Embed presentation
Downloaded 84 times


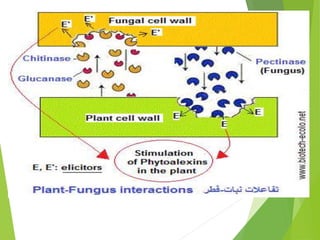


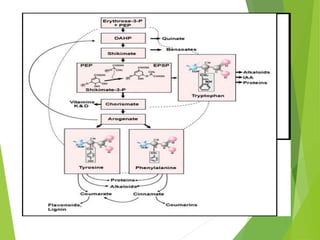
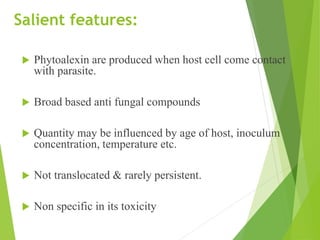







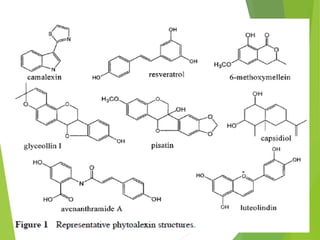



The document discusses phytoalexins, which are low molecular weight antimicrobial compounds derived from plants that serve as part of the defense system against pathogens. Various types of phytoalexins, such as ipomoeamarone and gossypol, are produced in response to pathogen exposure and their quantity is influenced by several factors including host age and temperature. Phytoalexins are characterized by their broad-spectrum antifungal properties and typically do not persist in host tissues.

















