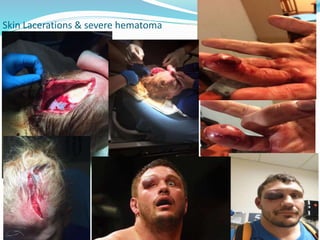
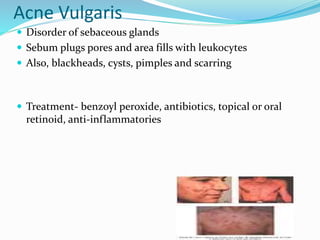
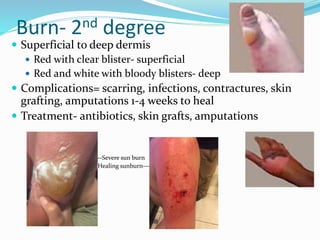
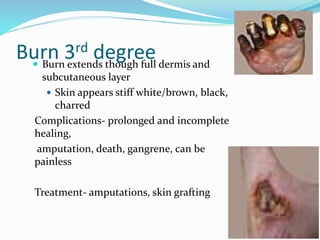
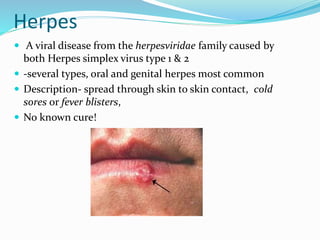
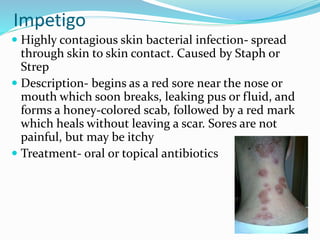
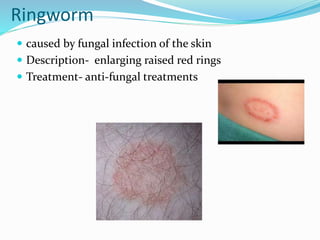
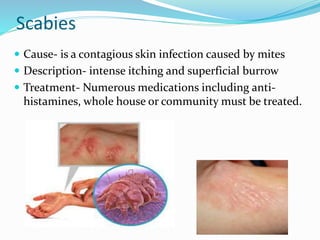
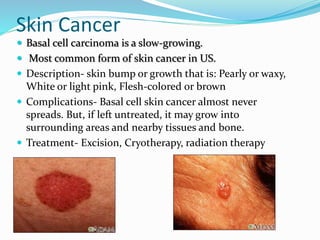
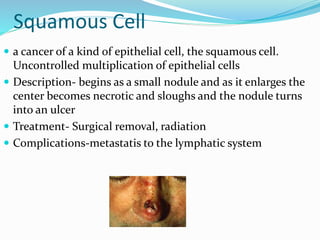
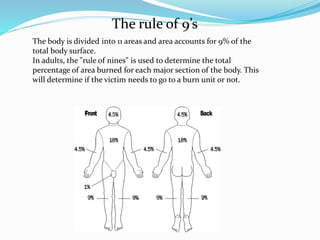
This document provides information on various skin conditions and disorders. It describes conditions like acne, athlete's foot, burns of varying degrees, dermatitis, eczema, herpes, impetigo, psoriasis, ringworm, scabies, and several types of skin cancer. It also defines different types of skin lesions like macules, vesicles, pustules, and papules. Treatments are mentioned for many of the conditions.