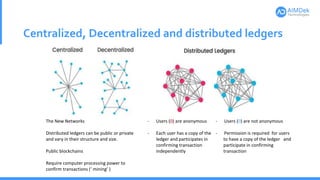
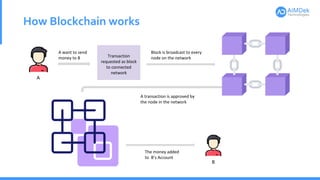
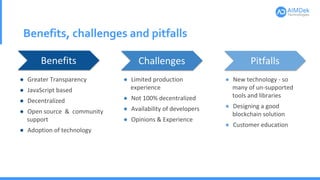
This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology. It defines key blockchain concepts like blocks, blockchains, consensus algorithms, and mining. It explains how blockchain works through transactions being grouped into blocks and added to the distributed ledger across nodes in the network. Examples of real-world blockchain applications are given for voting systems, supply chain management, and healthcare data sharing. Benefits of blockchain include transparency, decentralization, and open source development, while challenges include limited production experience and need for customer education.