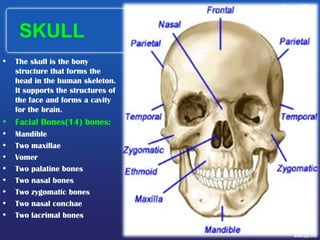
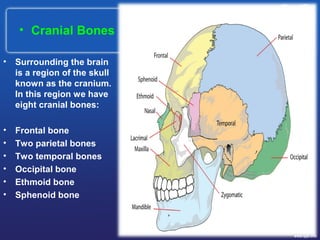
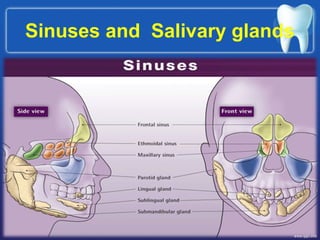
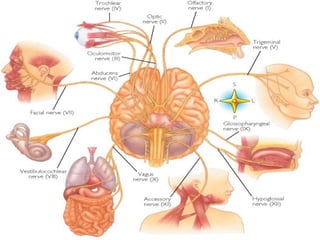
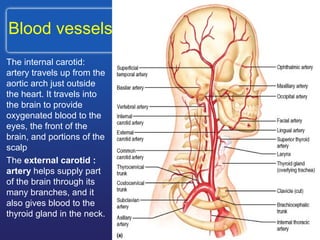
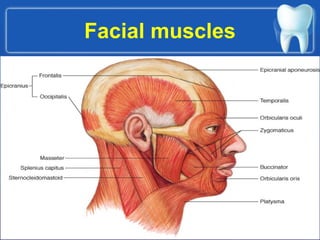
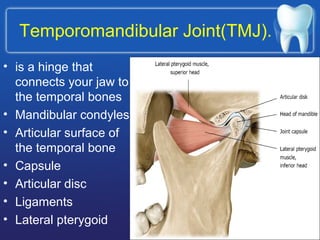
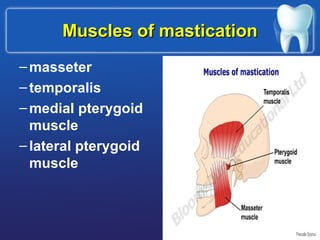
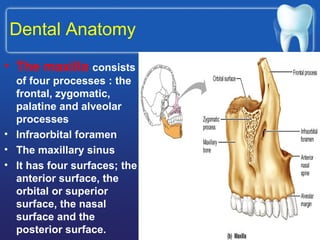
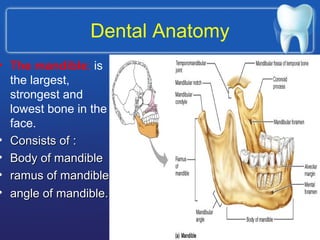
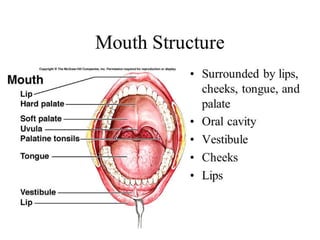
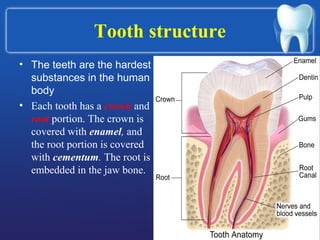
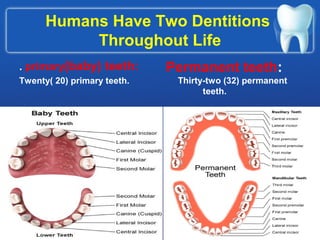
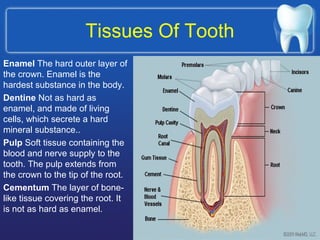
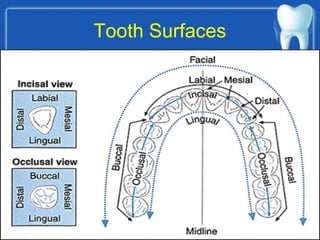
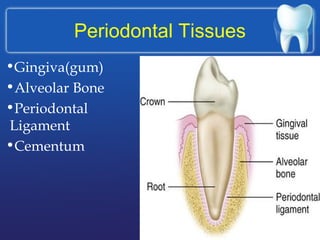
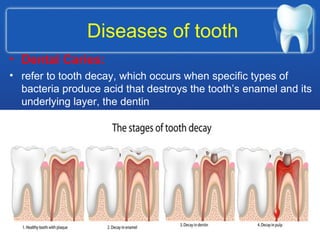
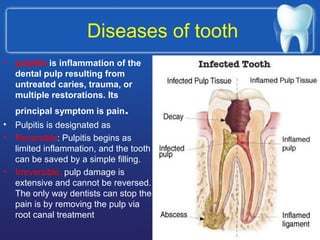
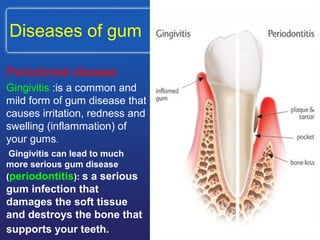
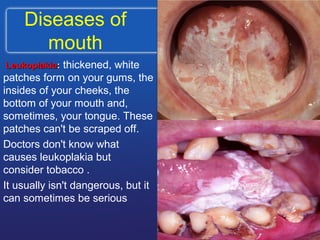
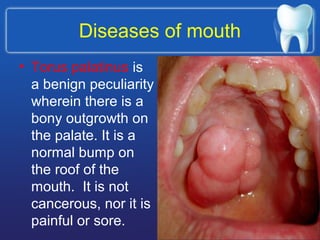
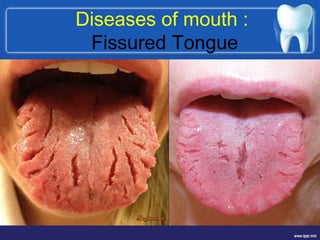
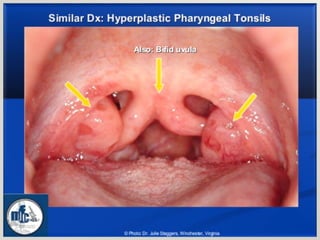
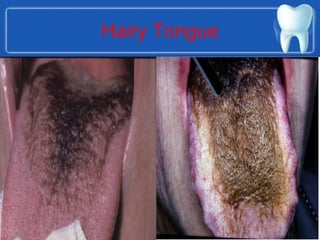
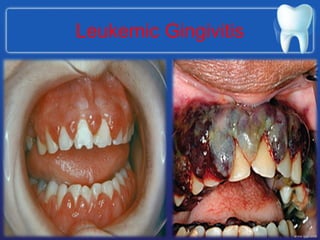
This document summarizes the anatomy and diseases of the human head and teeth. It describes the bones that make up the skull, including the cranial and facial bones. It discusses the blood vessels, muscles, nerves and joints of the head. It provides details on dental anatomy, the structure and tissues of teeth, and common dental diseases like caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periodontitis. It also outlines some oral diseases such as leukoplakia, torus palatinus, fissured tongue and hairy tongue.