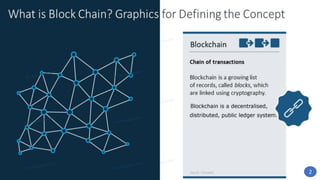
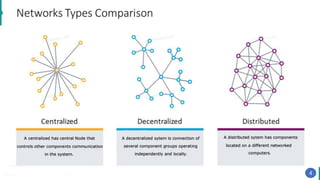
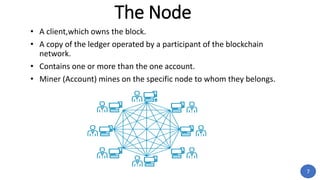
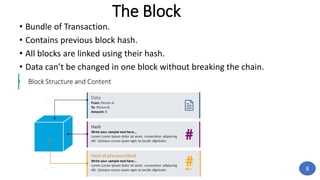
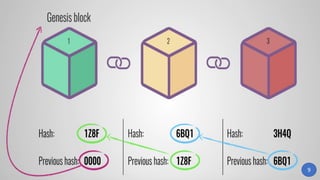
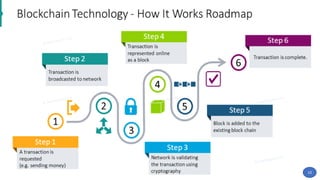
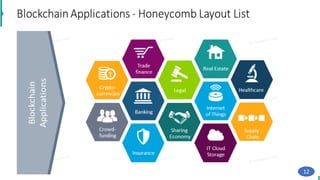
Blockchain technology was first conceptualized in 1991 but did not have a real-world application until Bitcoin was launched in 2009. A blockchain is a distributed ledger of transactions stored in blocks that are linked together via cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Nodes on the network run by participants hold copies of the blockchain and work to validate transactions and add them to new blocks through a process called mining. This process secures the network and allows participants to reach a consensus without the need for a centralized authority. Today, blockchain technology has applications across many industries that require trustless transactions.