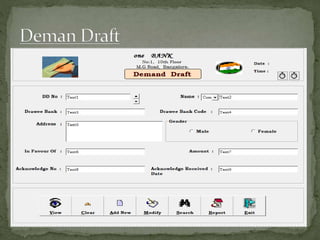
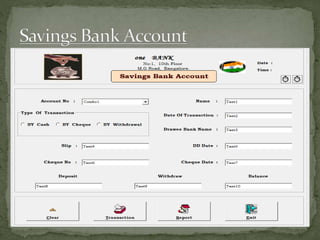
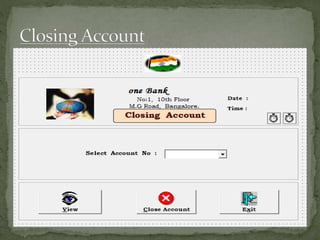
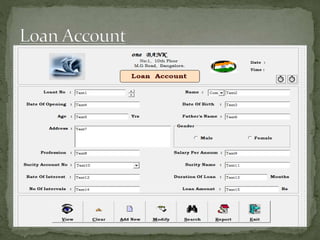
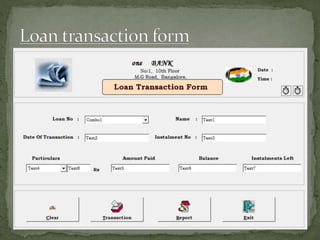
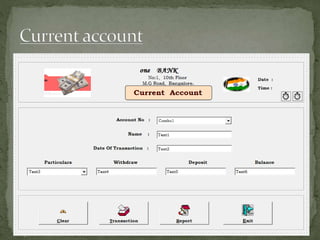
The document discusses various topics related to banking. It defines banks and their role in facilitating financial transactions. It describes the basic business model of banks, which involves taking deposits and providing loans. It also outlines the key functions of banks such as payment processing, offering different account types, generating revenue, managing risks, and more. The document also discusses computerized banking systems and how they can improve efficiency.