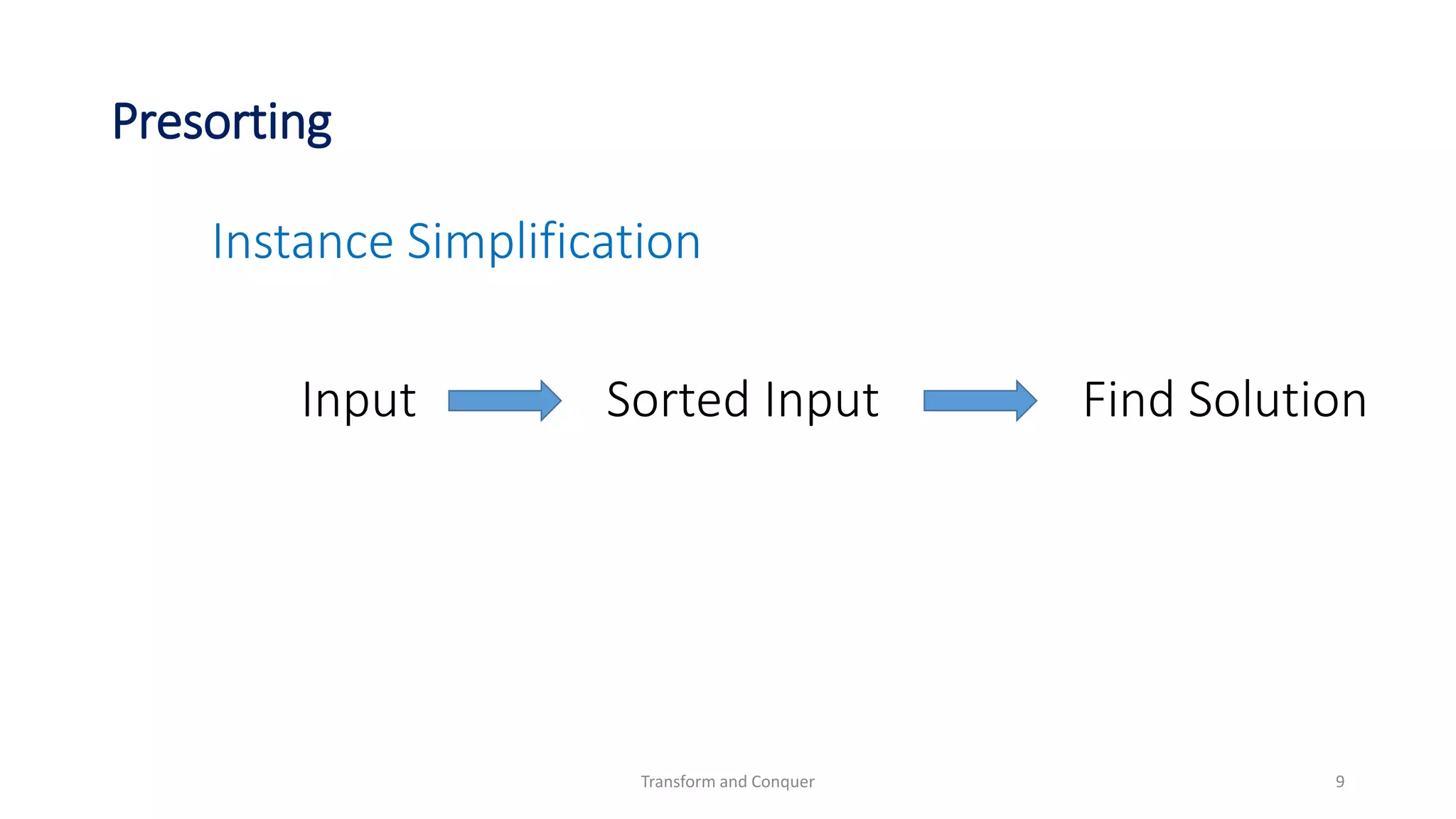
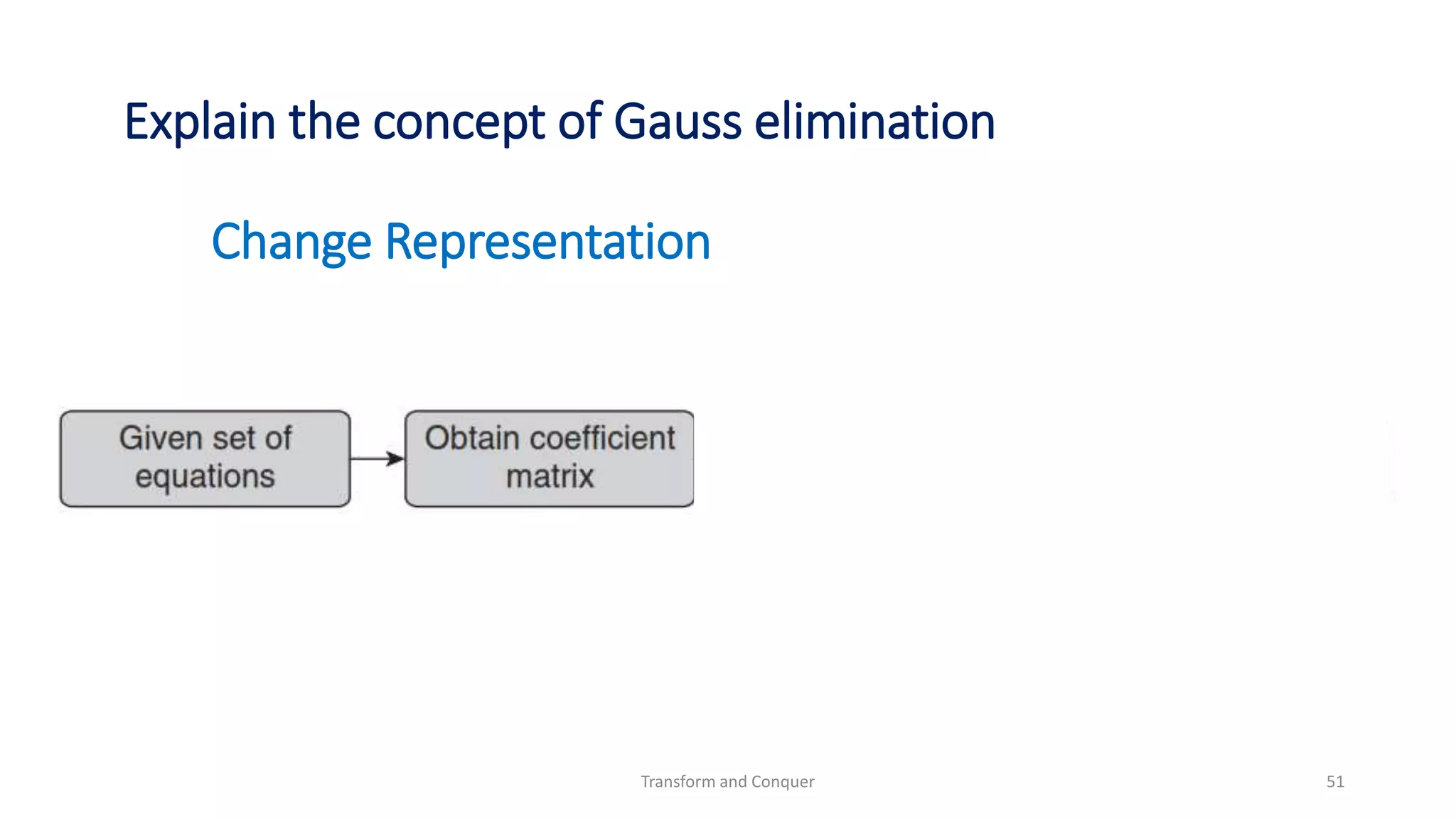
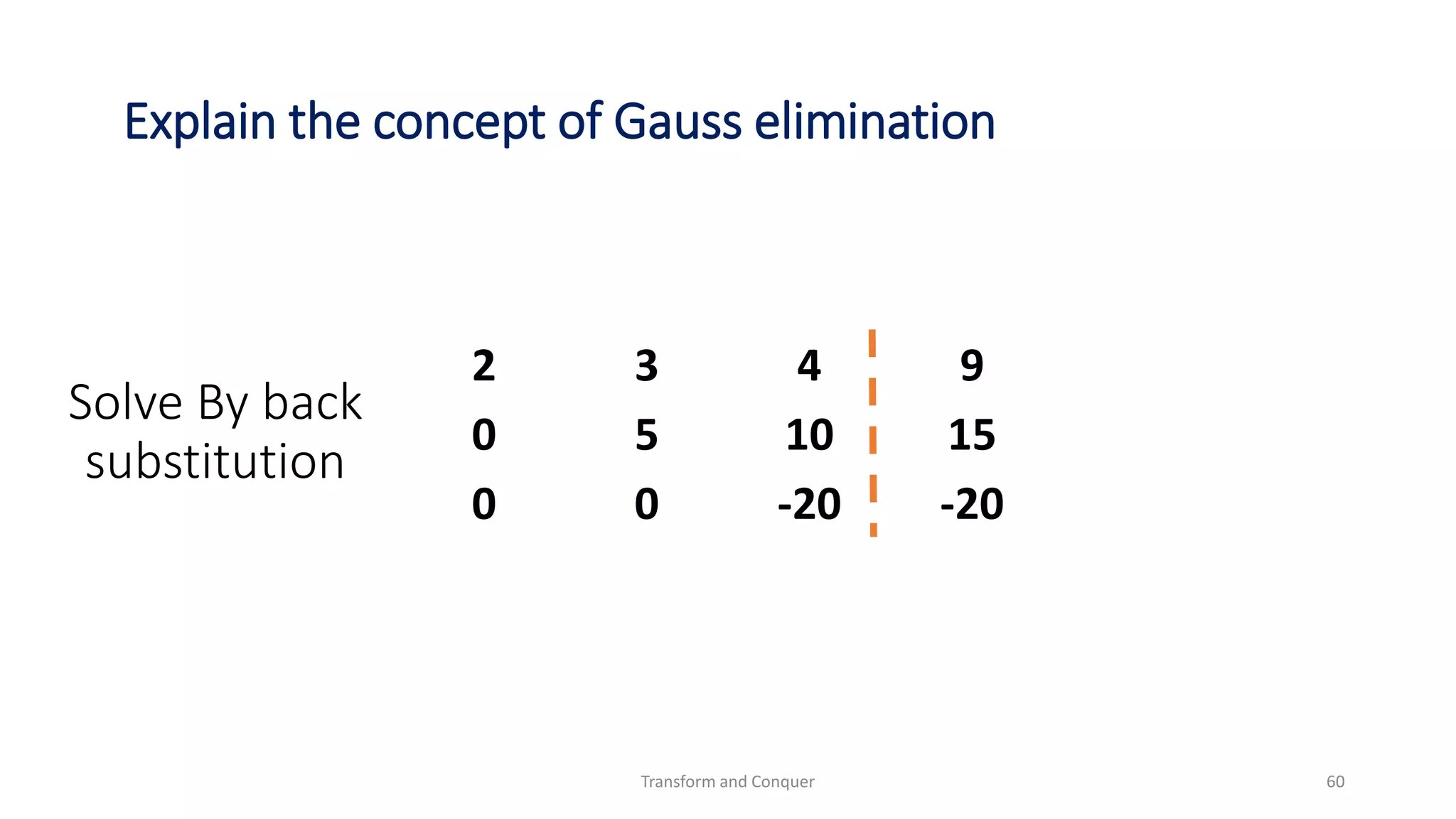
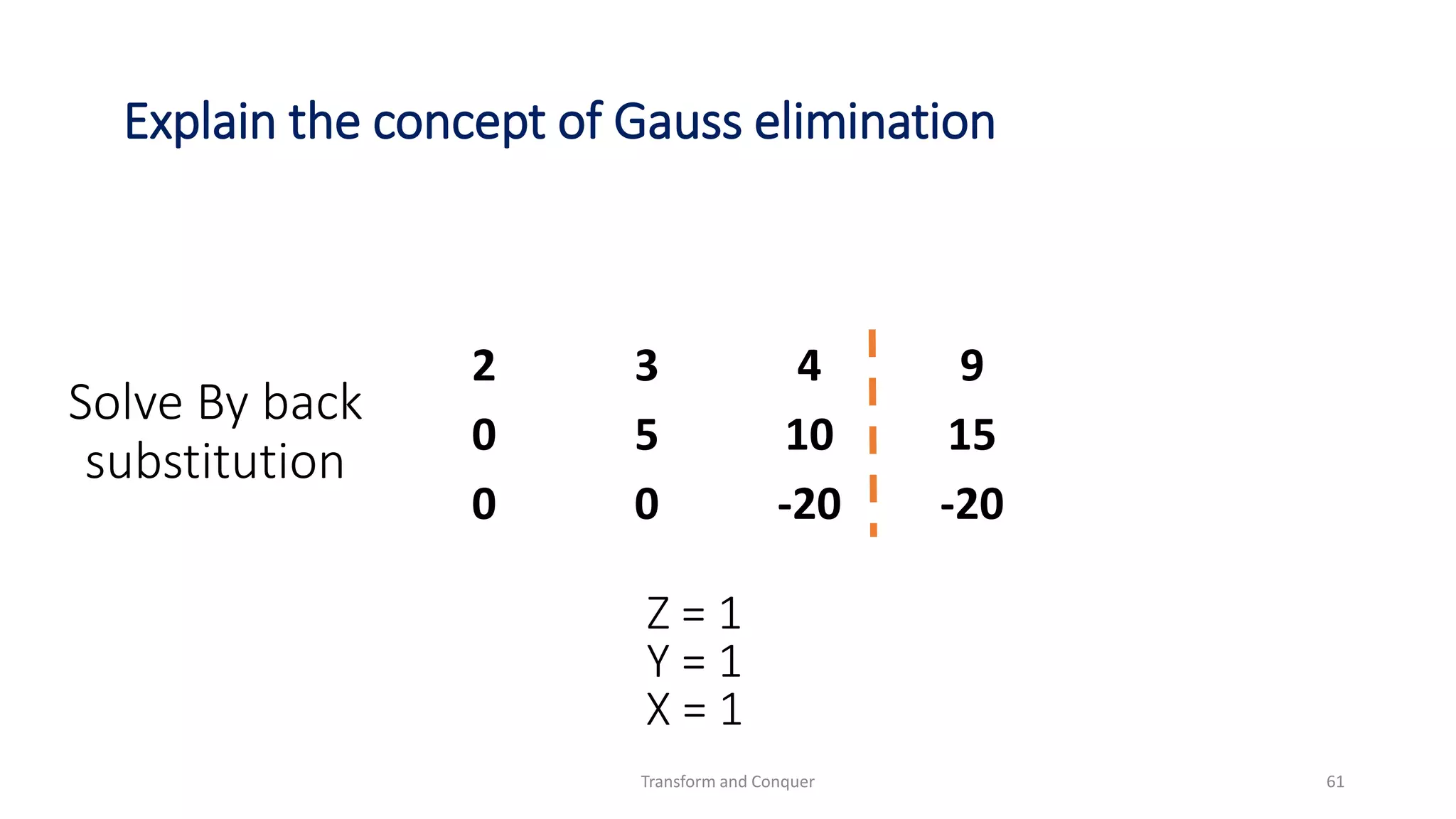
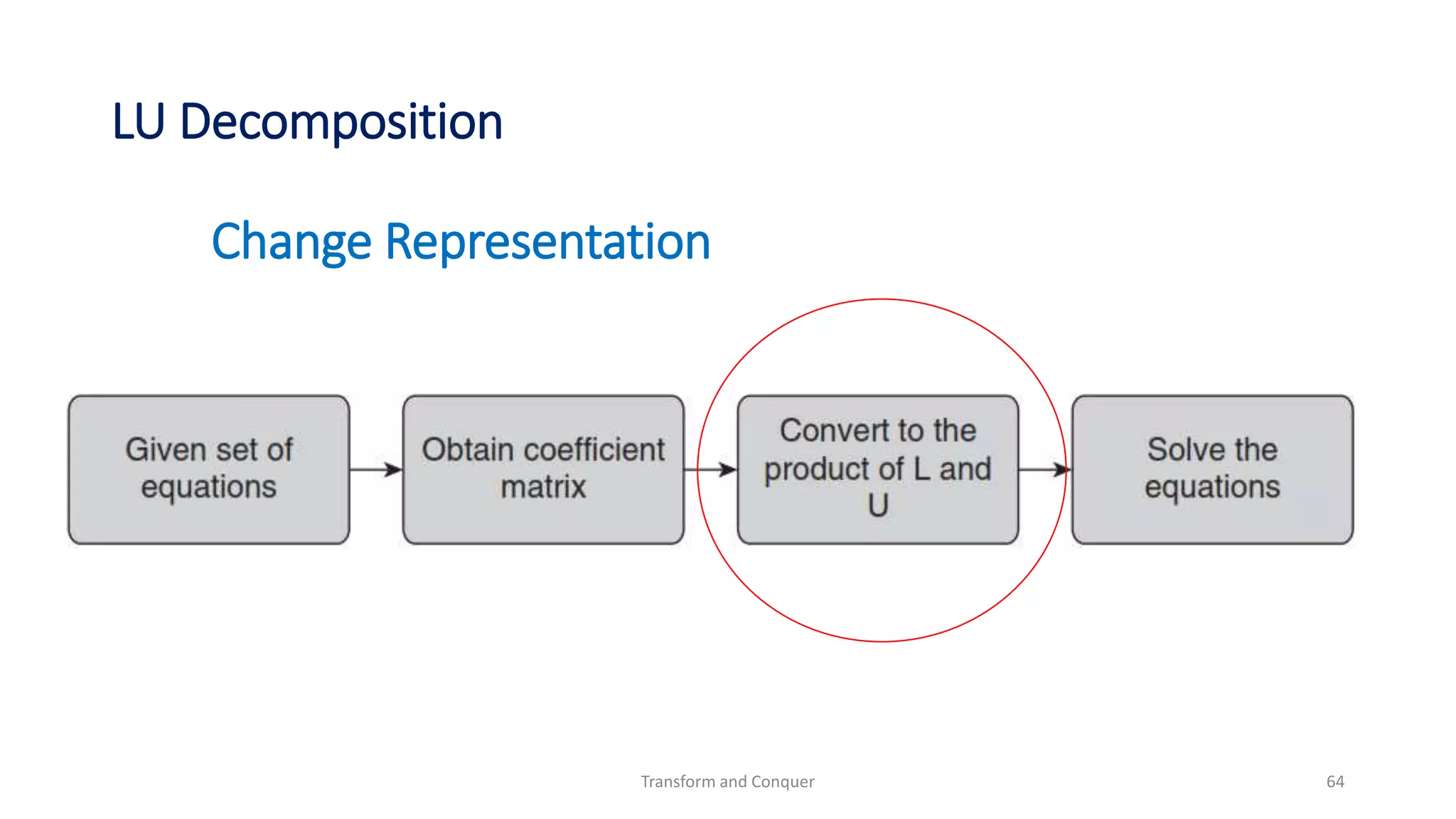
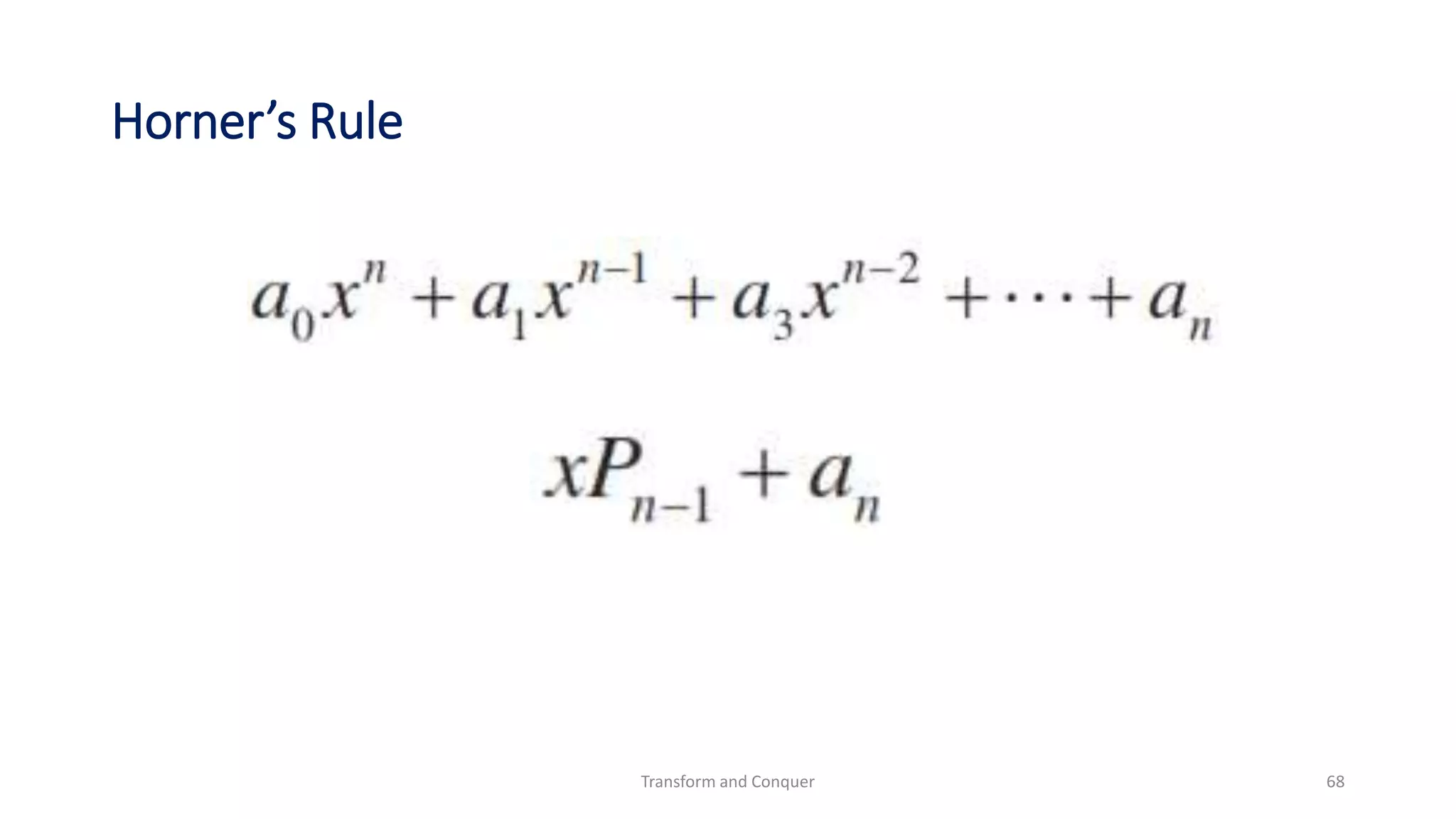
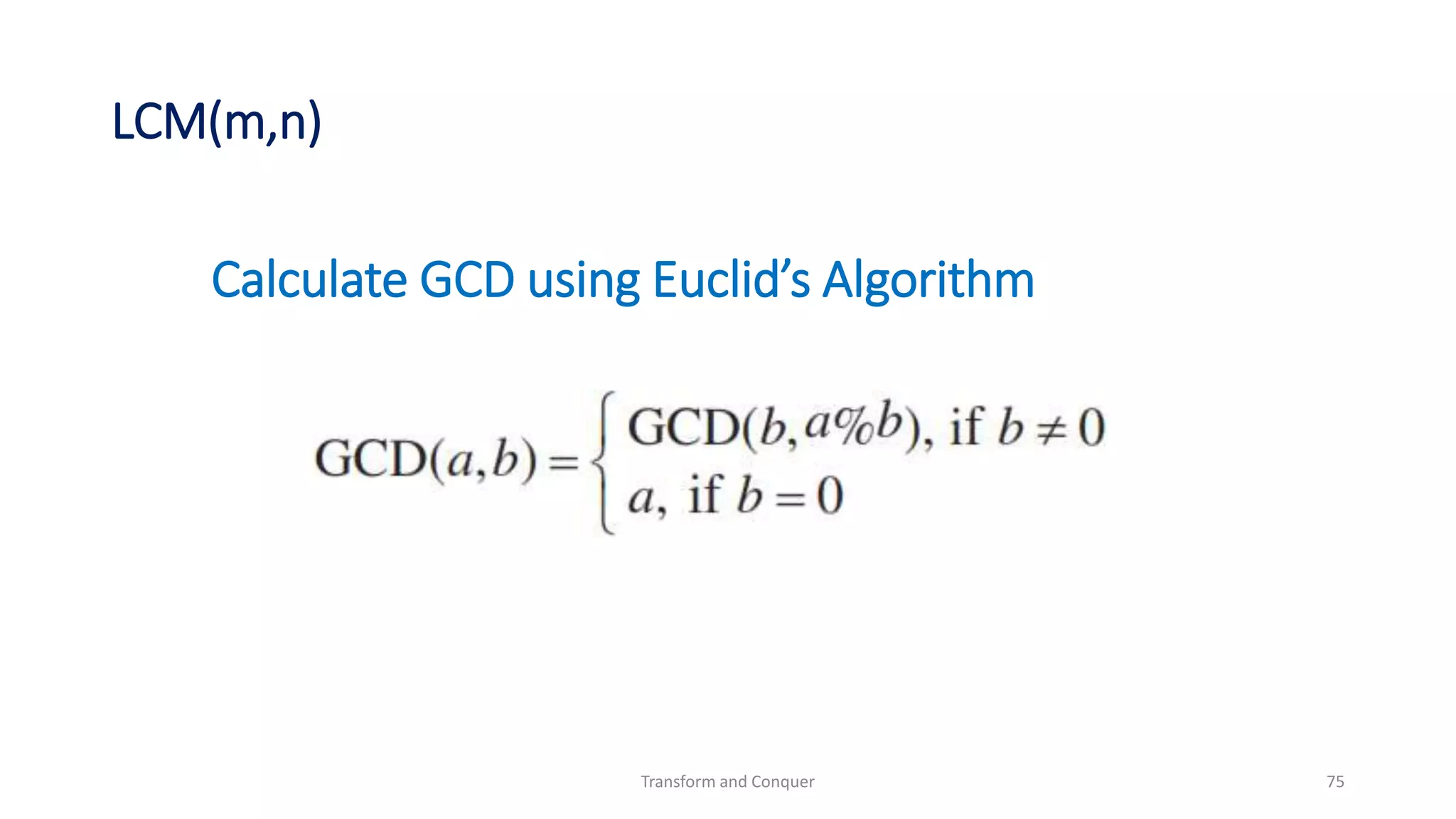
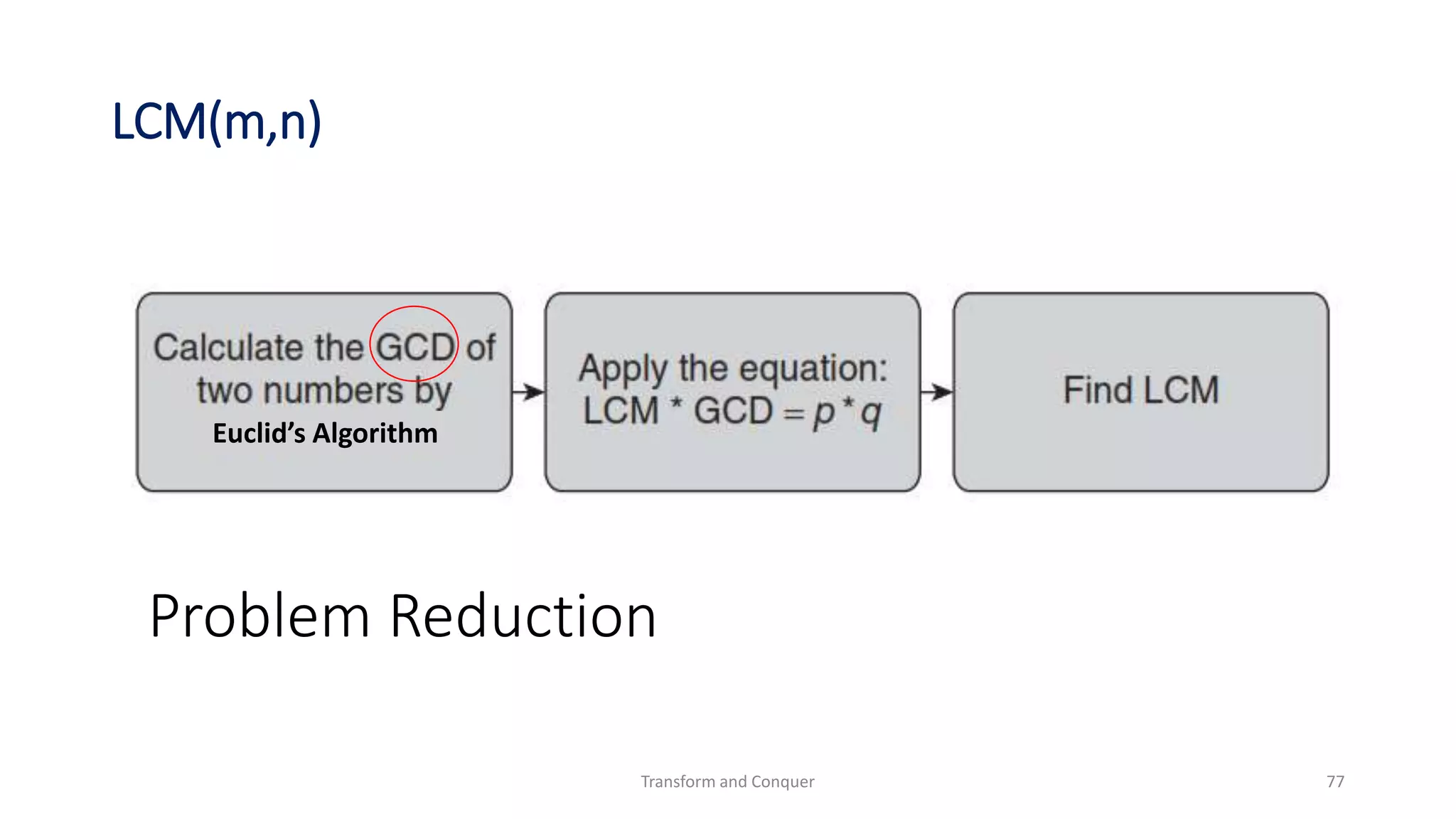
The document discusses the concept of 'transform and conquer' in algorithm design, detailing applications such as presorting, Gaussian elimination, Horner's rule for polynomial evaluation, and finding the least common multiple. It outlines methods for simplifying instances, changing representations, and problem reduction while analyzing the computational complexity of various algorithms. Numerous algorithms and examples are presented to illustrate these concepts and their applications.


























![Presorting
33
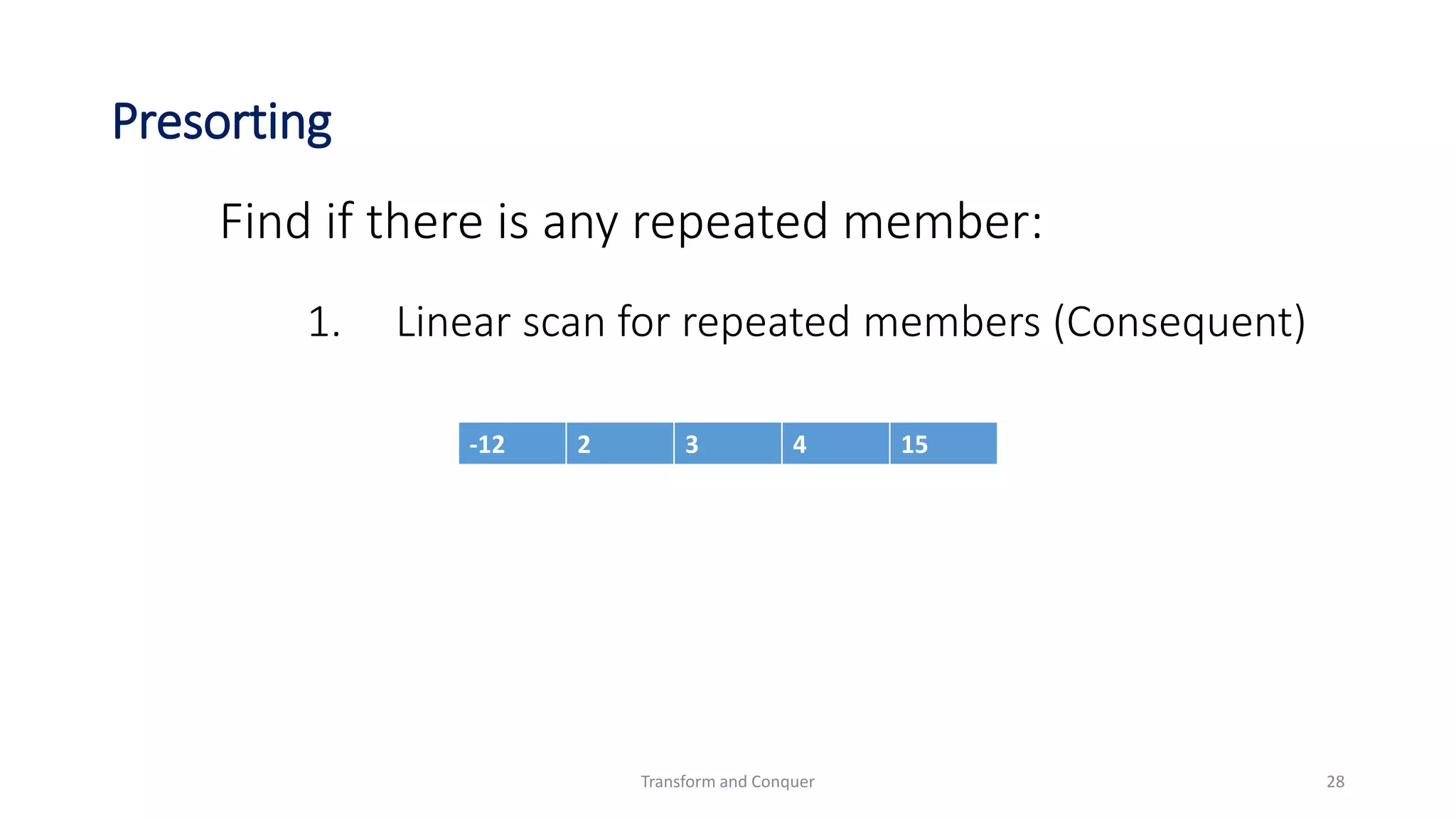
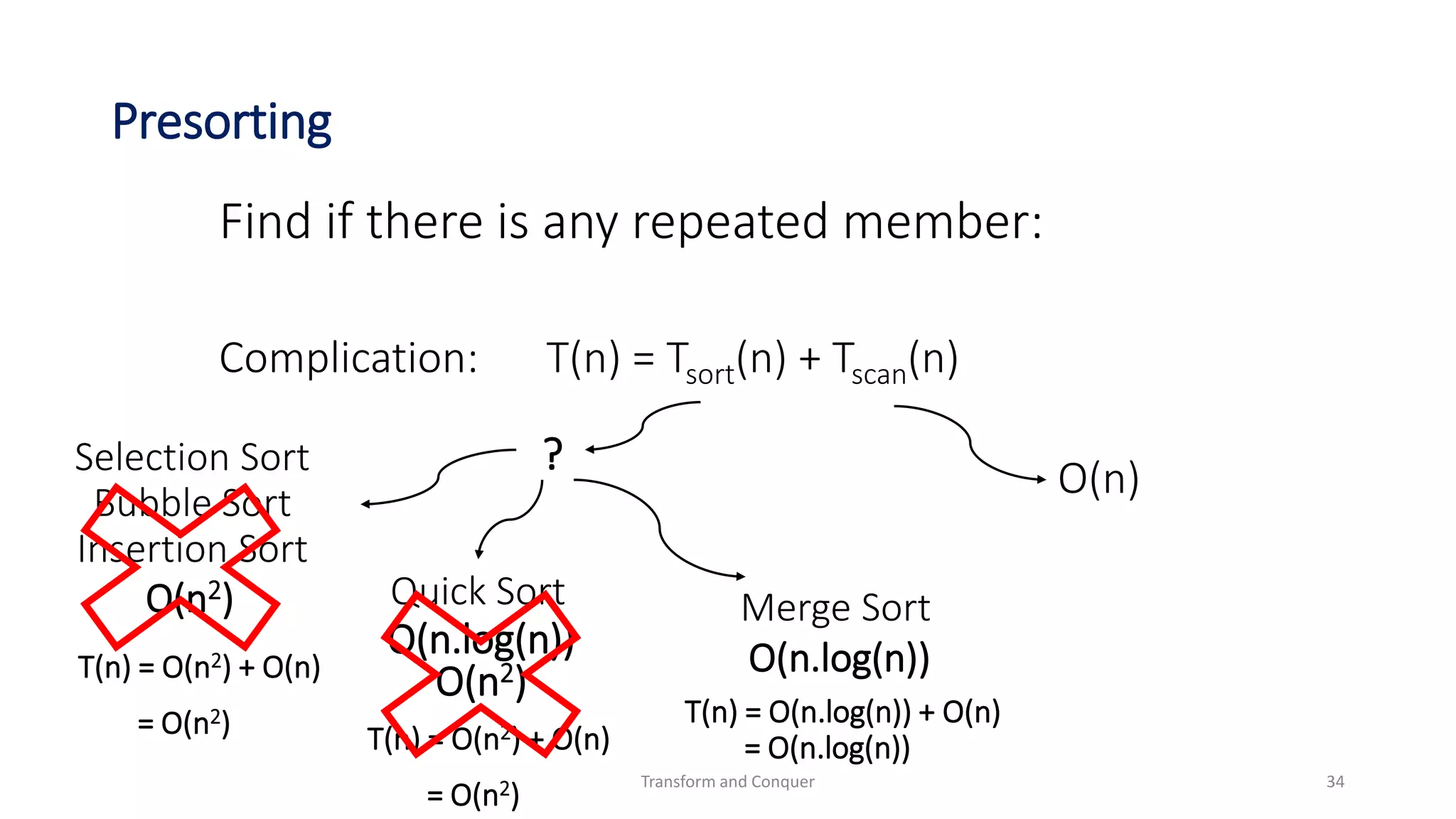
Find if there is any repeated member:
Algorithm:
1. Sort the list
2. For i = 0 to n – 2:
2.1 if a[i] = a[i + 1] then return false
3. return true
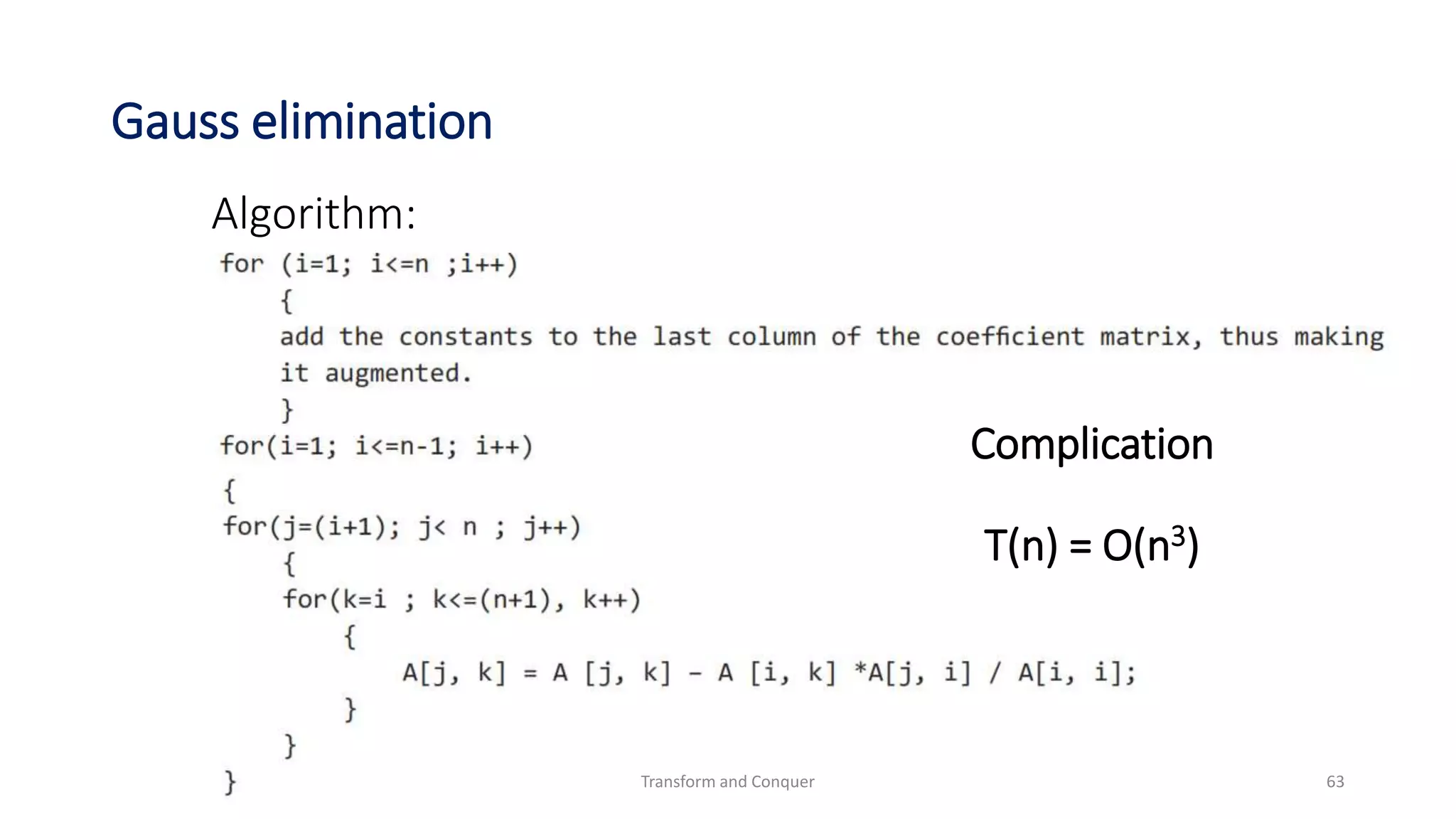
Complication:
T(n) = Tsort(n) + Tscan(n)
Transform and Conquer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transformandconquer-200106171827/75/Advanced-Algorithms-Transform-and-conquer-33-2048.jpg)






























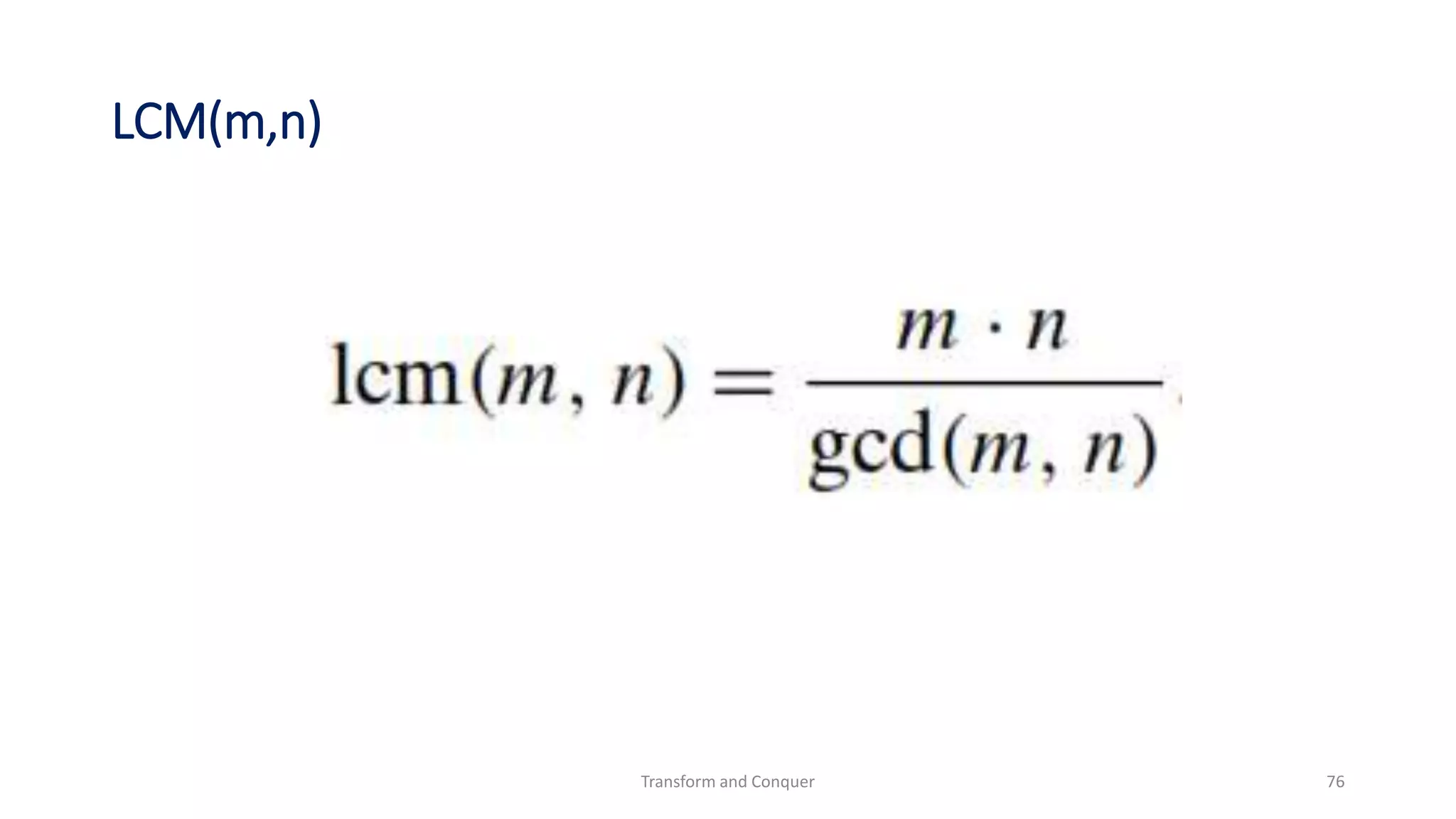
![Resources
78Transform and Conquer
Algorithms_design and analysis [Harsh Bhasin] chapter 15.
Levitin A.-Introduction to the design and analysis of
algorithms-AW (2011) [Anany Levitin] chapter 6.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transformandconquer-200106171827/75/Advanced-Algorithms-Transform-and-conquer-78-2048.jpg)
