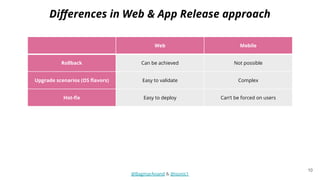
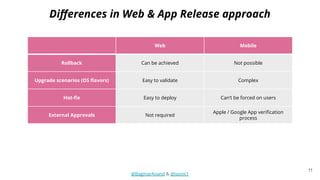
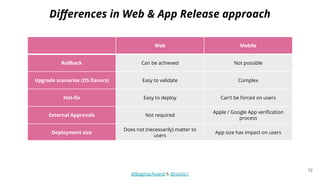
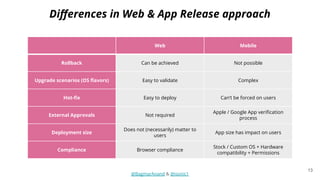
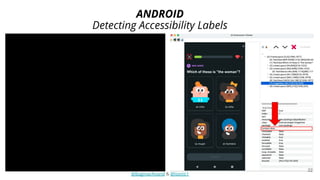
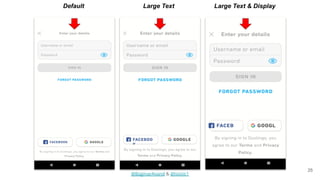
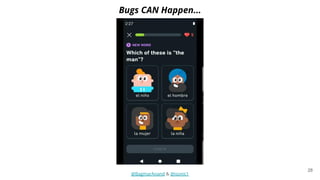
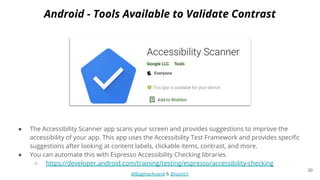
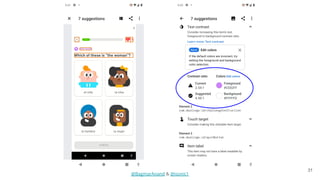
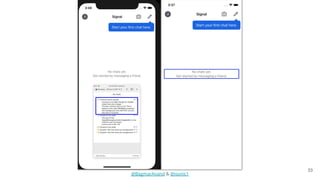
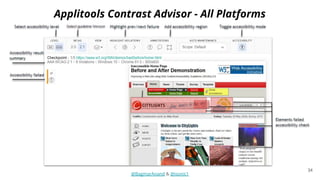
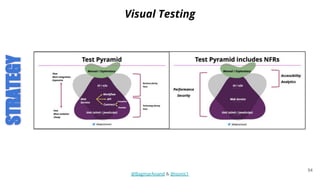
The document discusses different strategies for testing mobile apps, including testing functionality, usability, performance, and more extensively than just functionality. It addresses testing on real devices versus emulators, the need for accessibility testing, and tools for testing areas like contrast, text-to-speech, location services and network bandwidth. The document also discusses visual testing strategies like using AI to detect visual differences and validating user interfaces.